After seven years, it’s about time for a much needed update to this article.
One of the first blog posts I published on this website, the first version of this article was posted when I was still quite new to this whole travel writing thing. Actually, now that I look back, even though the original had some nice photos, it embarrassingly contained very little usable information. So after more than half a decade, I figured it was about time to address that problem.
My writing style has evolved quite a bit over the years, and so has the way I present information on this blog, so I’ve written an entirely new article that will combine both old and new photos to give readers a better idea what this beautiful natural space has to offer.
Suffice to say, if you haven’t had the chance to visit the Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Park, you’re not exactly alone.
The park tends to be quite a popular one with domestic tourists, but hasn’t really appeared on the radar of international tourists yet, which is quite unfortunate. As one of only two of Taiwan’s designated ‘National Forest Recreation Parks’ located within the greater Taipei region, Manyueyuan serves as a great escape for weekend tourists wanting to get a taste of Taiwan’s stunning natural environment.
This massive forest reserve is home to a number of mountains, one of New Taipei’s most important rivers, several waterfalls, a number of hiking trails, and just so happens to be a great spot for bird and butterfly watching. Even better, a trip to the park can also be combined with a number of other popular tourist attractions within the area, making a day-trip there an eventful one.
Unfortunately, the one drawback is that getting to the park can be a bit of a hassle, especially for international tourists, as public transportation options are limited. Thankfully, there are now tour groups like Parkbus, which offer group trips to the park (and other hard to reach mountainous areas around the Taiwan), so if you’re interested in that kind of thing, I highly recommend checking them out as they’ll take care of all your travel-related headaches.
Link: Manyueyuan National Forest Recreation Area 滿月圓國家森林遊樂區 (Parkbus)
That being said, getting to the park on your own isn’t impossible, and I hope that this article will help to show you why all the effort it takes to get there is worth it.
In this updated version, I’ll introduce the park, the beautiful waterfalls within as well as the various hiking trails you’ll be able to enjoy when you visit. To start though, lets first take a look at Taiwan’s National Forest Recreation Parks, so that you can have a better idea of what’s actually going on in these environmental sanctuaries.
National Forest Recreation Parks (國家森林遊樂區)
Established by the Forestry Bureau in 1965 (民國54年), the government has designated a number of Taiwan’s mountainous areas as protected ‘Forest Recreation Parks’ (國家森林遊樂區). Over the six decades since these protected areas were established, the number of parks on the list has grown significantly, with many of them once utilized by the Forestry Bureau for the purpose of extracting natural resources.
Currently there are twenty-two designated areas around the country that have established Forest Recreation Parks, but that list of parks can often be somewhat confusing, even for locals, given that they often receive slightly different designations, and may or may not be included within what are considered National Parks (國家公園) or National Scenic Areas (國家級風景特定區). Officially, the list includes some twenty-two established areas, which are classified simply as ‘Forest Parks’ or ‘Forest Wetland Parks’, making the actual number of these spaces slightly misleading, given that they differ greatly in size and scope.
Nevertheless, no matter how you classify them, these parks range from tropical monsoon forests in the south and east of the country to temperate high-mountain forests in northern and central Taiwan. In each case, the Forestry Bureau has developed a system of walking paths and hiking trails within where visitors are able to enjoy the natural beauty of Taiwan at their leisure.
Below, I’ve compiled a list of the (current) areas classified as 'Forest Recreation Areas,’ each of which have become popular with local and international tourists, with a few of them becoming rather iconic.
-
Taipingshan Forest Recreation Area (太平山國家森林遊樂區)
Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Area (滿月圓國家森林遊樂區)
Neidong Forest Recreation Area (內洞國家森林遊樂區)
Dongyanshan Forest Recreation Area (東眼山國家森林遊樂區)
Guanwu Forest Recreation Area (觀霧國家森林遊樂區)
Mingchih Forest Recreation Area (明池國家森林遊樂區)
Wuling Forest Recreation Area (武陵國家森林遊樂區)
Basianshan Forest Recreation Area (八仙山國家森林遊樂區)
Dasyueshan Forest Recreation Area (大雪山國家森林遊樂區)
Hehuanshan Forest Recreation Area (合歡山國家森林遊樂區)
Aowanda Forest Recreation Area (奧萬大國家森林遊樂區)
Alishan Forest Recreation Area (阿里山國家森林遊樂區)
Tengjhih Forest Recreation Area (藤枝國家森林遊樂區)
Kenting Forest Recreation Area (墾丁國家森林遊樂區)
Shuangliu Forest Recreation Area (雙流國家森林遊樂區)
Jhihben Forest Recreation Area (知本國家森林遊樂區)
Siangyang Forest Recreation Area (向陽國家森林遊樂區)
Chihnan Forest Recreation Area (池南國家森林遊樂區)
Fuyuan Forest Recreation Area (富源國家森林遊樂區)
Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Park
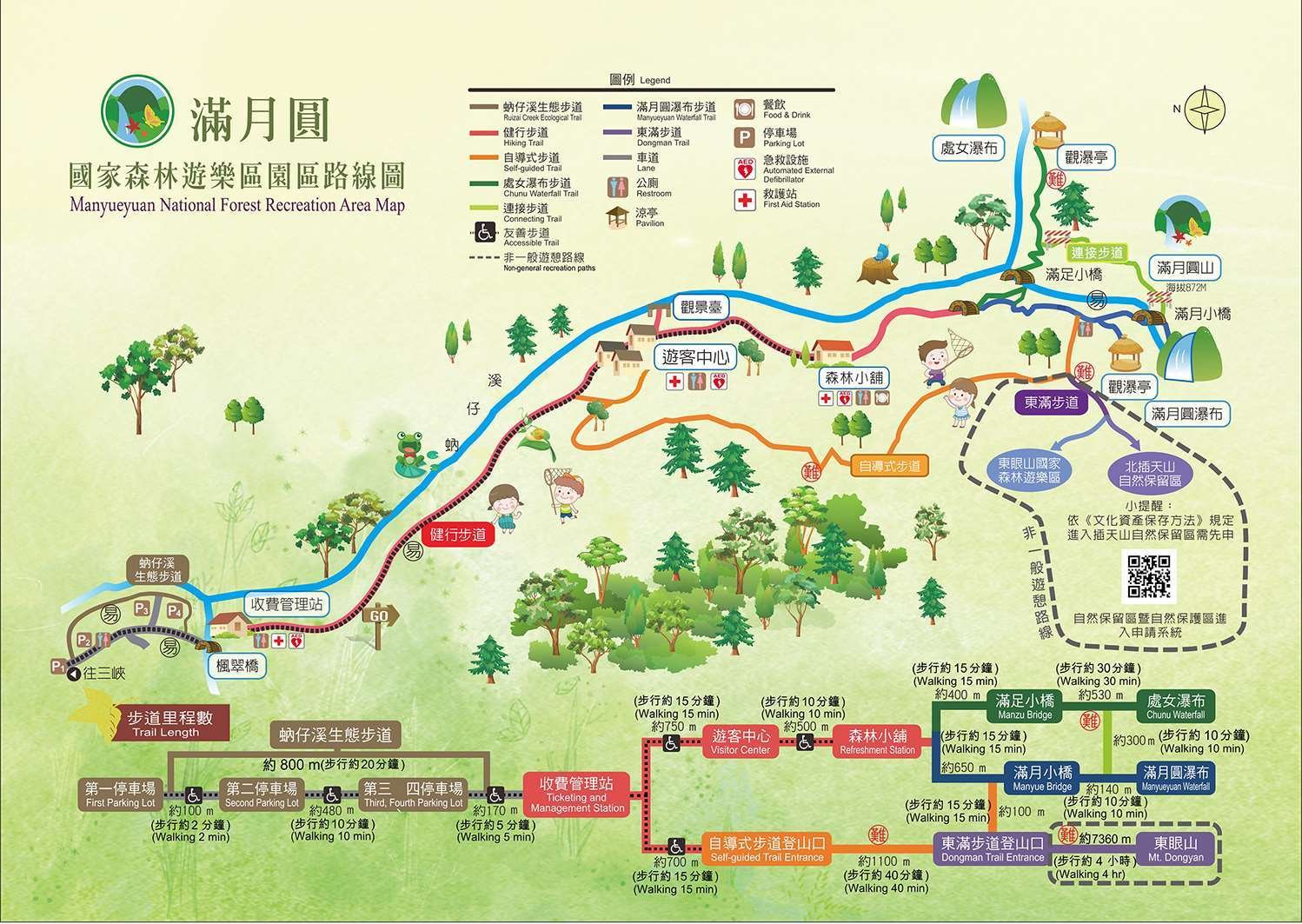
The Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Park (滿月圓森林遊樂區) is located on the territorial border between New Taipei City’s Sanxia District (三峽區) and Taoyuan county’s northern Fuxing District (復興區). As one of two designated forest parks in the greater Taipei area, the park is an invaluable environmental sanctuary in addition to being a pretty popular tourist attraction, with people traveling from around the country to visit. Consisting of 1573 acres of protected land, a number of forest trails, and some really beautiful waterfalls, a visit to the park has a little something for everyone looking to enjoy the outdoors.
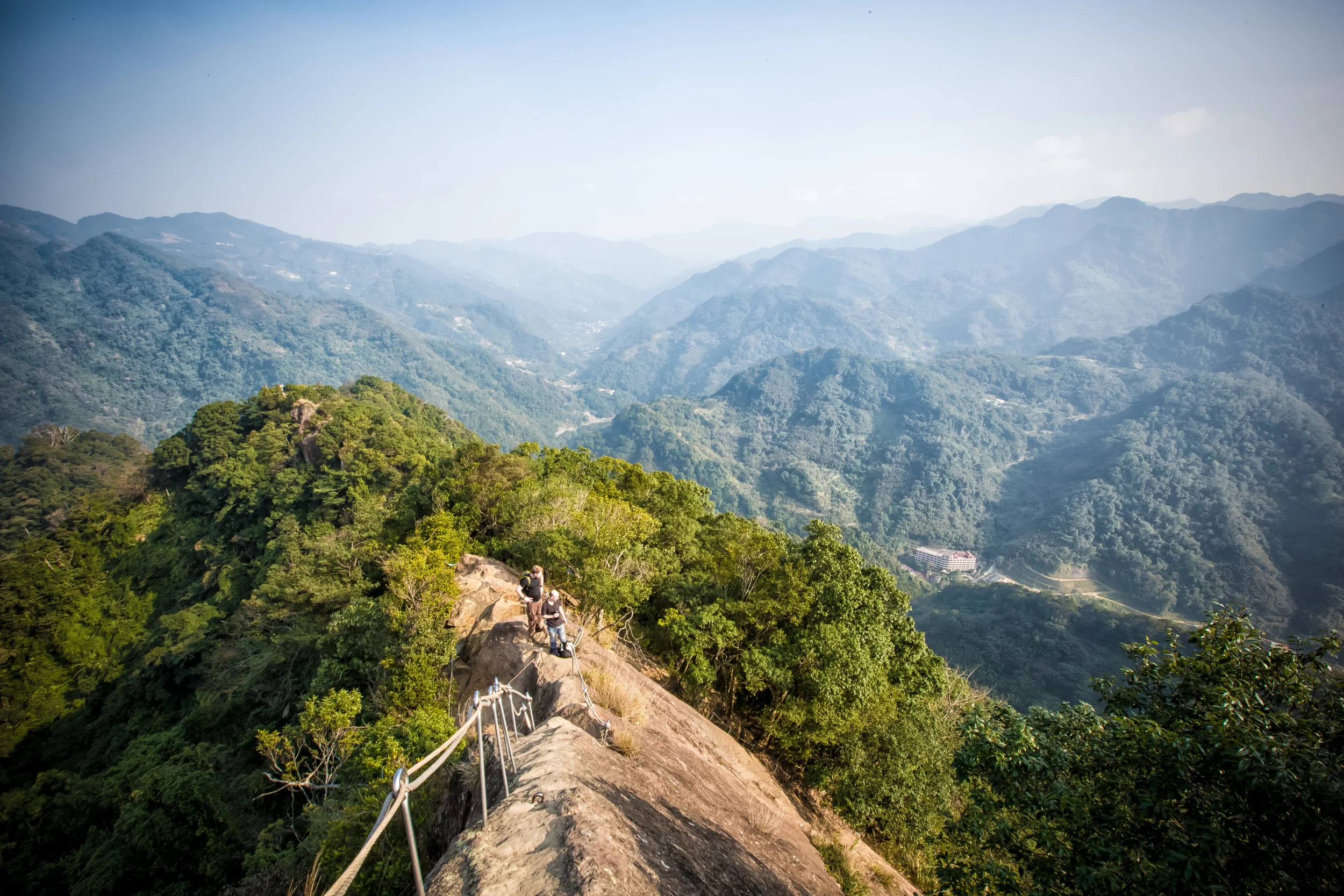
Located within the mountainous area just outside of Sanxia, the Manyueyuan Forest Park is situated on land that combines parts of Manyueyuan Mountain (滿月圓山), Southern Xiongkong Mountain (熊空南山), Beichatian Mountain (北插天山), Laka Mountain (拉卡山) and Dongyan Mountain (東眼山). The elevation within the park ranges between 300 meters to 1700 meters above sea level, offering visitors and adventurous hikers a glimpse of Taiwan’s various temperate environments within a single space.
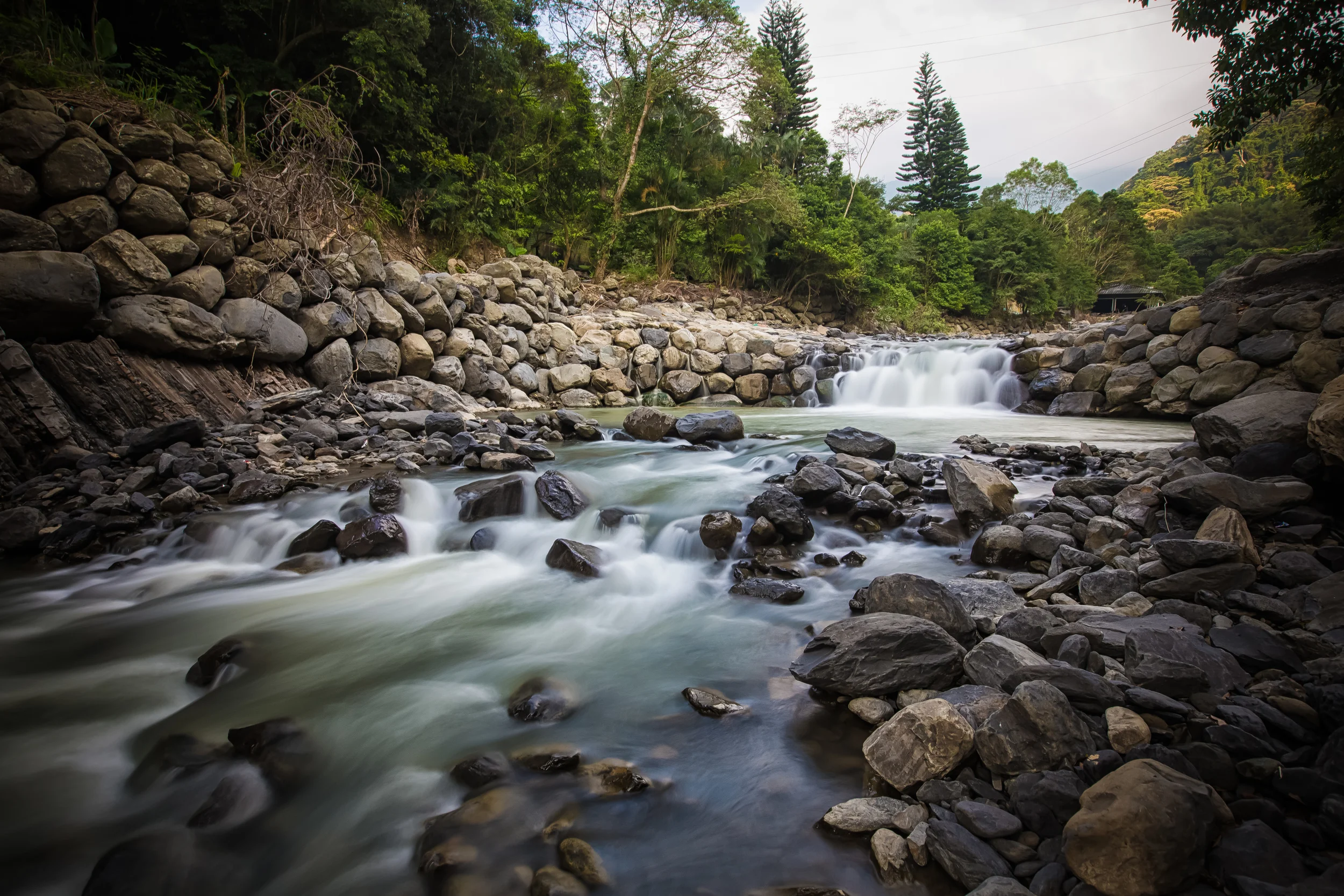
That being said, the mountains aren’t the only important natural aspect of the park as it is also home to the Ruizai Creek (蚋仔溪), which is a tributary to the Dabao River (大豹溪), one of New Taipei City’s most important rivers. Working hand-in-hand with the mountainous habitat, Ruizui Creek flows through the park, and over the years has crafted a beautiful river valley, acting as the lifeblood of the park, and as the source of the various waterfalls within.
While Manyueyuan is a protected forest sanctuary today, the area was originally the native home of the Llyung Topa (拉流斗霸), a tribe of Tayal Indigenous people (泰雅族), who made their homes along the river. More commonly known today as the Dabao Tribe (大豹社), named after the Dabao River (大豹溪), the people who lived in the area were essentially forced from their homes further into the mountains, first by the Qing and then later the Japanese.
When the Qing government removed its prohibition regarding entering Taiwan’s mountainous regions (開山撫番), Chinese inhabitants of Taiwan started a violent effort to force their way into the mountains of Sanxia in order to extract the area’s rich camphor reserves. This campaign resulted in what is referred to as the Takoham Incident (大嵙崁社事件), a violent affair that left many on both sides dead. Then, when the Japanese took control of Taiwan in 1895 (明治28年), a similar push into the mountains took place, resulting in guerilla-style warfare and unfortunately ended with a well-equipped army marching into the mountains and forcing the Indigenous people to leave their ancestral homeland.
It goes without saying that the encroachment of the Japanese on indigenous territories across the island often resulted in violence and misery for Taiwan’s indigenous people, but as they stood in the way of the empire’s ambition for the extraction of the island’s precious natural resources, the violence was relentless and unforgiving.
Ironically, there’s (somewhat of a hidden) Japanese memorial to the members of the Japanese army who were killed during the conflict on a mountain near Manyueyuan. Not many people know about it, but it is a sad reminder of the historic suffering of the Dabao Tribe. I recommend giving the article linked below a read if you’re interested in a rare English-language article dedicated to the history of what happened to the Llyung Topa people.
Serving as a base for the extraction of the area’s rich reserve of camphor, the Manyueyuan area was also part of a Japanese reforestation effort that brought prized Japanese cedar (柳杉) to Taiwan for future extraction. Nevertheless, unlike the neighboring Dongyanshan Forest Recreation Area (東眼山國家森林遊樂區), little evidence remains of the historic logging industry within the park today. That being said, the cedar that was planted by the Japanese has been given well over a century to grow, creating a beautiful forest that boasts a wide variety of local and imported trees.
Note: Manyueyuan Forest Park is one of the best locations in Northern Taiwan to view the changing colors of the maple leaves. However, when this does happen, the park tends to explode with visitors, as it is probably one of the most popular times of the year to visit. For a Canadian like myself, there’s a bit of nostalgia to see the red and yellow maple trees, but if you choose this time of the year to visit, you’re also going to have to put up with a lot of traffic as well.
With the decline of the camphor industry in the 1960s, the Forestry Bureau (林務局) moved almost everything out of the area and later reserved an estimated 1,500 hectares of land to be eventually converted into a protected ‘Forest Recreation Park’ (國家森林遊樂區). The Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Park, named after Manyueyuan Mountain (滿月圓山) opened to the public in 1988 (民國77年), providing the people of Taiwan with a beautiful natural sanctuary, a short distance from the capital. Over the three decades that the the park has been open to the public, it has undergone a number of changes, but the important thing to keep in mind is that it remains a sustainable natural habitat for Taiwan’s wildlife, a protected forest reserve, and a popular tourist attraction.
However, even though the park famously combines both the mountains and the river, it would be an understatement to say that it also provides a very healthy habitat for wildlife, unfortunately, that hasn’t always been the case.
Taking into consideration the history of the forest and the harvesting of its natural resources over the past century, many of the area’s original human and wildlife residents moved to safer areas higher up in the mountains. The good news though is that thanks to the reforestation effort, and several long periods of closure (for a period of renovation, and then again during the COVID-19 pandemic), the park has started to come alive again. Recently installed motion-activated infrared cameras have started to show a significant return of the area’s wildlife. The cameras, which are used to collect data on the wildlife within the park, have recorded an increase in sightings of rare mammal and bird species that have made their return to the area.
Link: Sightings of elusive wildlife on the rise in Manyueyuan (Taipei Times)
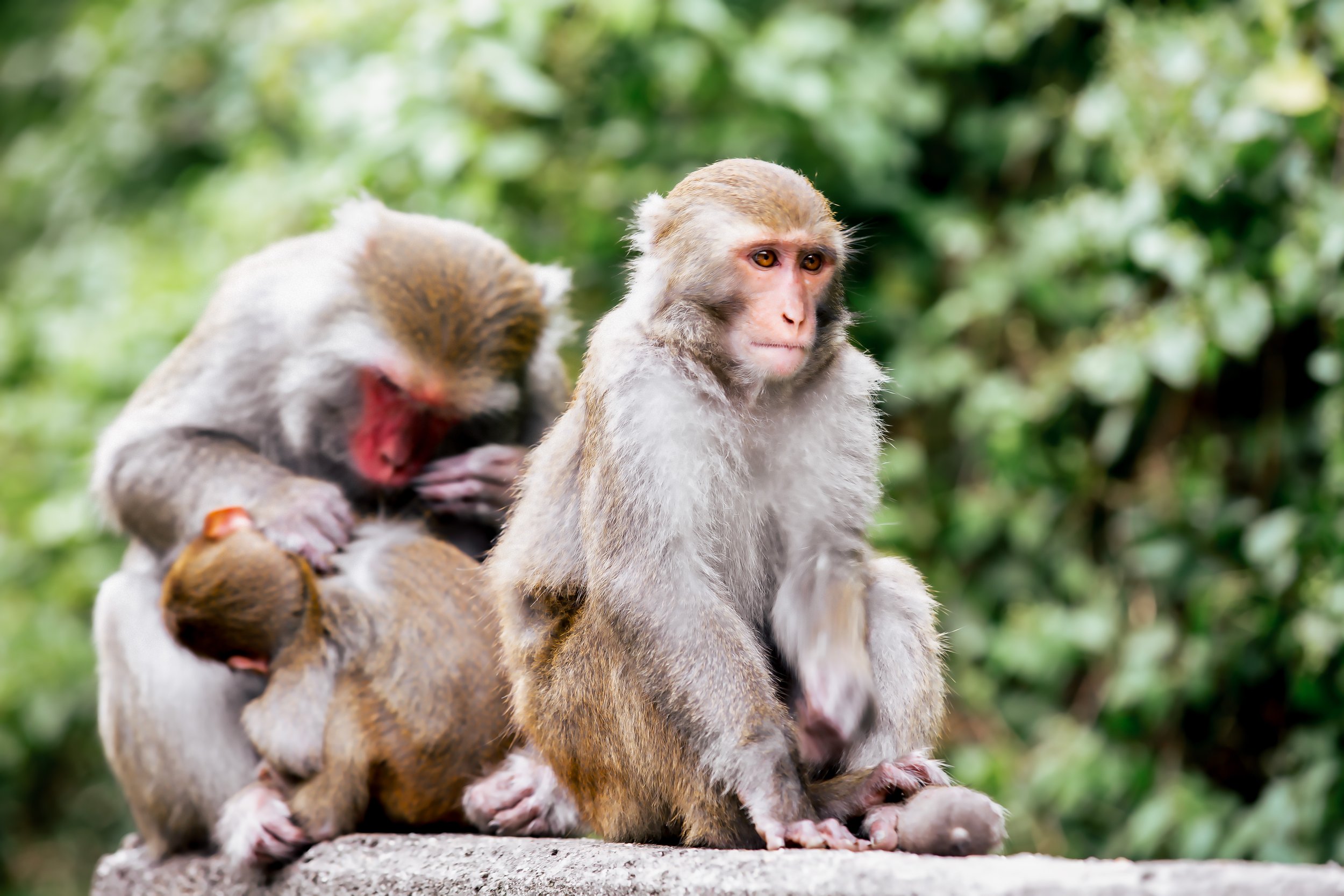
The most visible (and less disturbed by human activity) are the Formosan Rock Macaques (台灣獼猴), which most visitors to the park are likely to encounter at some point foraging for food in the trees along the trails. If you’re lucky, you might also encounter Formosan Red-Bellied Squirrels (赤腹松鼠), Reeves’ muntjacs (台灣山羌), crab-eating mongooses (食蟹獴), ferret-badgers (鼬獾), Swinhoe's pheasants (藍腹鷴) and Taiwan bamboo partridges (台灣竹雞). The park is also home to a wide variety of other birds, reptiles and amphibians, and during the spring and summer months, an impressive variety of butterflies, making it an ideal location for bird watchers, who you’re likely to encounter in the forest taking photos of the over fifty different species of birds in the park.
That being said, Manyueyuan is often referred to by locals as a ‘Waterfall Paradise’ (瀑布天堂), and even though the forest trails, bird and butterfly watching attract visitors on a regular basis, the park’s beautiful waterfalls are probably one of the biggest reasons why so many people visit. Below, I’ll introduce each of the waterfalls as well as a few of the other important points of interest within the park before moving on to introducing the various hiking trails that are open to the public.
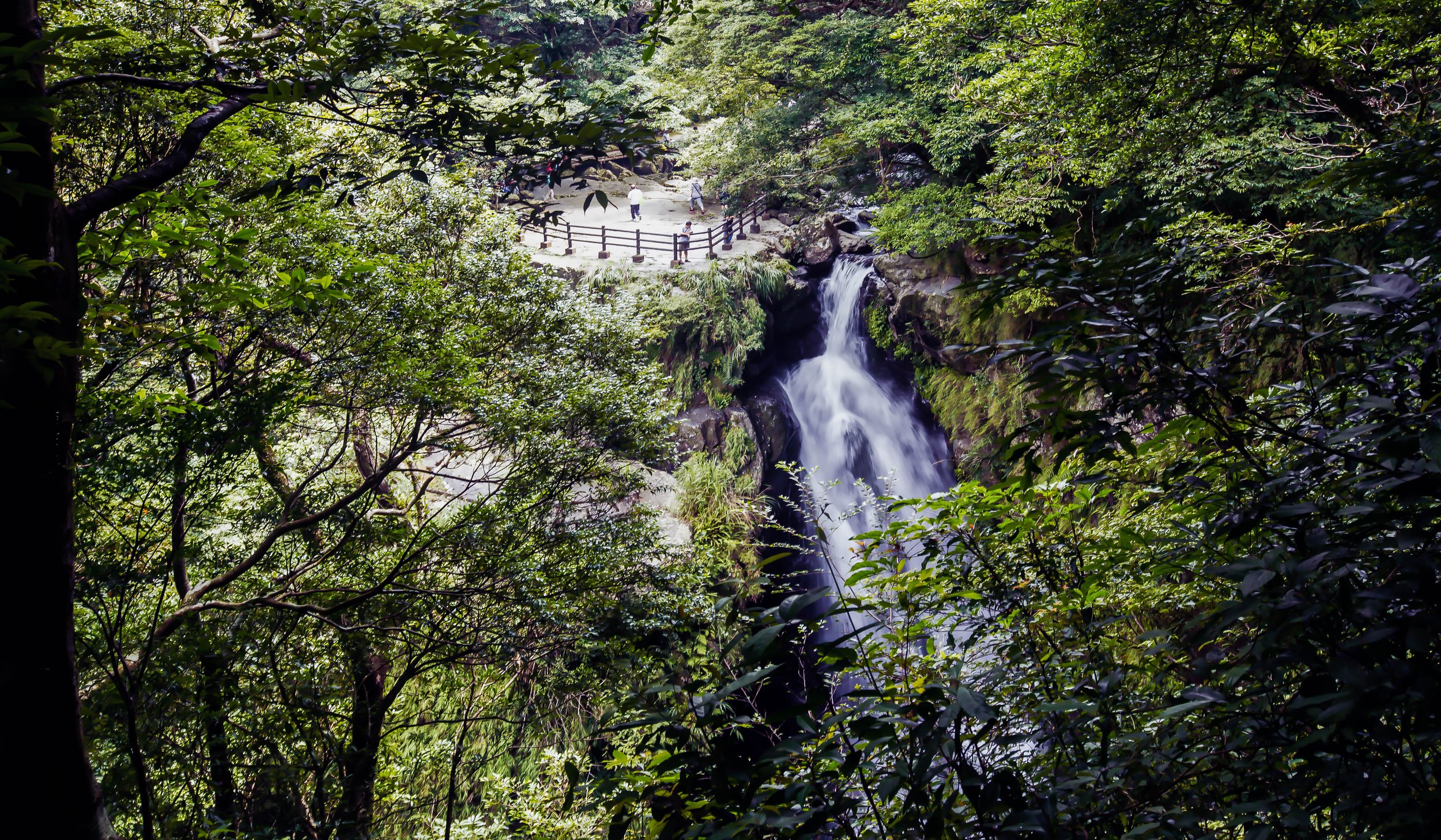
Manyueyuan Waterfall (滿月圓瀑布)
Manyueyuan Waterfall, which is be literally translated as “Full Moon Waterfall” is a twenty-meter high waterfall that can be viewed from several different vantage points. Unfortunately, no matter which side you’re viewing the steep waterfall from, you can’t really get a full view of it as half of it is obscured by a large stone.
Note: Due to it being obscured in this way, the waterfall has been nicknamed by locals as a ‘dragon waving its tail’ (神龍擺尾) because you can see the top of the falls, but not the bottom. I don’t particularly get the analogy, but it’s probably quite clever.
As you approach the falls along the hiking trail, there is a trail that climbs up a hill high above the falls on the right where you’ll find a covered pavilion where you can sit and enjoy the beauty of the falls. On the other hand, as you approach the falls, you’ll have to cross the “Full Moon Bridge” (滿月小橋) where you can enjoy the beauty of the river valley, and the lower section of the waterfall as it reappears from behind the large rock. Once you pass the bridge, you’ll walk up a set of stairs to the left of the waterfall that will take you to a platform space at the top of the falls.
Personally, I recommend anyone who visits the park to climb the hill to the right of the waterfall just before you reach the bridge as it offers a panoramic view of the falls from above, which is the best vantage point.
Silver Curtain Waterfall (銀簾瀑布)
Located not too far away from the top of the Manyueyuan Waterfall, you’ll find the Silver Curtain Waterfall. While not as large or impressive as the other two waterfalls within the park, the two meter high and five meter wide falls can be quite beautiful in the right light, especially if you are lucky enough to visit on a day when the sunlight is shining over the falls, which creates the ‘silver curtain’ effect.
To reach the falls, simply continue walking past the top of the Manyueyuan Waterfall until you reach the end of the flat stone area. The end of the trail is marked by guard rails, which have been put in place to prevent anyone from getting too close to the water.
Virgin Waterfall (處女瀑布)
What I personally consider the star attraction of the park, the (oddly named) ‘Virgin Waterfall’ is located along the left tributary of the Ruizai Creek. The twenty-five meter high cascading waterfall a stunning sight whenever you visit, but if you’re visiting on a sunny day, the waterfall is going to treat you to a beautiful rainbow display, created by a mixture of the light and mist. The probability of seeing the rainbow created by the waterfall is pretty high, but you may have to be patient, so I recommend if you are planning a visit to the park, plan to have a picnic or a rest while on one of the waterfall viewing platforms, so that you can get a glimpse of the light show.
Conveniently located next to the waterfall you’ll find a three-storey viewing platform that features benches on each of its level and offers beautiful vantage points to take photos of the waterfall. Sitting in the gazebo on a hot day is both calm and comforting as the waterfall treats visitors to a cool mist that acts like a natural air-conditioner, while it also dazzles with its rainbow displays.
And just to let you know, I have been lucky enough to see a rainbow at the waterfall every time I’ve visited the park, so I’m sure that if you’re patient enough, you’ll be treated with one as well.
Tourist Visitor Center (遊客中心)
The recently completed Visitor Center is located along the main hiking trail that visitors will take from the front gate prior to reaching any of the other hiking trails within the park. The large buildings are beautifully designed and feature washrooms for guests in addition to some impressive and informative displays about the natural environment within the park. The three exhibition spaces within the tourist visitor center are the Forest Building (森林館), River Building (溪流館) and the Butterfly Building (蝴蝶館), each of which has been opened within the last few years and features exhibitions that are probably more suitable for children, but are quite enjoyable nonetheless.
Refreshment Station (森林小舖)
Within the park, you’ll also find a small, but beautiful canteen, where a number of snacks and drinks are available for hungry hikers. The menu within the canteen tends to change quite regularly, but you can expect local snacks like dumplings, braised tea eggs, buns, rice dumplings, etc. There also a variety of hot teas, coffee and Taiwanese soups available. For the less adventurous, there are a number of packaged instant noodle options.
The prices within the shop are pretty much what you’d expect from any eatery around Taiwan, so don’t worry about it being a tourist trap.
Manyueyuan Hiking Trails (滿月圓健行步道)
Now that I’ve introduced the waterfalls and various points of interest within the park, I’m going to take some time to introduce the network of trails that have been set up for all our of enjoyment. The trails within the park are all well-developed and well-maintained, some of which have been recently given a fresh coat of paint, making them quite accessible for people of all ages.
That being said, not every trail within the park is considered ‘easy’ and although most of them are quite leisurely, it’s important that visitors keep track of where they are and where they intend to visit while in the park so that they don’t miss out.
Its also important to point out that even though most of the trails well-developed, not all of them are accessible for visitors with certain physical disabilities, or those with strollers. The Virgin Waterfall trail for example has quite a few stairs, making it relatively difficult if you’re traveling with a small child. So if you’d like to hike these trails, you might want to find a spot to fold up your stroller and leave it behind.
Ruizai Creek Ecological Trail (蚋仔溪生態步道)
The Ruizai Creek Ecological Trail is essentially just a newly developed trail that curves its way the park’s four designated parking lots, leading up the main entrance to the park. The trail is more or less just an added bonus to the rest of the park as it is just an off-shoot of the parking lot from the main road and provides visitors with the opportunity to check out the wide river basin prior to it joining up with the much larger Dabao River downstream. It also allows you to avoid any of the cars and scooters coming and going on the road to the other parking lots.
Total Length: 800 meters
Time Required: 20 minutes at the most.
The ‘Hiking Trail’ (健行步道)
Starting from the main entrance and following the river all the way past the Visitor Center and the Refreshment Station, the so-called ‘Hiking Trail’ is a (mostly) flat trail that connects to the other trails within the park. From the ticketing booth, the trail does have a gradual incline, but it is quite accessible for anyone who would like to enjoy a leisurely walk through the park. Similar to the Ruizai Creek Trail mentioned above, it’s part of the walking section of the park that most visitors have to pass by, but although it is forested in sections, it is just a leisurely walking trail that runs parallel to the river and offers views of the stream with plenty of places to stop and rest. That being said, this is essentially one of the most important trails within the park as it connects to all of the others, allowing visitors to head off in different directions.
While on the trail, you’ll find a number of informative displays that the have been set up to help inform visitors of the various species of wildlife and vegetation within the park.
Total Length: Between 1250 meters - 2km (the trail splits off at one section)
Time Required: 25-30 minutes.
Virgin Waterfall Trail (處女瀑布步道)
As an offshoot of the ‘Hiking Trail’ you’ll eventually come across a fork in the road where you’ll see signage that points in the direction of continuing along the path toward the Manyueyuan Waterfall, or cross the river on your way toward the Virgin Waterfall. Both waterfalls are worth the time and the effort, but if you only have enough time to check out one of them, this should be the one you choose.
The trail to the Virgin Waterfall isn’t a long one, but it is considered to be more difficult than the others due to the incline of the trail, which includes a number of stairs that takes you up along another section of the Ruizai Creek. From the start of the trail, you’ll cross the Manzu Bridge (滿足小僑) and then start your climb to the waterfall. Even though the hike is a little less than a kilometer long, it’ll feel like the most strenuous exercise that you’ll have had on your journey through the park thanks to all the stairs.
The trail ultimately comes to an end when you reach the Virgin Waterfall, which has a nice three-storey covered pavilion for you to view the waterfall and rest.
If you’re lucky, you may also be able to make use of the ‘Connecting Trail’ (連接步道) to take an easier and direct route back and forth from the Manyueyuan Waterfall Trail. I’ll introduce that trail in more detail below.
Total Length: 930 meters (+300 meters with connecting trail)
Time Required: 45 minutes (+10 minutes with connecting trail)
Manyueyuan Waterfall Trail (滿月圓瀑布步道)
As another offshoot of the main ‘Hiking Trail’ you’ll reach a fork in the road where you can turn right and continue along the path toward the Manyueyuan Waterfall. This trail is considerably easier than the Virgin Waterfall mentioned above in terms of the incline of the path, but it does feature a number of stairs that hikers will have to climb on either side of the waterfall to reach the end of the trail.
Much of this trail is covered covered by the forest, and is noticeably a lot more damp than the rest of the park as it is the area where you’ll find the Ruizai Creek at its strongest.
As mentioned earlier, the trail splits off into two sections, one where you’ll cross the beautiful ‘Full Moon Bridge’ (滿月小橋) and make your wall up to the top of the waterfall to an area where you can also enjoy the Silver Curtain Waterfall.
The other part of the trail is a section where you’ll climb a steep set of stairs prior to crossing the bridge. It will bring you to a platform high above the waterfall where you can enjoy panoramic views while sitting in a roof-covered pavilion.
Similar to the Virgin Waterfall trail mentioned above, hikers can make use of the ‘Connecting Trail’ (連接步道) to take an easier and more direct route to the other waterfall, rather than climbing all the way back down and starting all over again.
Total Length: 930 meters (+300 meters with connecting trail)
Time Required: 45 minutes (+10 minutes with connecting trail)
Connecting Trail (連接步道)
Making things convenient for hikers, there is a ‘Connecting Trail’ between the Virgin Waterfall Trail and the Manyueyuan Waterfall Trail that allows visitors to save quite a bit of time biking between the two waterfalls. That being said, it’s important to note that the ‘Connecting Trail’ has experienced long periods of closures in recent years due to the instability of the trail as it passes from one waterfall trail to the other. Unfortunately, it’s possible that the trail might be closed at any given time, so although it is an extremely convenient way to pass between the two waterfalls, you may end up discovering that it is blocked off with notices warning hikers not to enter.
You’ll want to keep this in mind as you hike through the park and ultimately be prepared to hike back to the start of the other trail.
Total Length: 300 meters
Time Required: 10 minutes
Self-Guided Trail (自導式步道)
What is it they say about taking the road less travelled?
Starting as an off-shoot from the ‘Hiking Trail’ that follows the river through the park, the ‘Self-Guided Trail’ follows a completely different route through the forest, ultimately connecting to the Manyueyuan Waterfall trail at the end. This trail tends to be the most secluded of all the trails in the park as well as being considered the most ‘difficult’, but it does offer those who take it a much different view of the lush untouched forest, where you’re also much more likely to encounter some of the local wildlife.
Taking a stroll through this section of forest tends to be pretty quiet, with far fewer hikers than the other trails, and it’s also a pretty good section for checking out the butterflies in spring and summer. This is also the area where you’ll find the trailhead for the Dongman Hiking trail, which will take you from Manyueyuan Forest Park to the Dongyanshan Forest Park.
If it’s your first visit to the park and you’d like to enjoy a bit of a hike, I recommend starting with this trail and taking it all the way to the Manyueyuan Waterfall before making your way back to the entrance along the much easier and more leisurely ‘Hiking Trail’.
Total Length: 1100 meters
Time Required: 40 minutes
Dongman Hiking Trail (東滿步道)
The longest trail in the park is an interesting one because it is essentially a one-way hike that’ll take the entire day and connects you from one Forest Recreation Park to another. The name “Dongman” (東滿) is a combination of the first characters in “Dongyanshan” (東眼山) another Forest Recreation Park located in the mountains of Taoyuan and “Manyueyuan” (滿月圓).
Hikers are free to choose to start the roughly eight kilometer hike in the Forest Park of their choice with one starting at a lower elevation and the other starting at a higher elevation. The trail is known for its panoramic views of the northern mountain range, but is considered an advanced hike, and should always be done in a group for safety.
The other thing that has to be reiterated is that since the hike starts in one park and ends in another, your method of getting there and getting home will be different, so it doesn’t make much sense to drive your car to one, do the hike, and end up stranded in the other. Fortunately, there are hiking groups like Parkbus that coordinate hikes to the trail and conveniently provides drop off at one park and pick up at the other, solving those logistical problems.
Trail length: 8km (4-5 hours one way)
Time Required: 4-5 hours (one way)
Getting There
Address: (新北市三峽區有木里174-1號)
GPS: 121.44470, 24.830391
Car / Scooter
If you have access to your own means of transportation, getting to the park is quite easy thanks to quick access to the expressway that runs between Sanxia (三峽) and Yingge (鶯歌). Simply get off of National Highway #3 at the Sanying Interchange (三鶯交流道) and make your way to Rural Highway North North 115. The best way to achieve this is to copy the address or the GPS coordinates provided above into your vehicle’s GPS or your phone’s Google Maps.
If you’re riding a scooter however, you obviously don’t have the option of taking the expressway, so you’ll have to find your way to Sanxia and then to the Rural Highway #115, where you’re able to drive.
In both cases you’ll ultimately follow the rural highway to the very end where you’ll find the park. Driving a car might seem like your best option, but it’s important to keep in mind that on weekends and during national holidays, the narrow mountainous road can get quite busy and you may find yourself stuck in a traffic jam on the way up the mountain.
If you’re on a scooter on the otherhand, you can simply zip past all the people sitting in traffic and enjoy the park at your leisure.
Public Transport
Unfortunately, the only way to get to Manyueyuan via public transportation is by bus, and that tends to be a bit of a pain in the ass.
First you’ll have to get yourself to Sanxia (三峽), and the best way to do that is to take Taipei Bus (臺北客運) #702 from Banqiao Station (板橋車站) or Taipei Bus (臺北客運) #812 from either Dingpu MRT Station (頂埔捷運站) or Yongning MRT Station (永寧捷運站) on the Blue Line (板南線) all the way to Sanxia Stop 1 (三峽一站). From there, you’ll need to hop on Taipei Bus #807, which will take you to the Manyueyuan Parking Lot.
While that sounds simple, it’s important to note that there are only a handful of buses that depart from Sanxia each day, so you’ll have to keep a tight schedule in order to ensure that you catch the bus there, and more importantly, your bus home.
Link: Taipei Bus #807 Real Time Location (Taipei eBus 大台北公車)
From Sanxia 1 Bus Terminal to Manyueyuan (三峽一站 - 滿月圓)
Weekday Departures: 05:20, 07:00, 09:30, 12:00, 15:00, 17:30
Weekend Departures: 06:00, 08:30, 11:00, 14:30, 17:30
From Manyueyuan Parking Lot to Sanxia (滿月圓 - 三峽一站)
Weekday Departures: 06:05, 07:45, 10:15, 12:45, 15:45, 18:10
Weekend Departures: 06:45, 09:10, 11:45, 15:15, 18:10
Once again, you’re going to have to be very careful about the amount of time you spend in the park if you are taking the bus home - If you miss the last bus out of the park, you’re going to find yourself stranded, and your only option might be to hitch a ride with another hiker who would be willing to drive you into town.
Park Admission Fees
It is somewhat uncommon for popular tourist destinations to charge an admission fee in Taiwan, but in this case, for the purpose of maintaining the quality of the trails, the administration of the park, and more importantly the wildlife conservation effort, a modest admission fee is collected at the entrance.
The current admission fee scheme is as follows:
Weekdays: Adults NT$80
Weekends & National Holidays: Adults NT$100
Group Rate (20 or more people): NT$80
Children: NT$50
Seniors (65+): NT$10
Hours
Weekdays: 08:00 - 17:00
Weekends: 07:00 - 17:00
The park is open year-round, but is closed for Lunar New Year’s Eve (除夕). The Visitor Center on the other hand doesn’t open on Tuesdays.
If you are looking for something to do on the weekend or during a holiday, a quick trip to Manyueyuan for a bit of nature is definitely worth a visit. Not only are the trails within the park beautiful, but you also get to see a couple of beautiful waterfalls and possibly even some wild monkeys.
And hey, if you arrive early enough and still have time and energy for another short hike, you can make your day complete and visit the nearby Cloud Forest waterfall (雲森瀑布), or just take a dip in one of the pool areas of the Dabao River on the way out of the mountain. Finally, why not end your day checking out Sanxia Old Street (三峽老街), where you can fill your belly with some pretty good food!
References
滿月圓國家森林遊樂區 (台灣山林悠遊網)
滿月圓國家森林遊樂區 (新北市觀光旅遊網)
滿月圓國家森林遊樂區 (Wiki)
三峽.滿月圓 (Tony的自然人文旅記)
國家森林遊樂區 (Wiki)
Manyueyuan Forest Recreation Area (Taiwan Forest Recreation)
Sightings of elusive wildlife on the rise in Manyueyuan (Taipei Times)