Today's post is going to be a short one and without the typical amount of context that I'm able to give with these things - I thought it important however to document this historic building due to the fact that on the day I took these photos I learned that it would soon be demolished.
Since then the building has been torn down and all thats left are photos to remember it.
For a bit of a backstory - During the Lunar New Year holiday I had taken an excursion to Jhudong to take photos of the semi-abandoned (and soon to be restored) Timber Industry Dormitories from the Japanese Colonial Era. On my way back I decided to take a different route and drove through the quaint and peaceful Hsinpu village to follow up on a lead I had on an abandoned church.
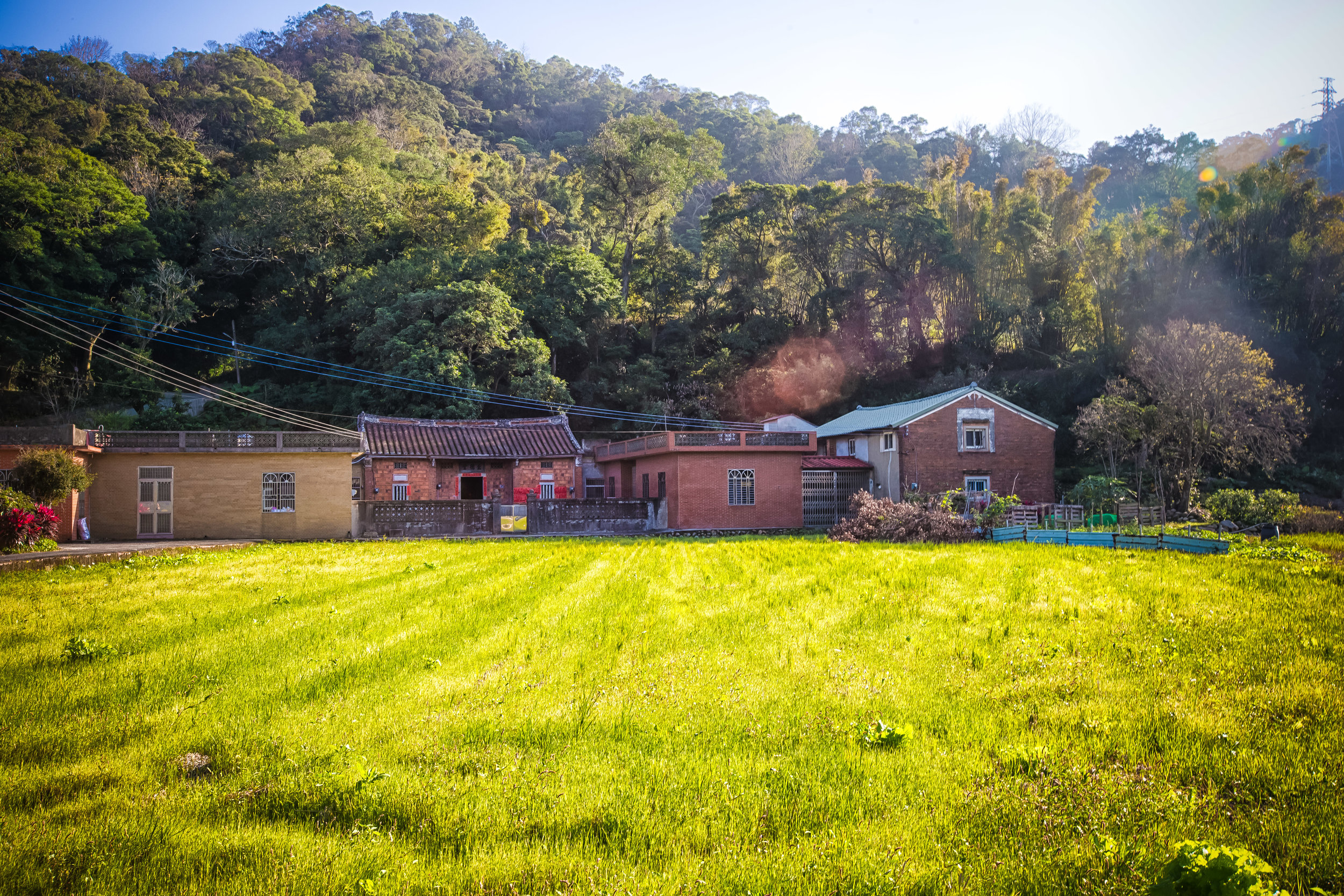
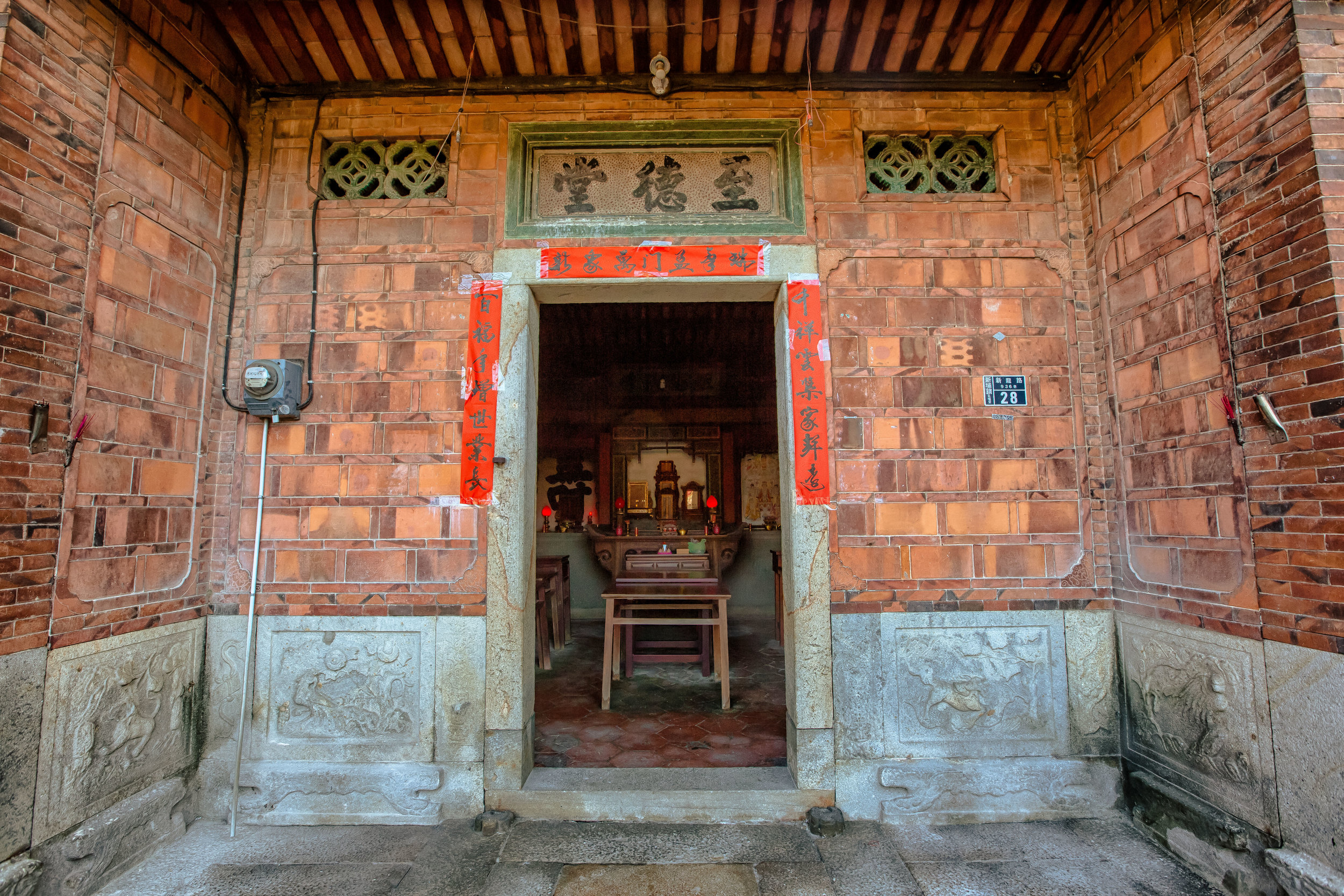
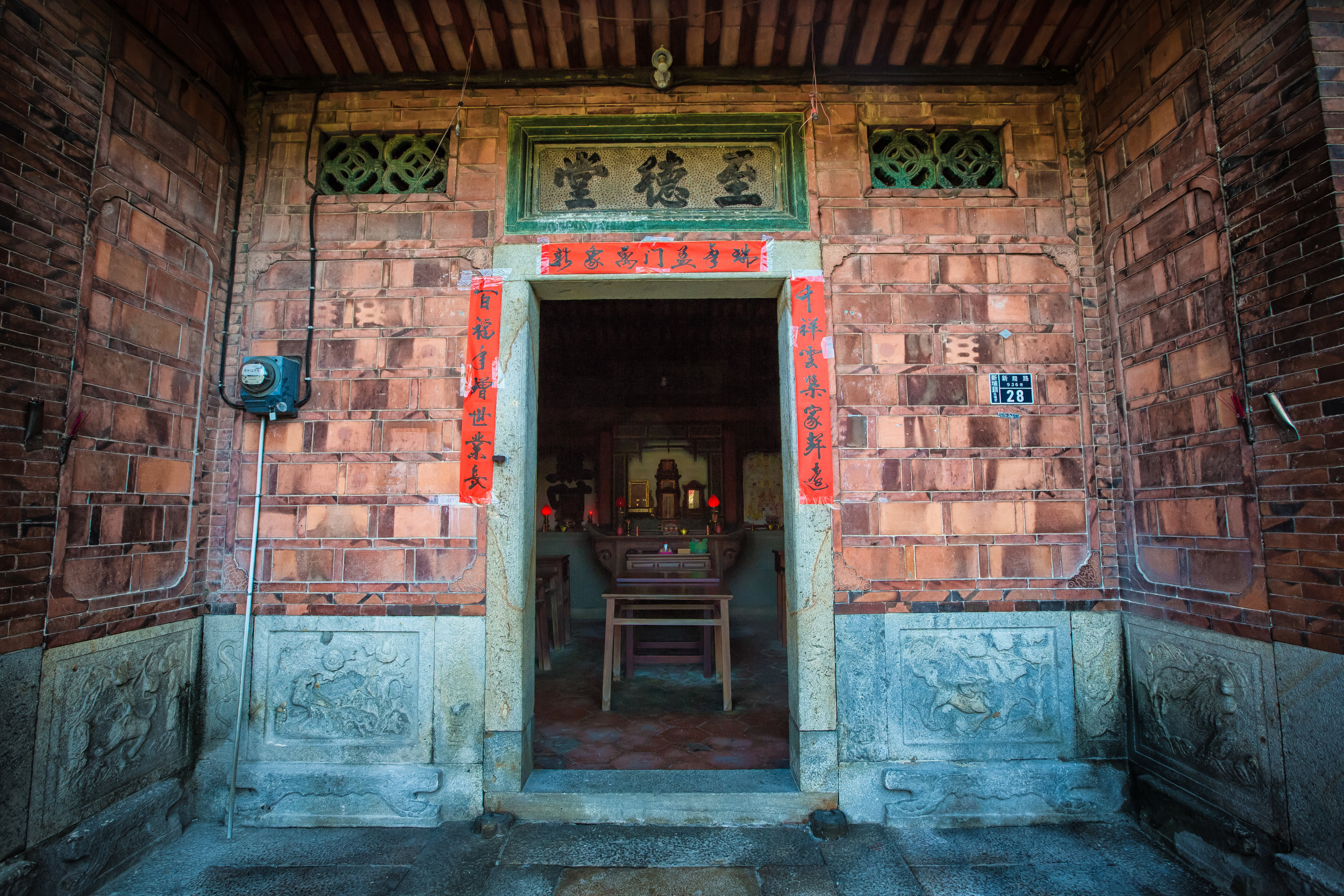
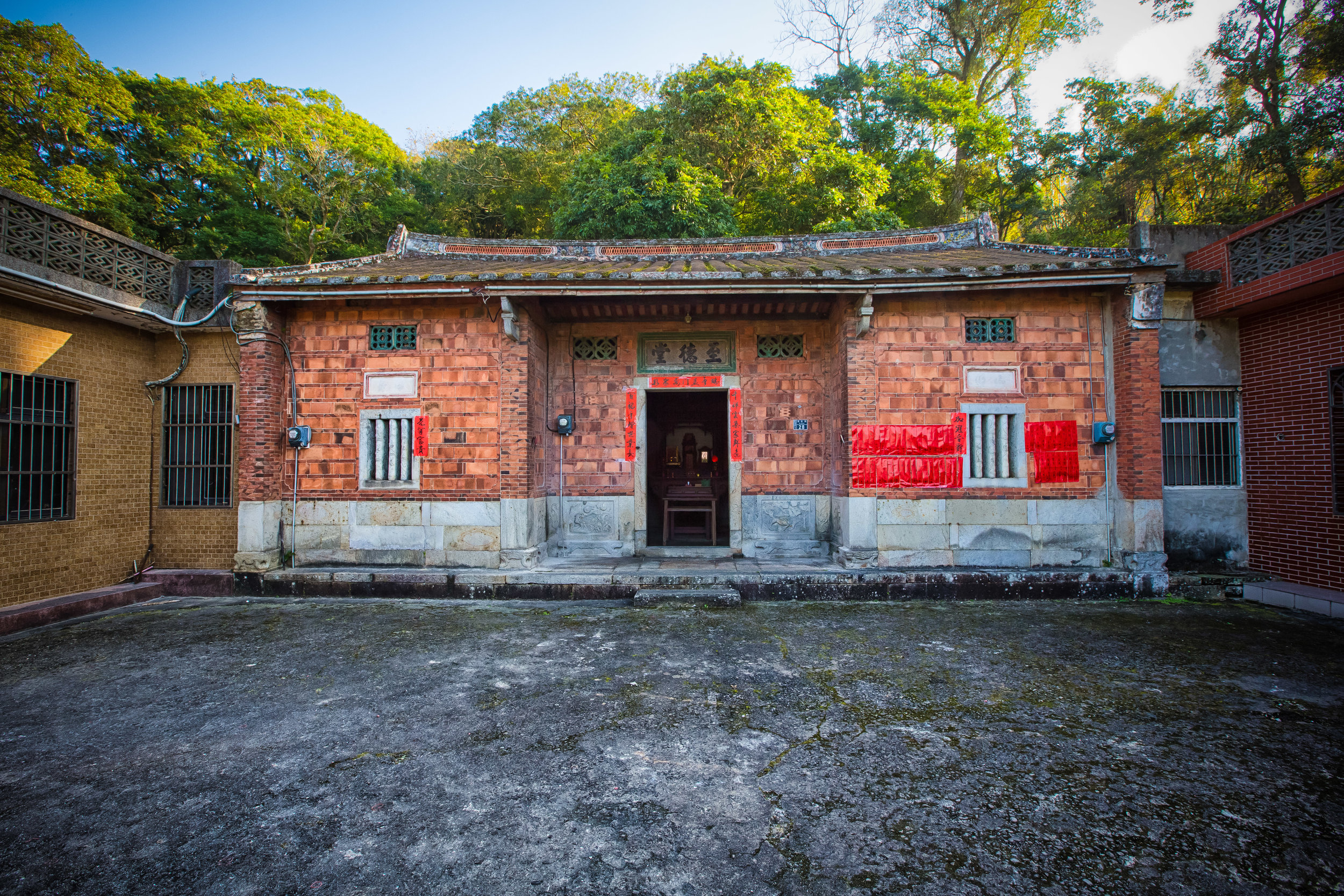
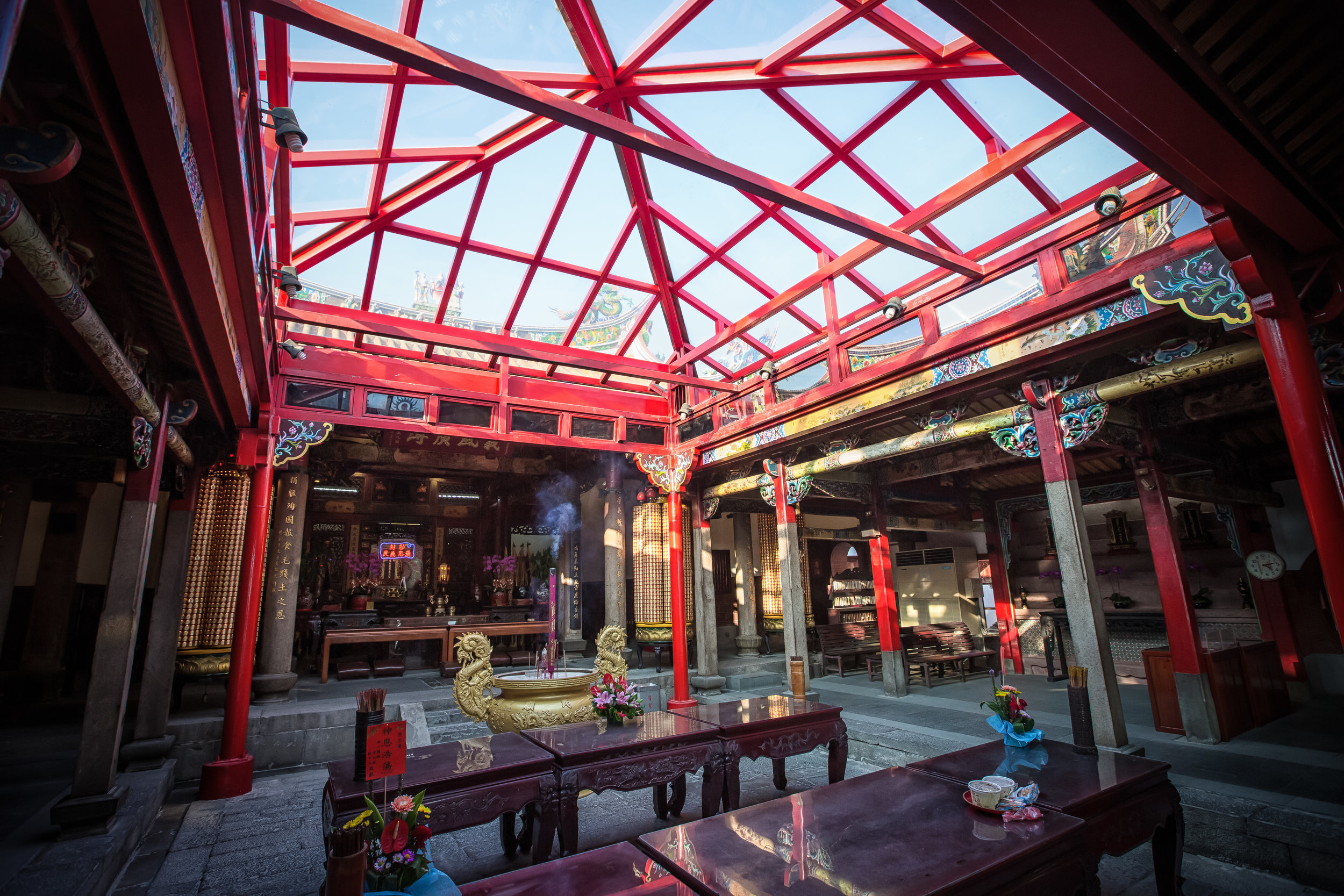
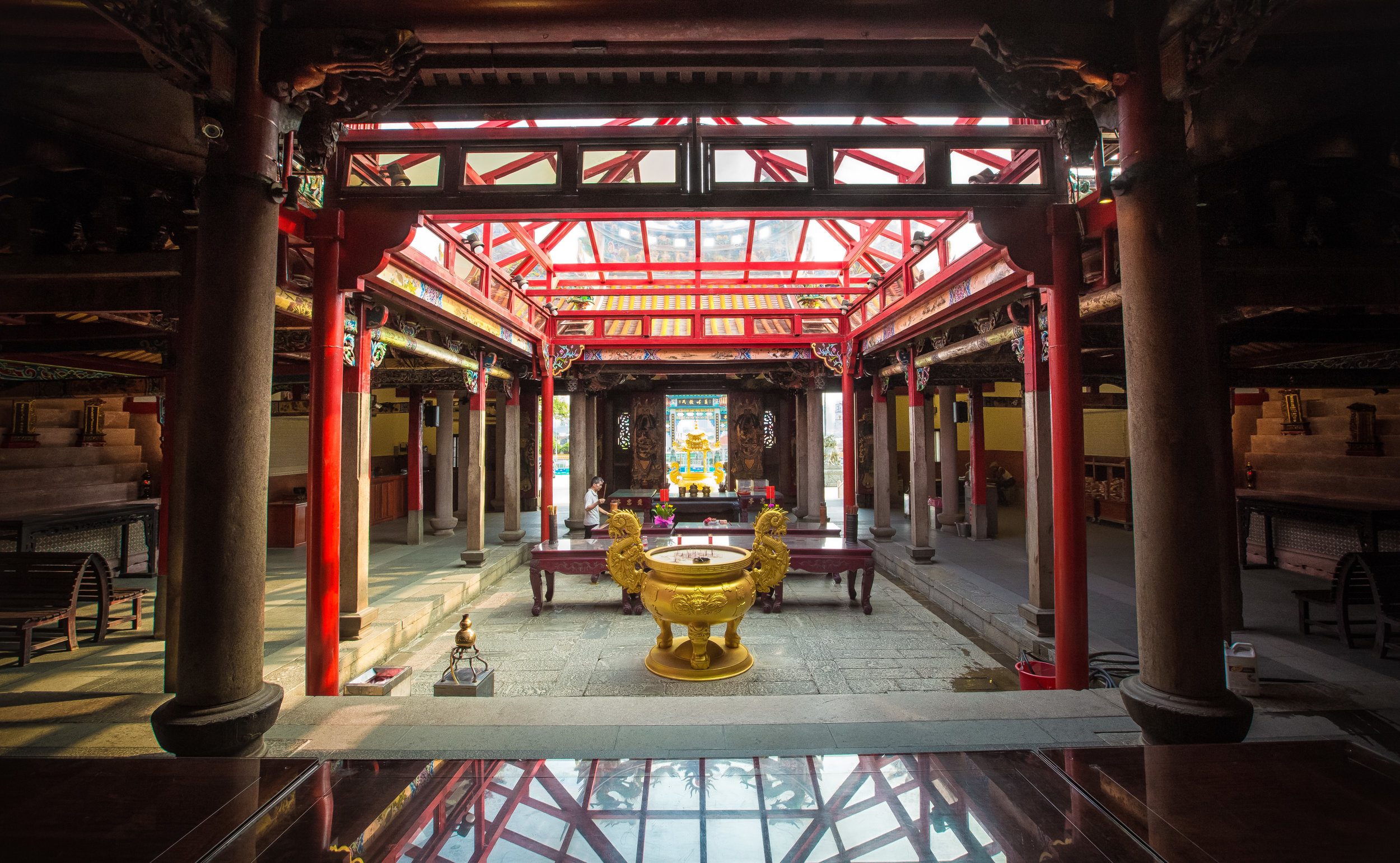
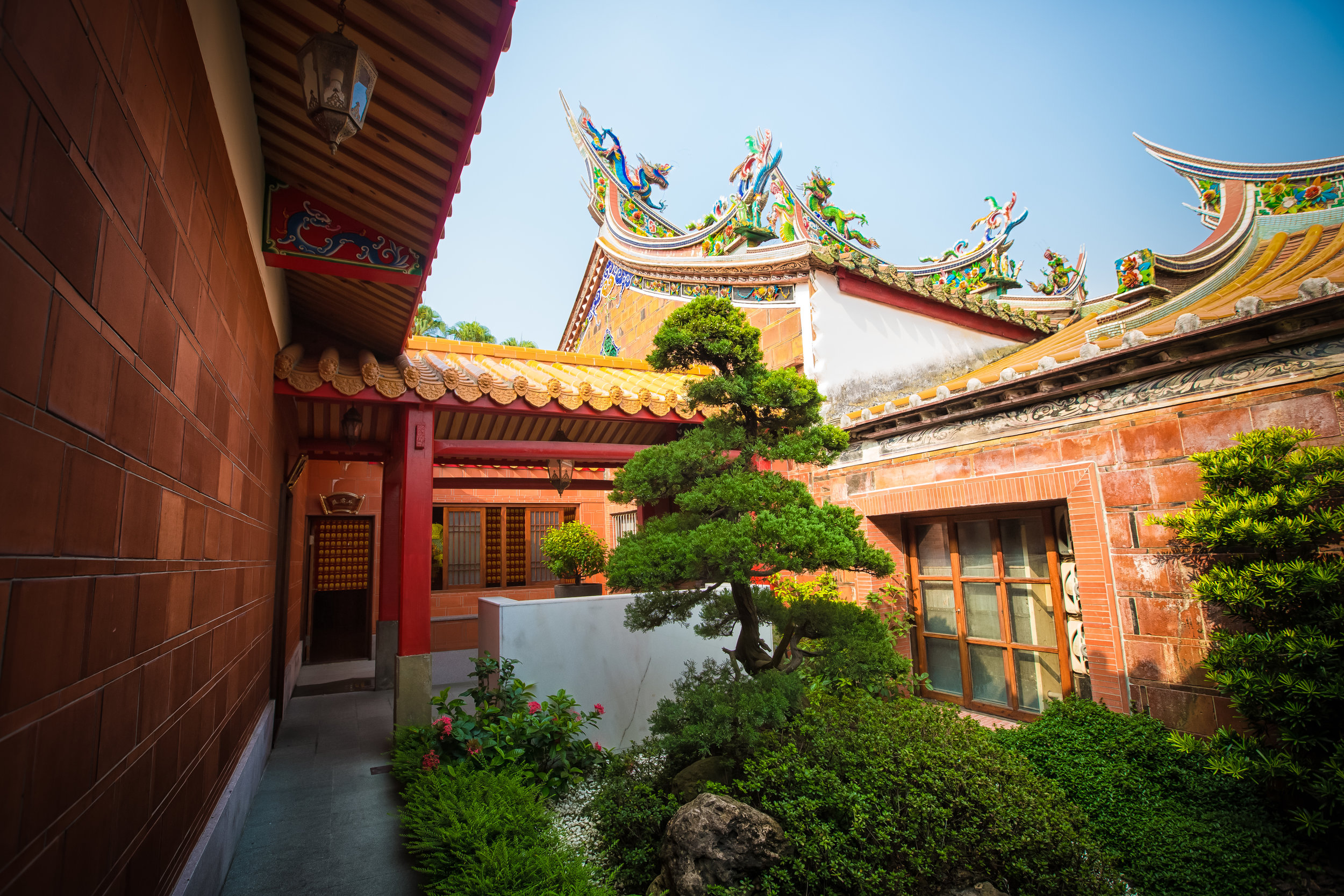
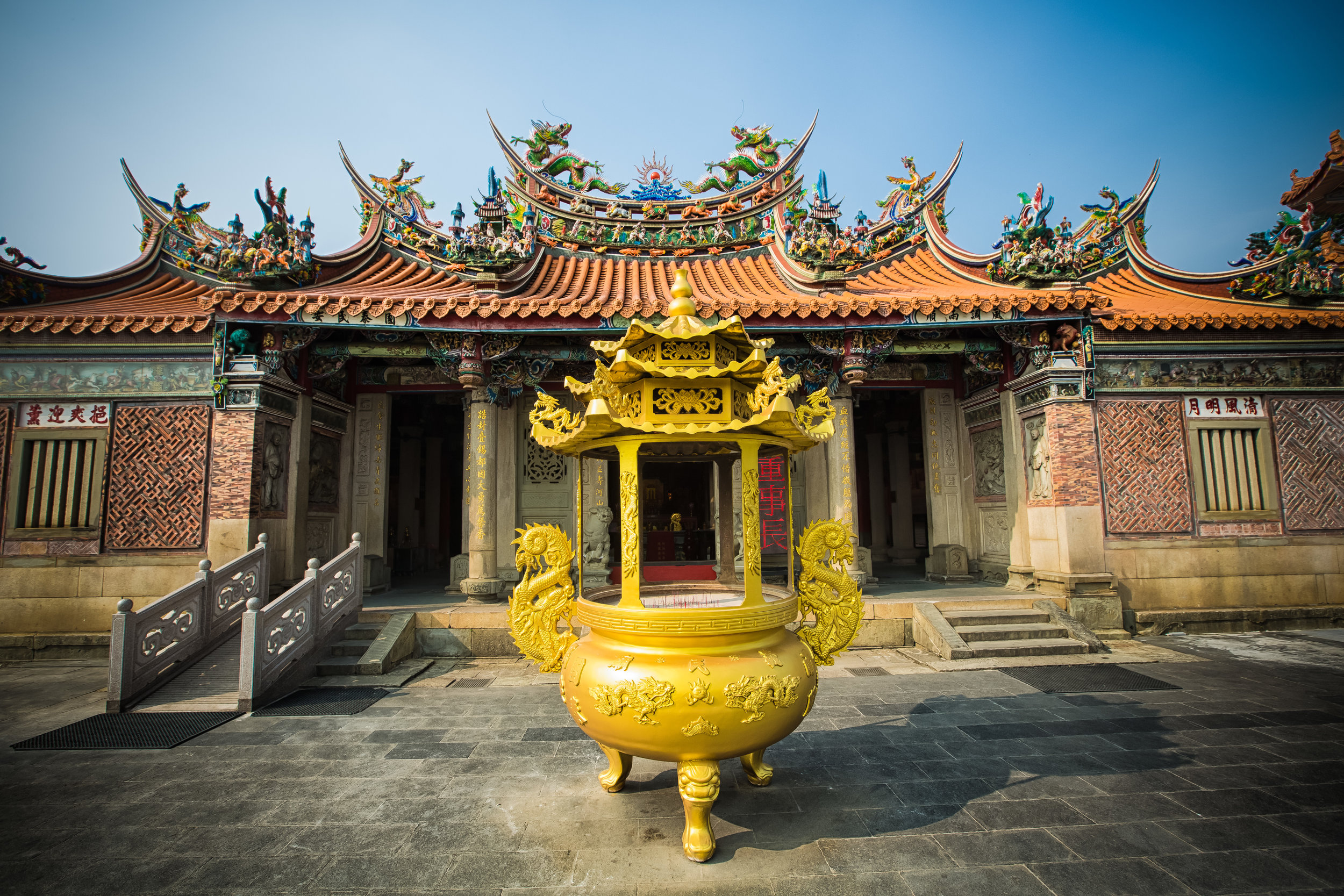
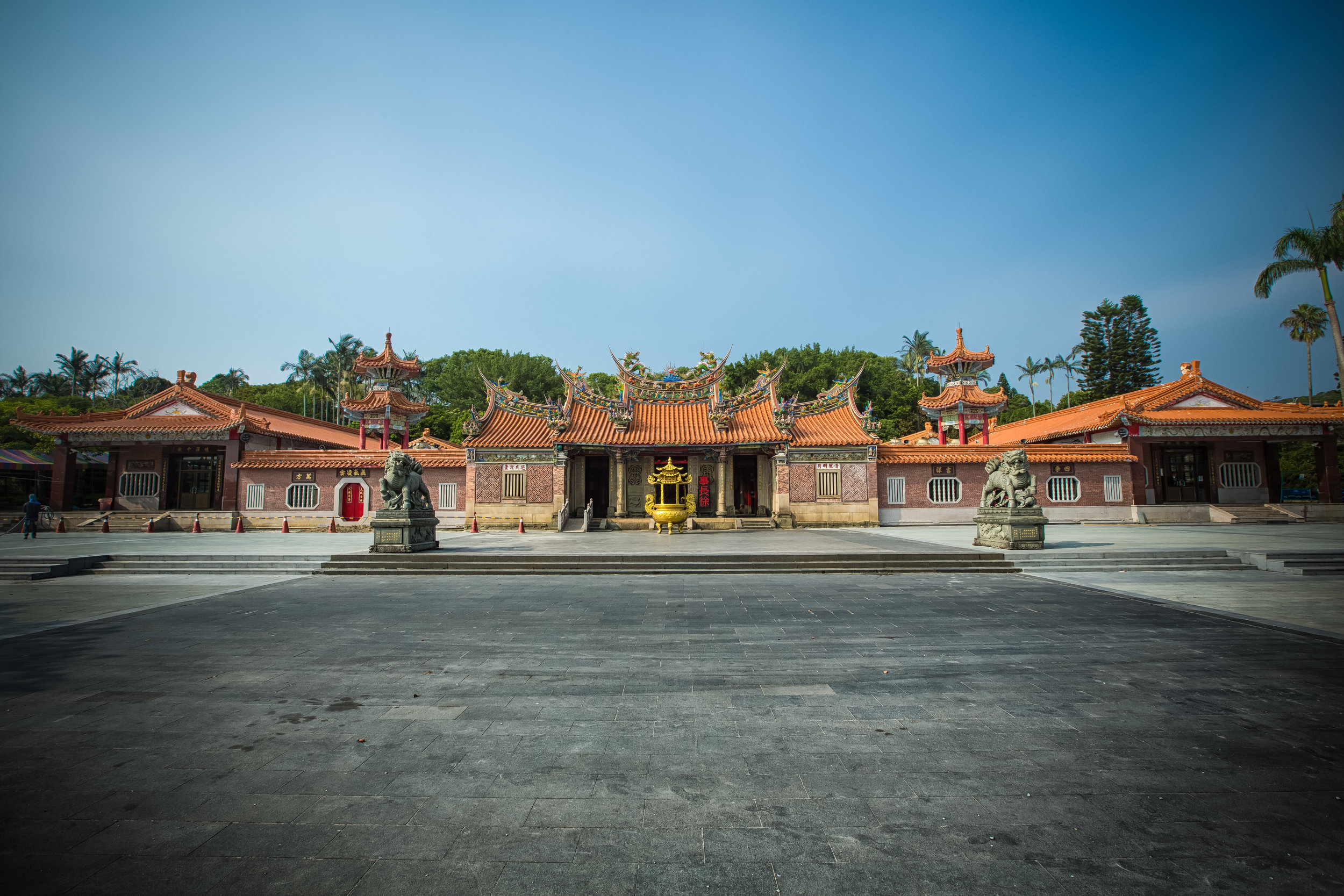
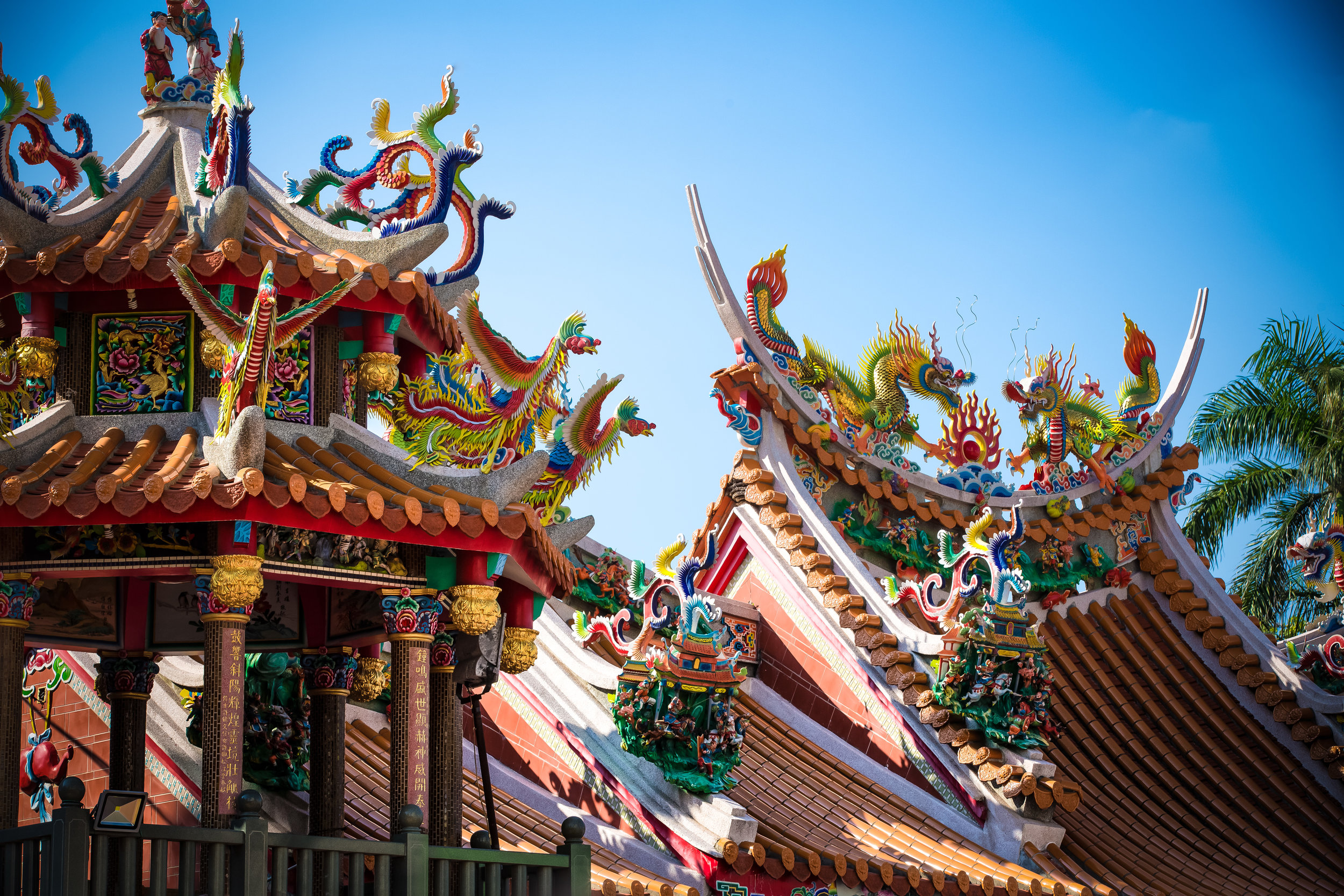
While driving down the road with rice paddies on either side between Hsinpu and Longtan I noticed a beautiful 'Sanheyuan' (三合院) - a traditional Taiwanese farmhouse.
These houses are actually quite common in that area of Hsinpu and in many parts of the Taiwanese countryside but are largely unkept and are more often than not in a sad state of disrepair.
What stopped me at this particular building though was that the door was wide open and it looked pretty much abandoned. The building was in rough shape which meant that no one was living in it anymore so I decided to get off my scooter and take a look to see what I could find.
As I approached the open gate however someone nearby called out to me and started walking over.
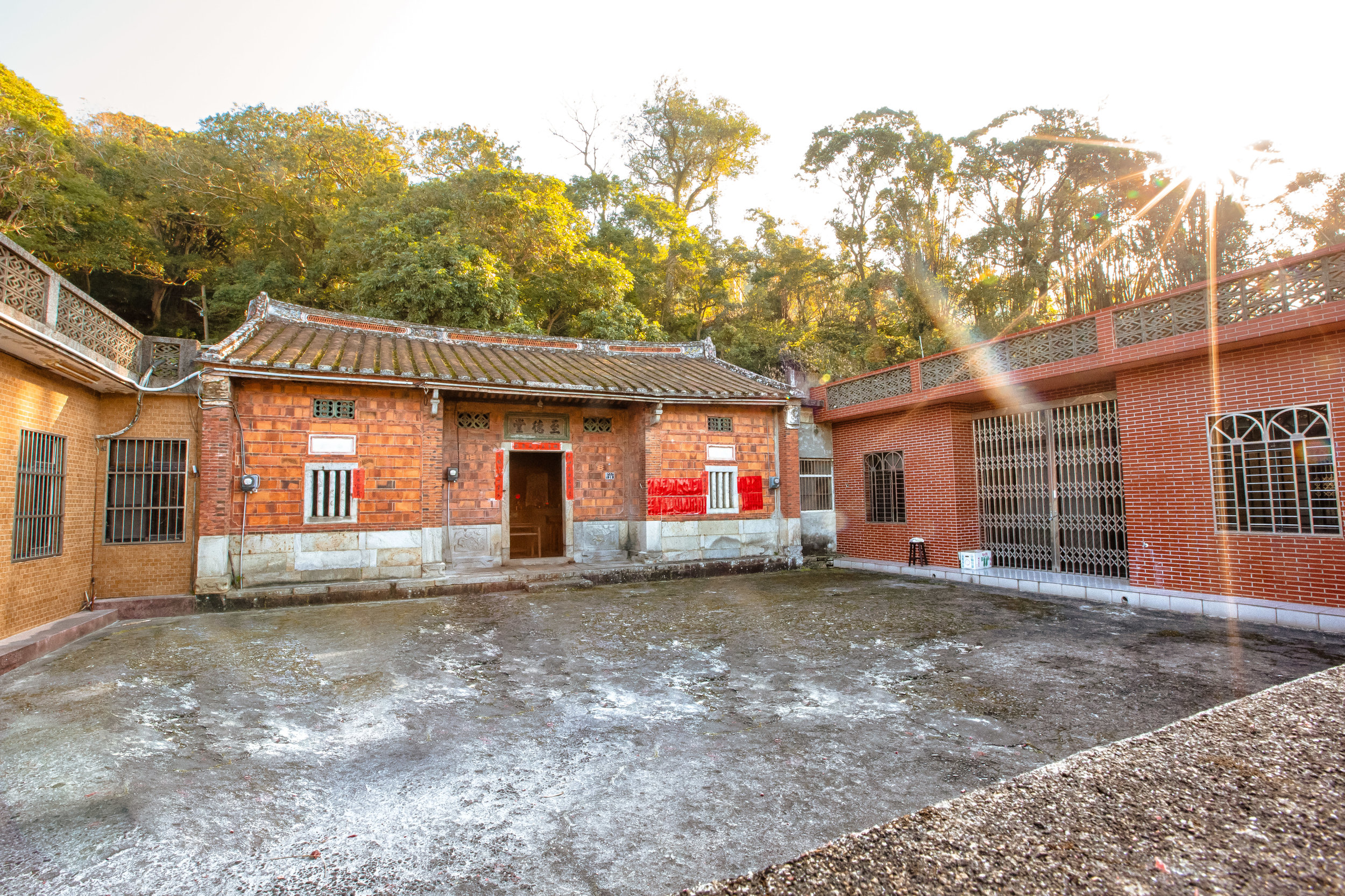
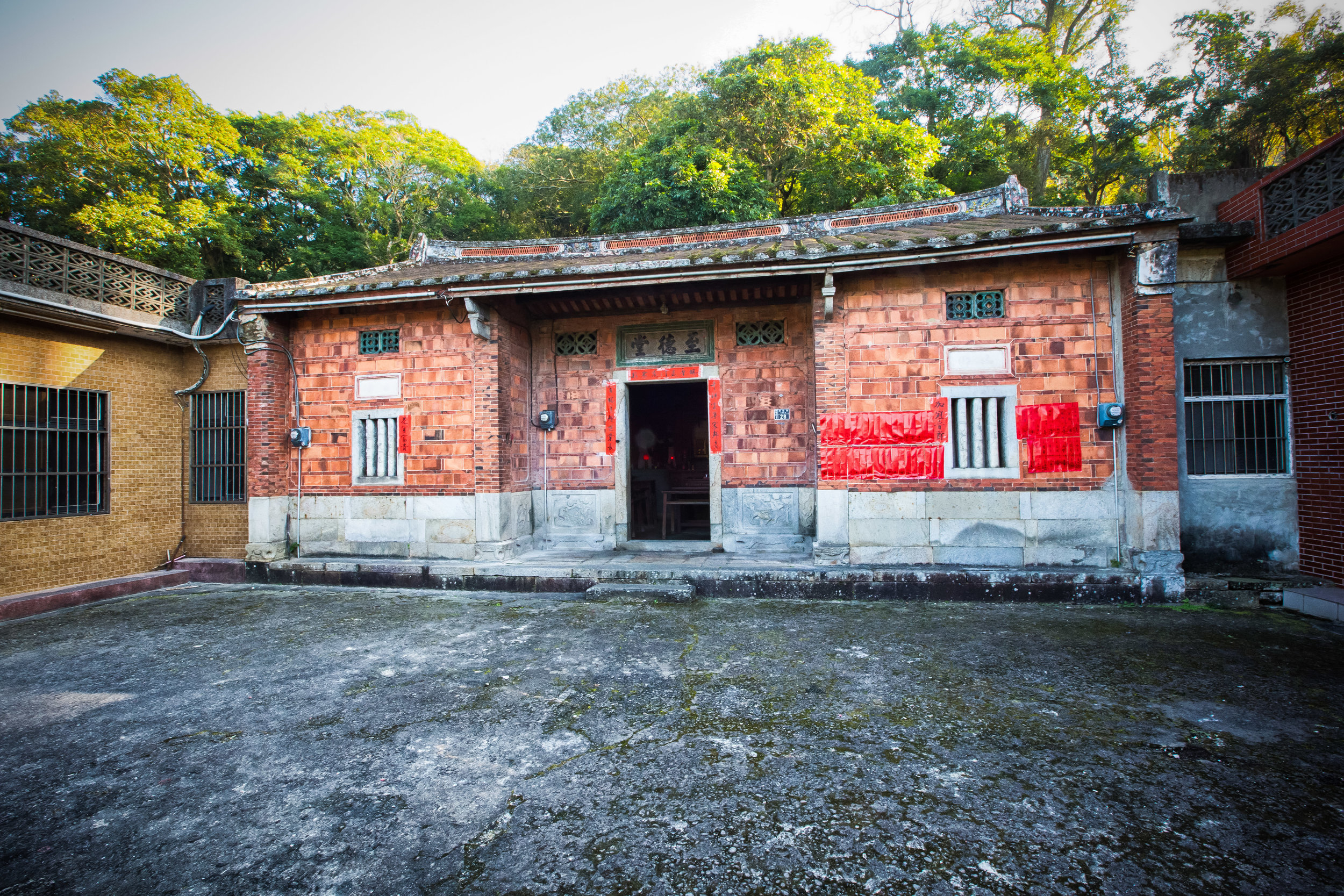
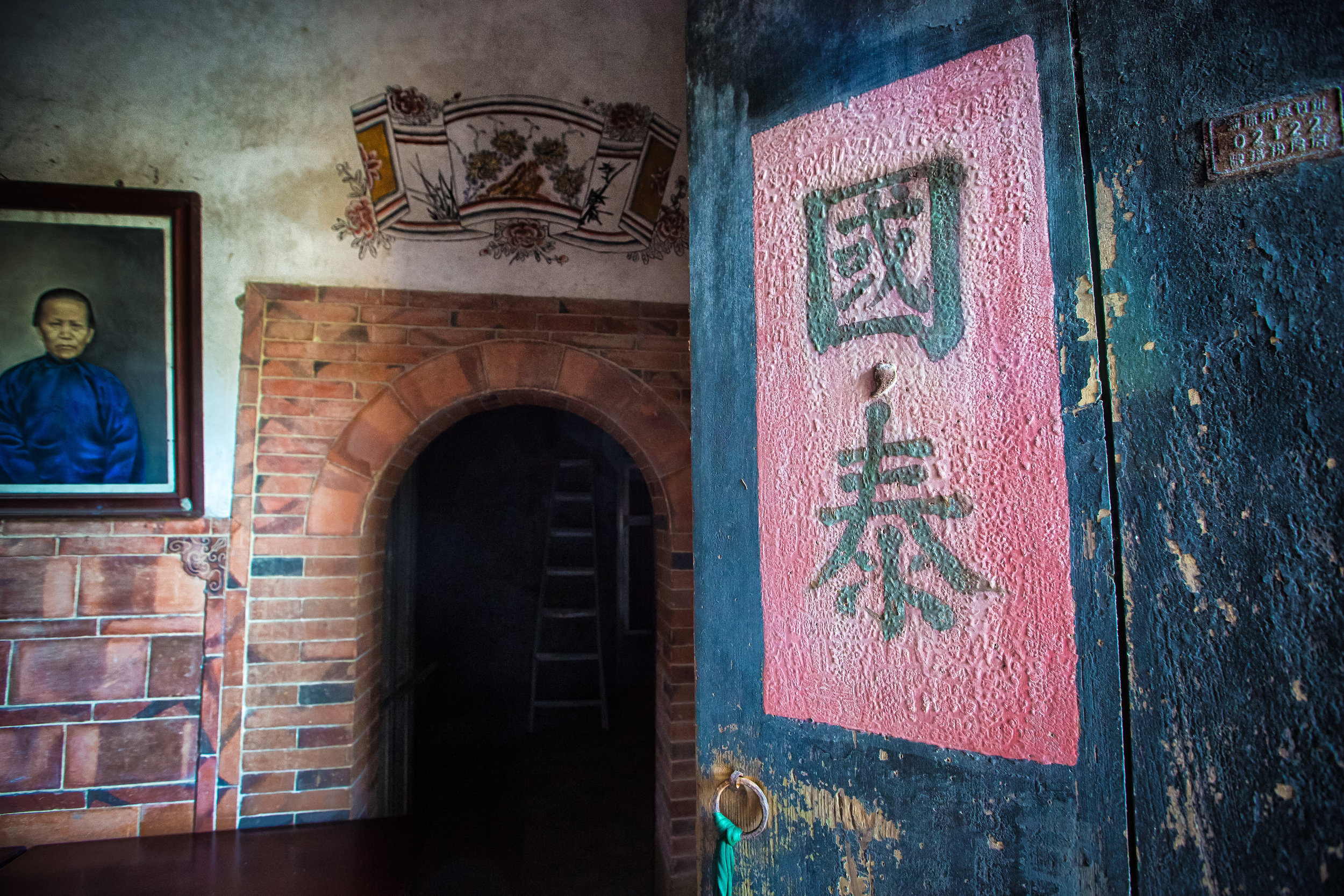
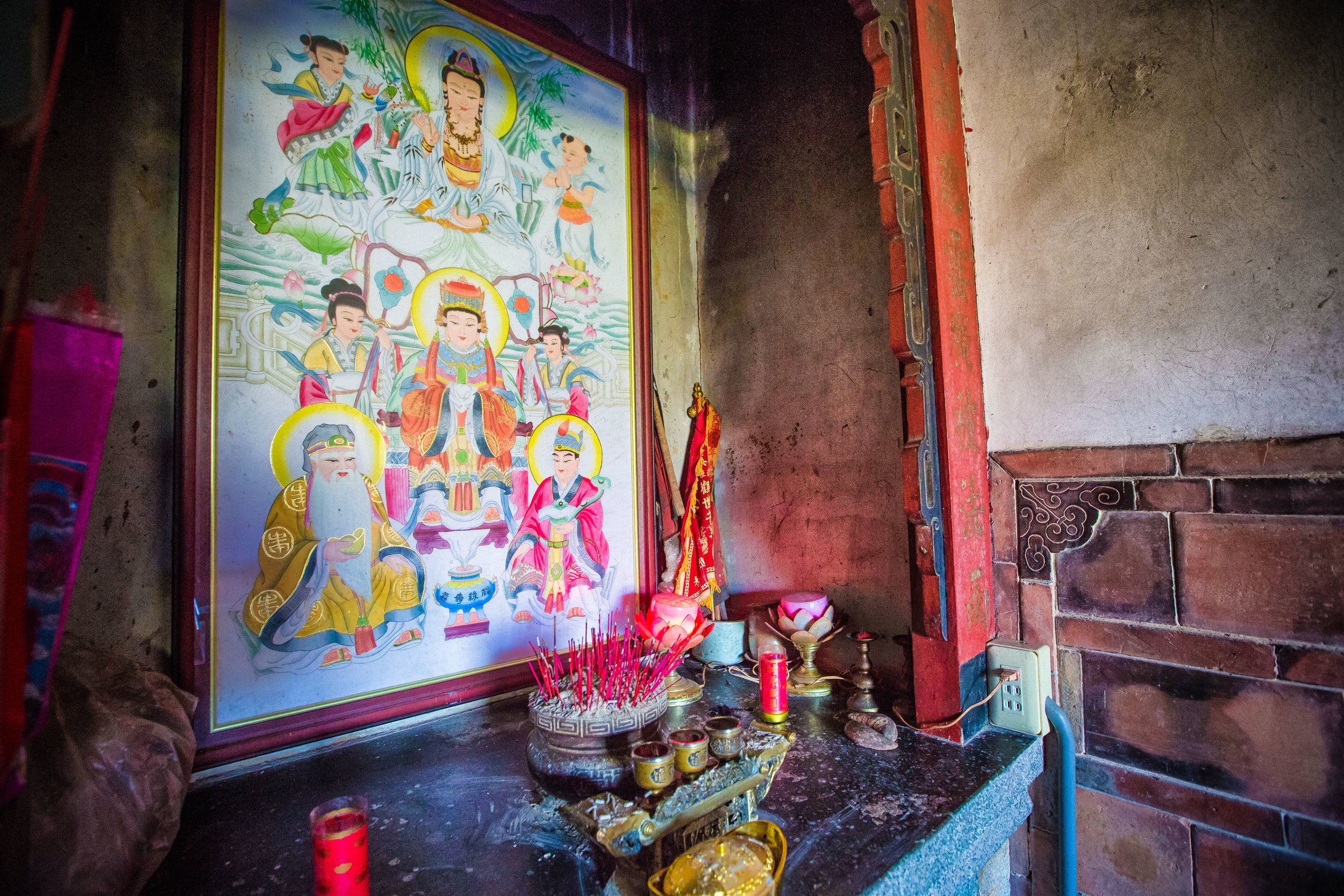
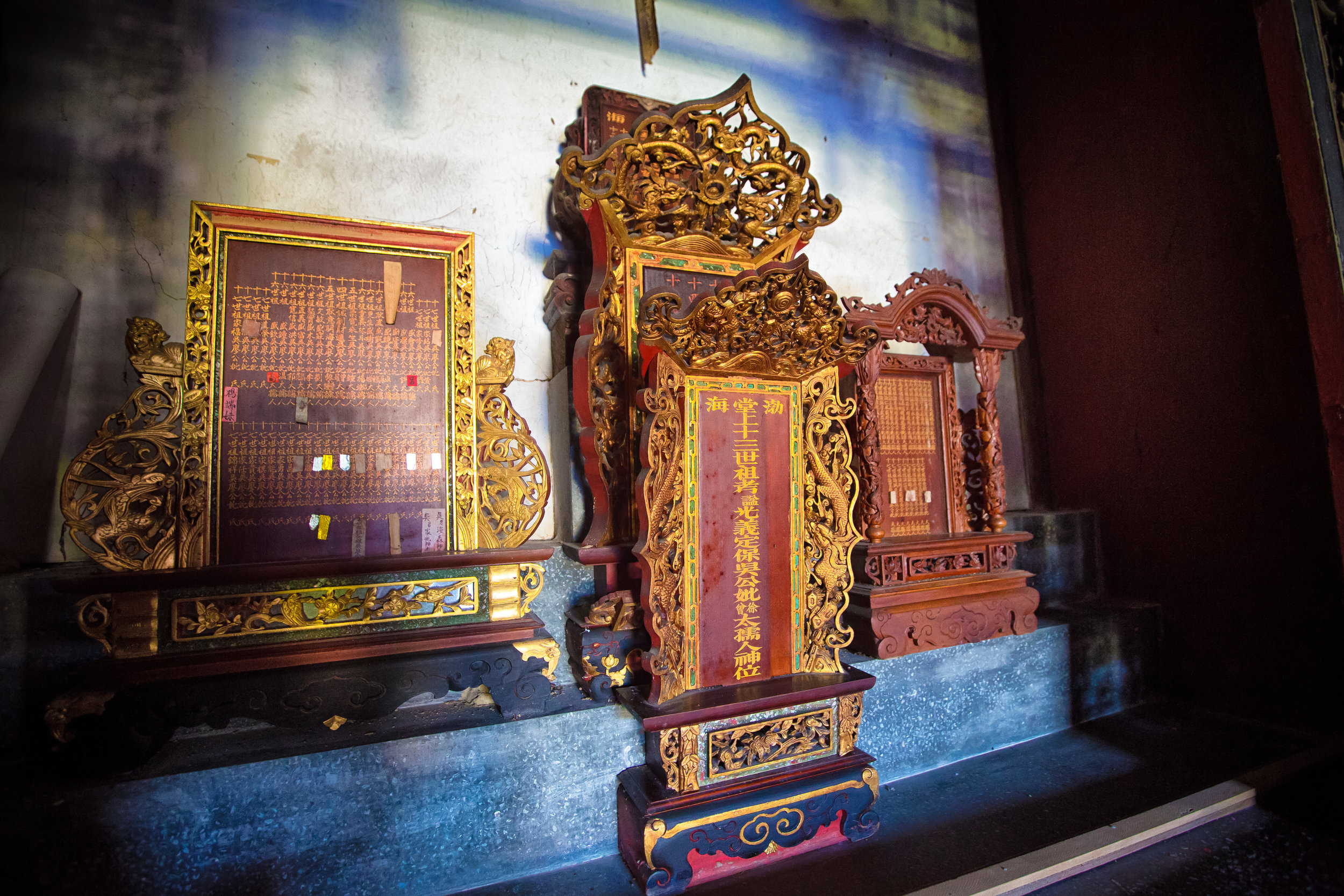
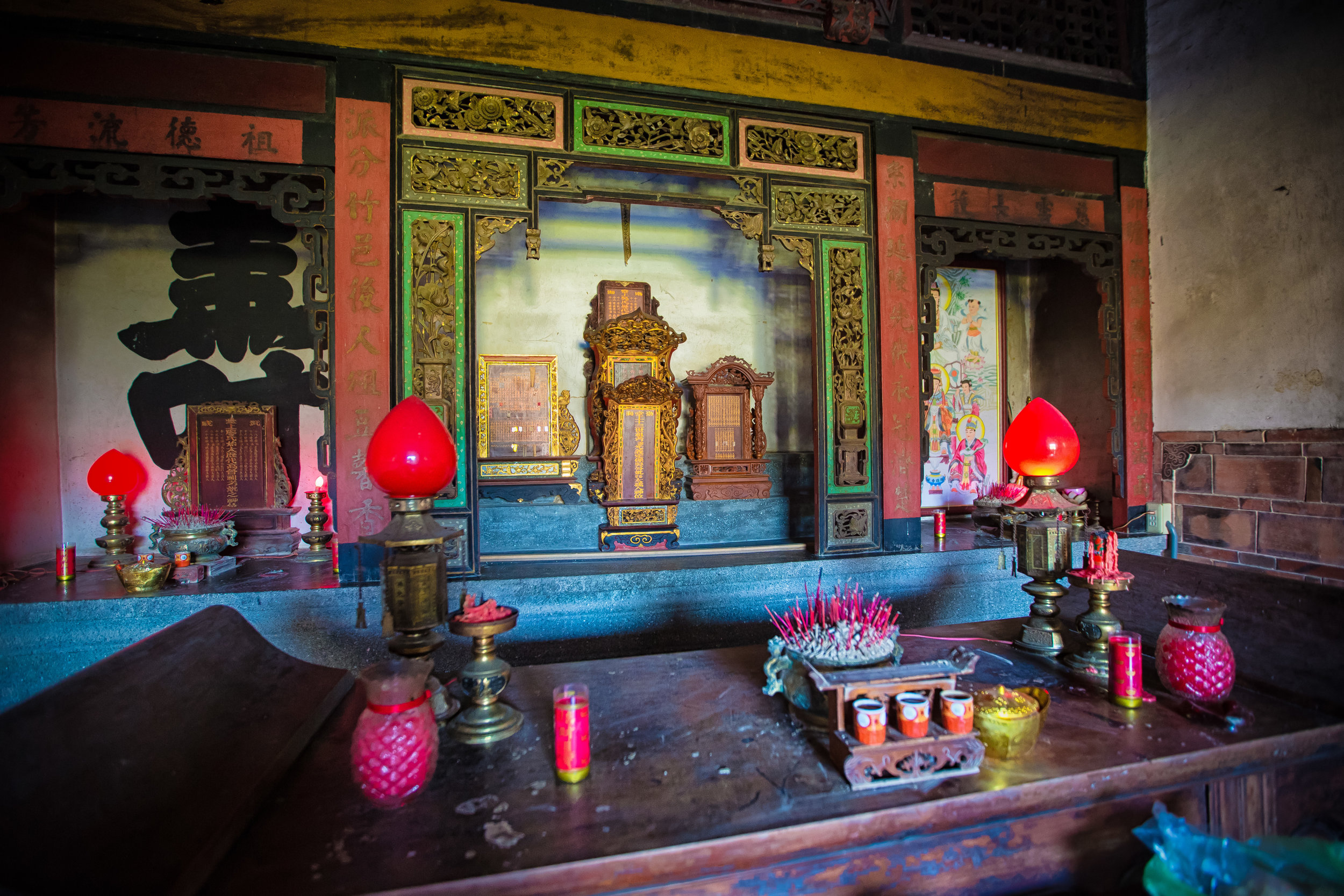
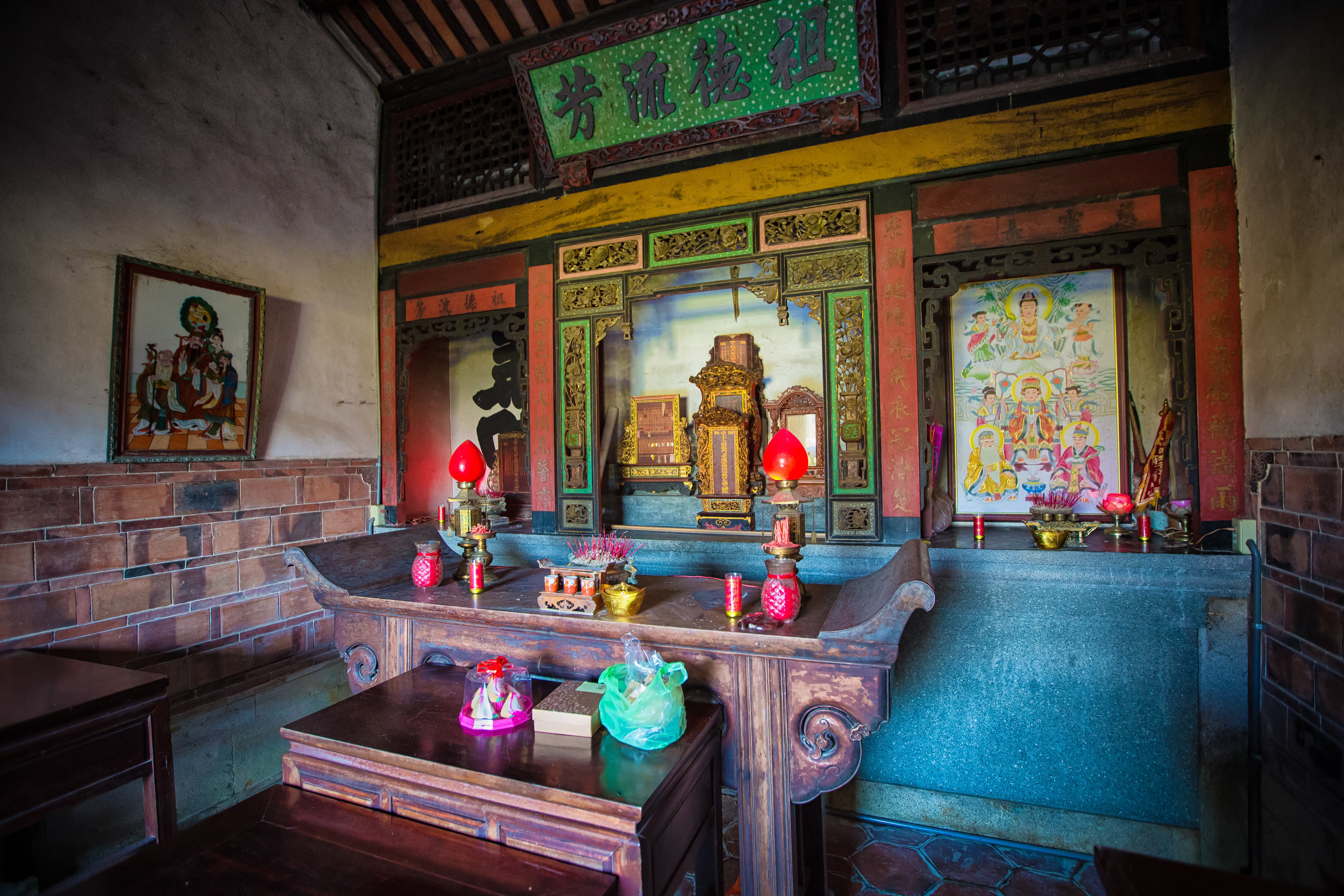
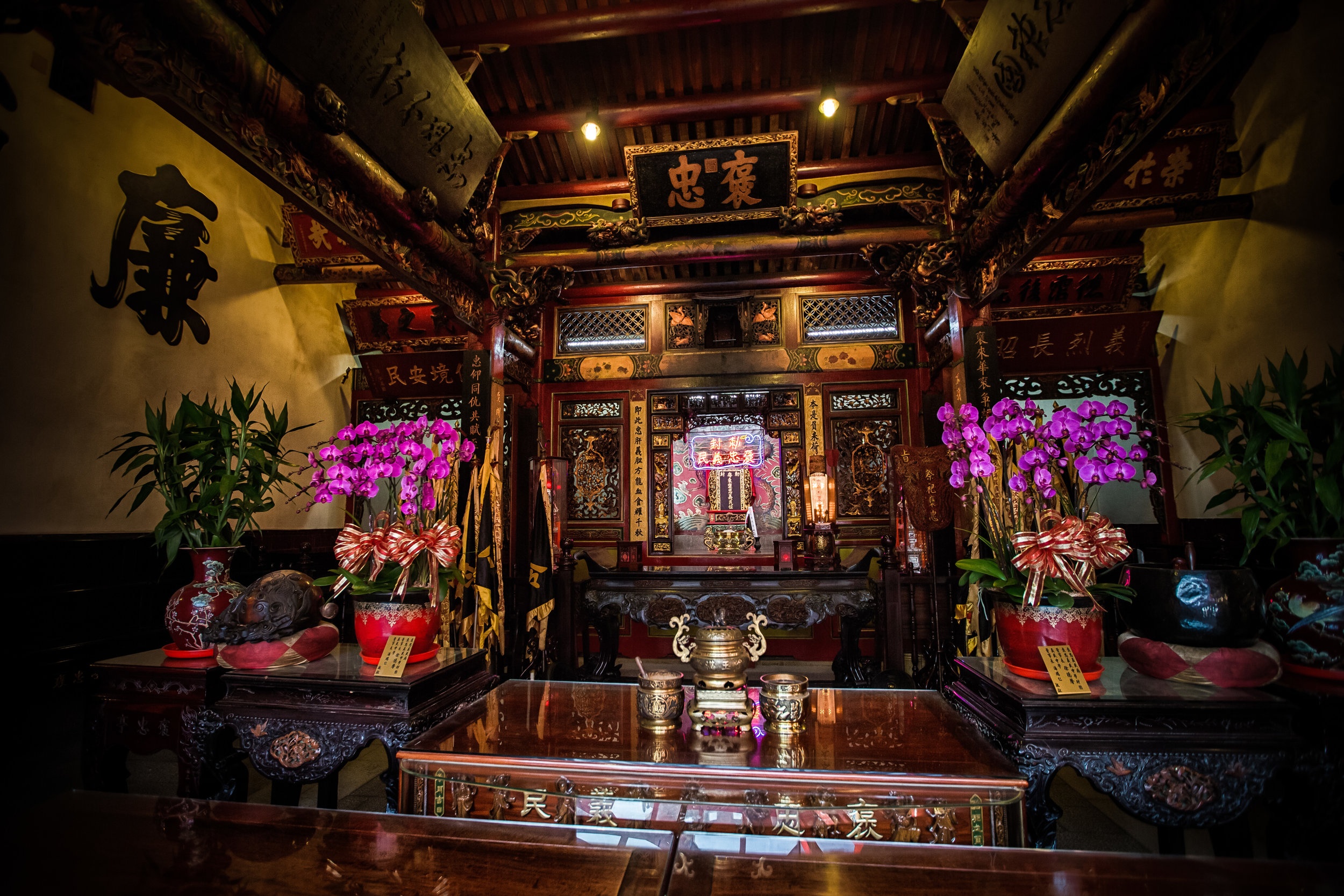
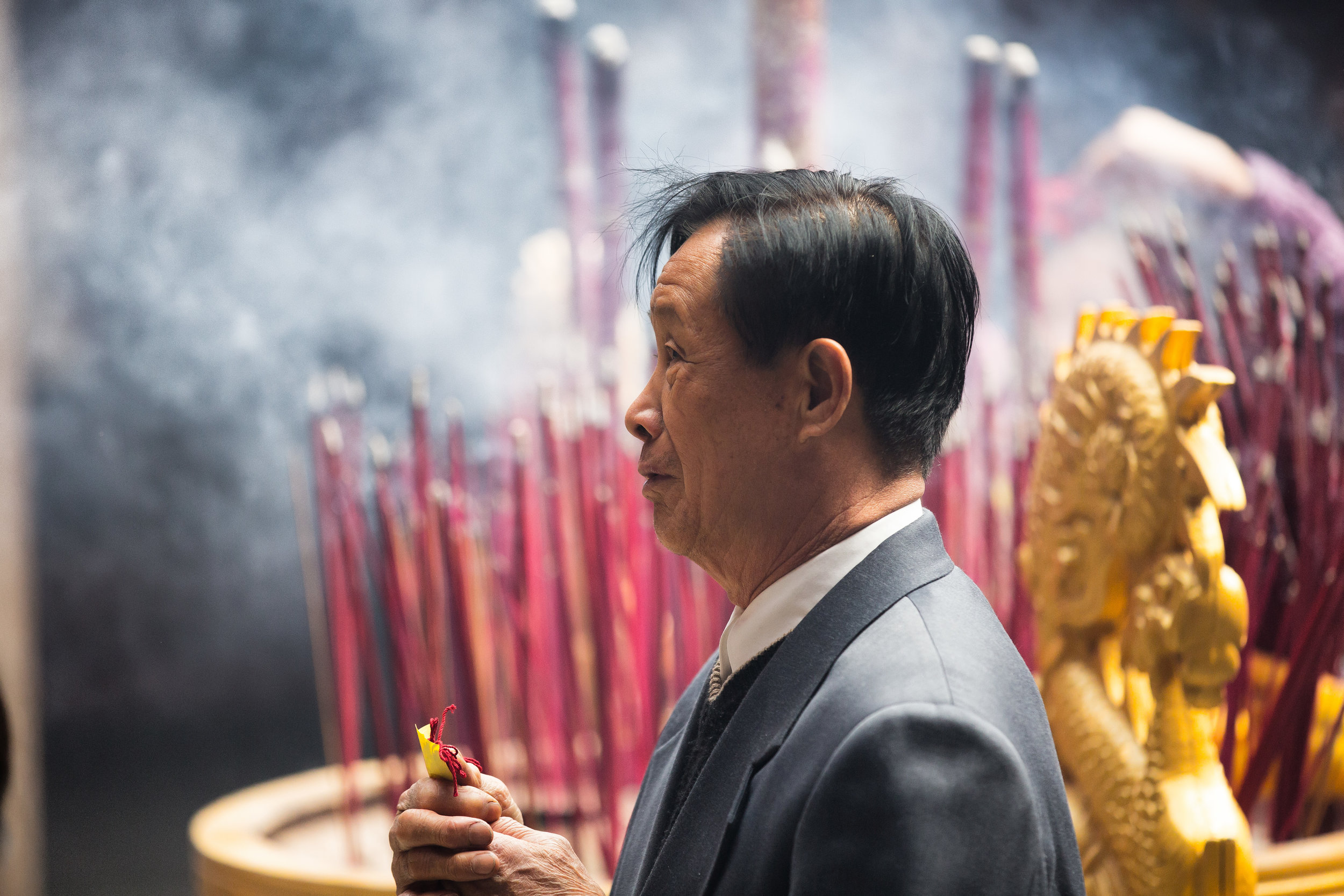
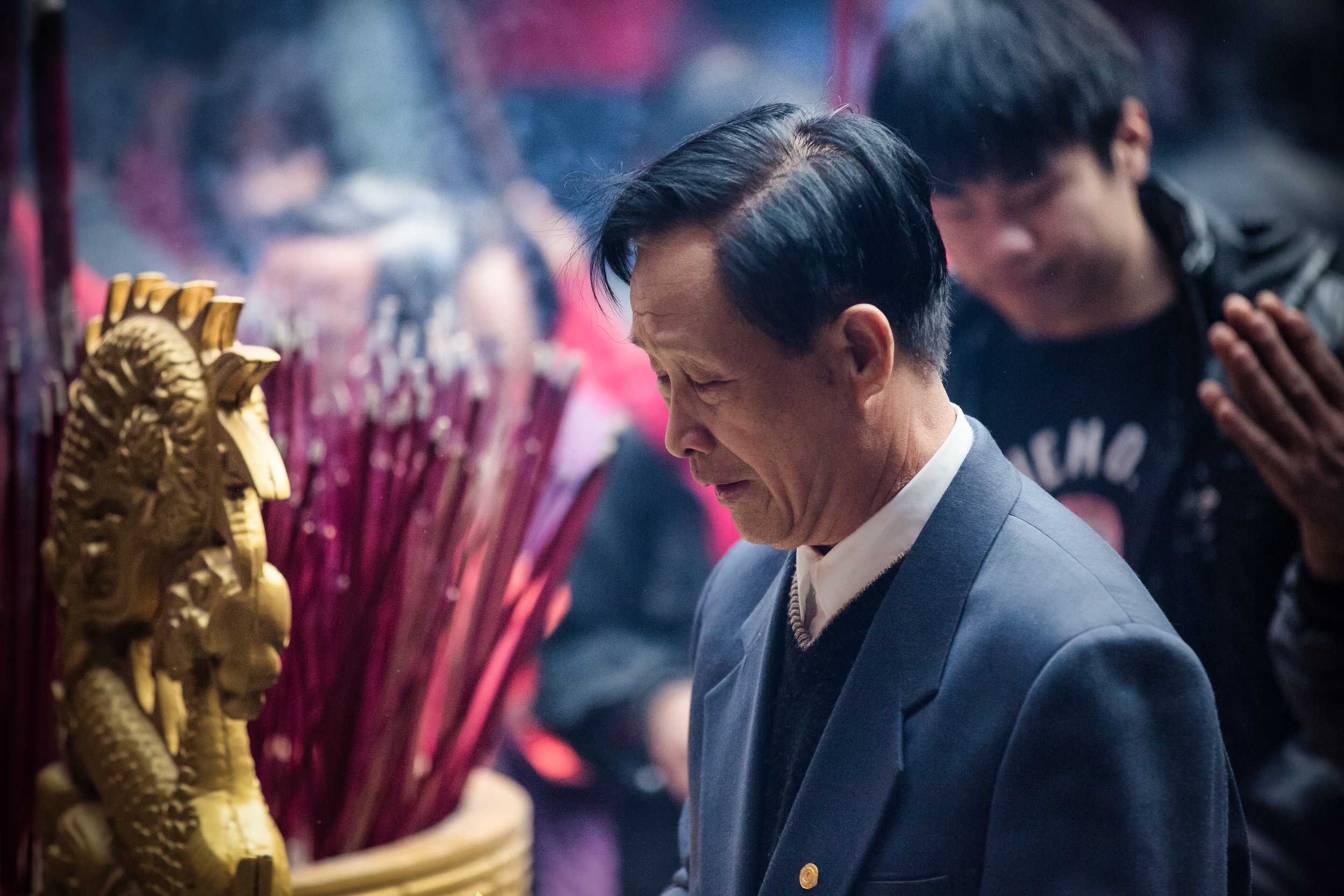
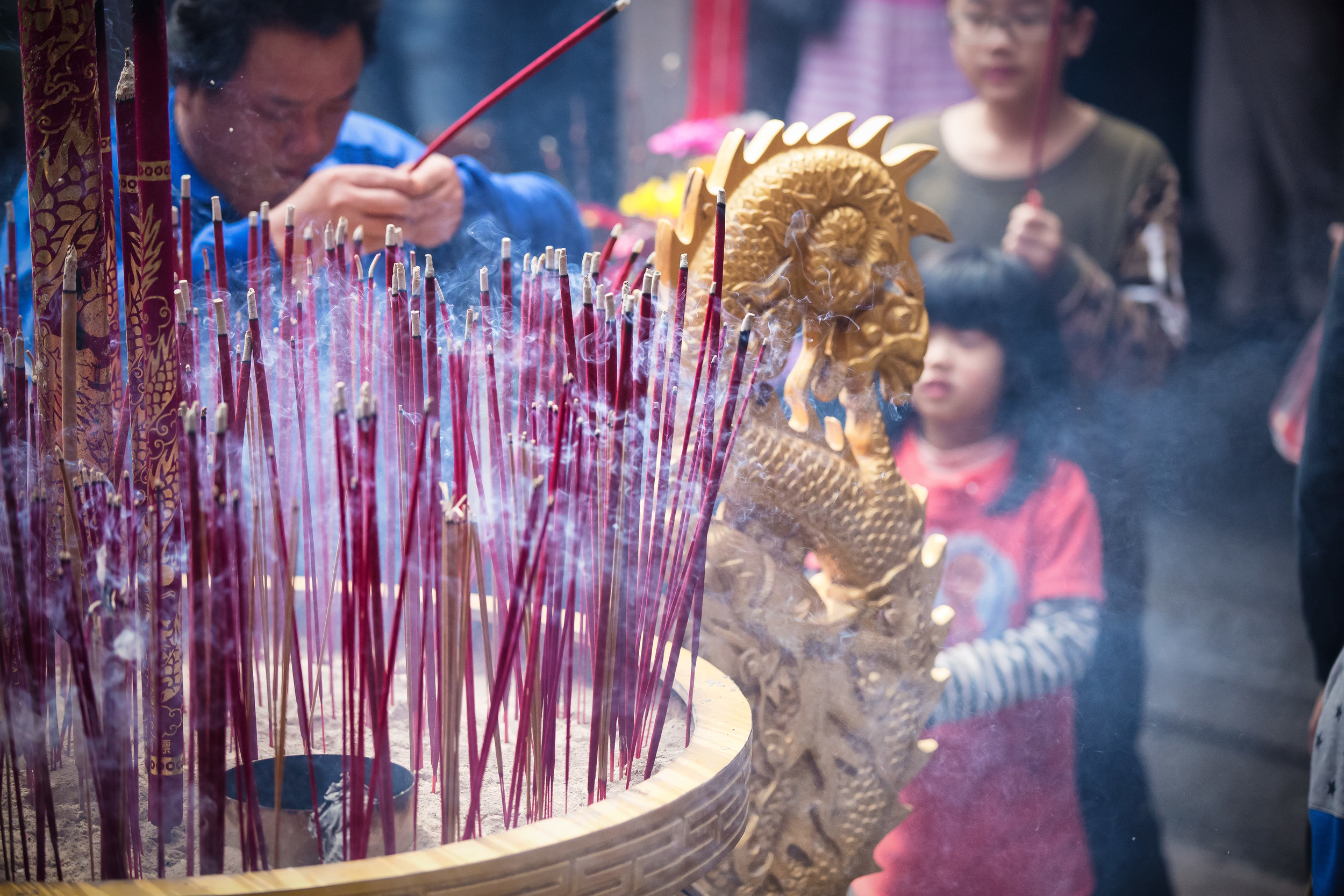
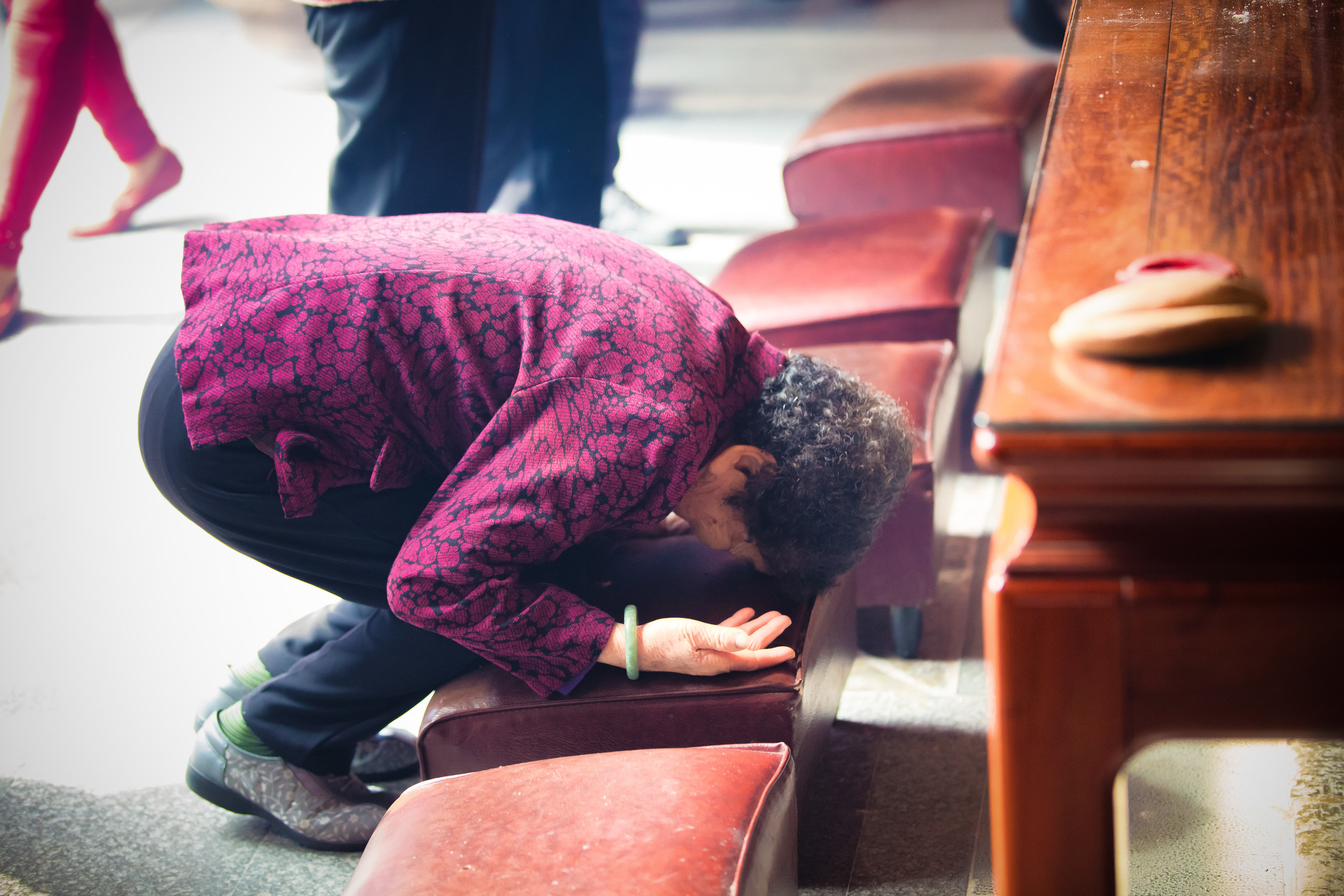
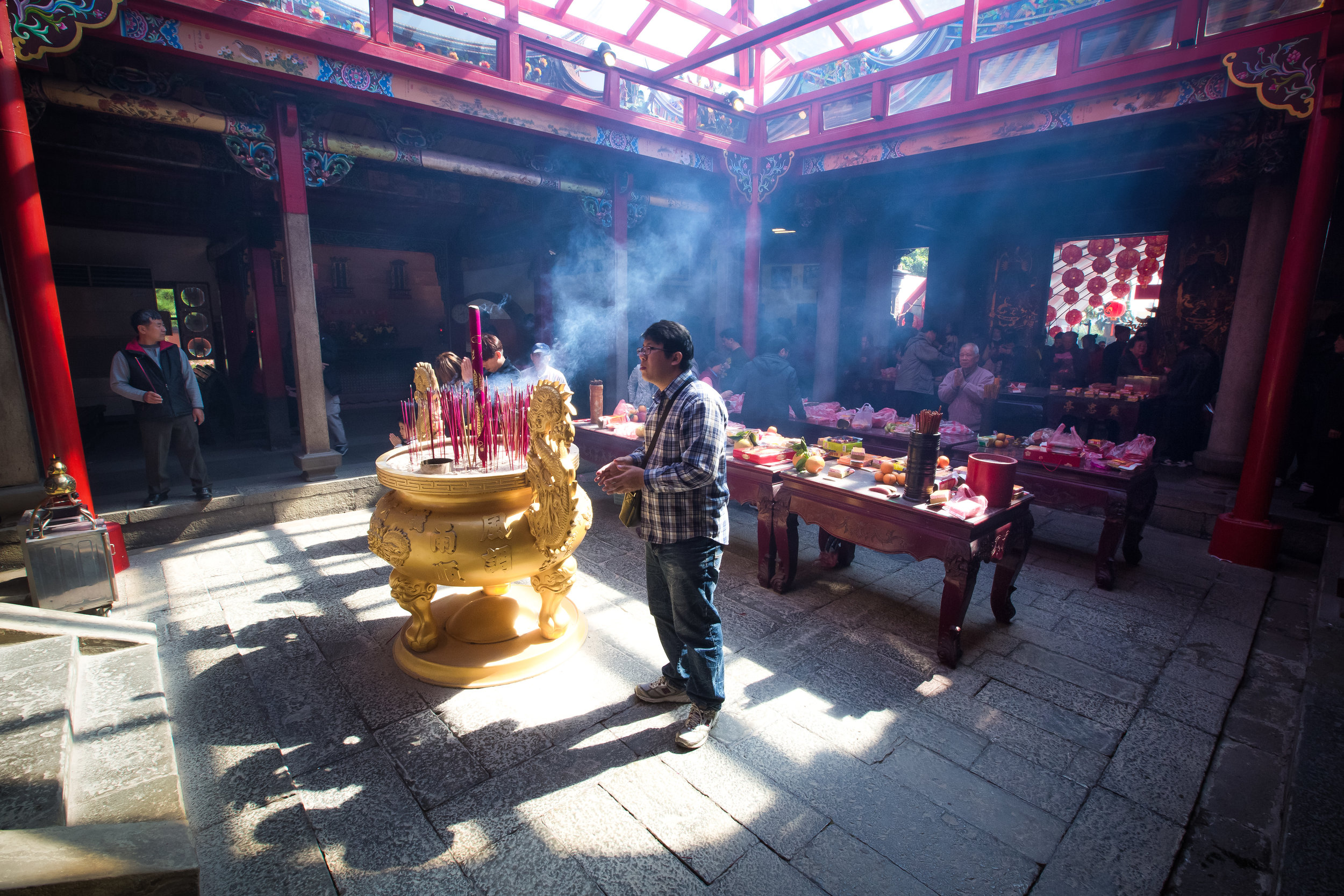
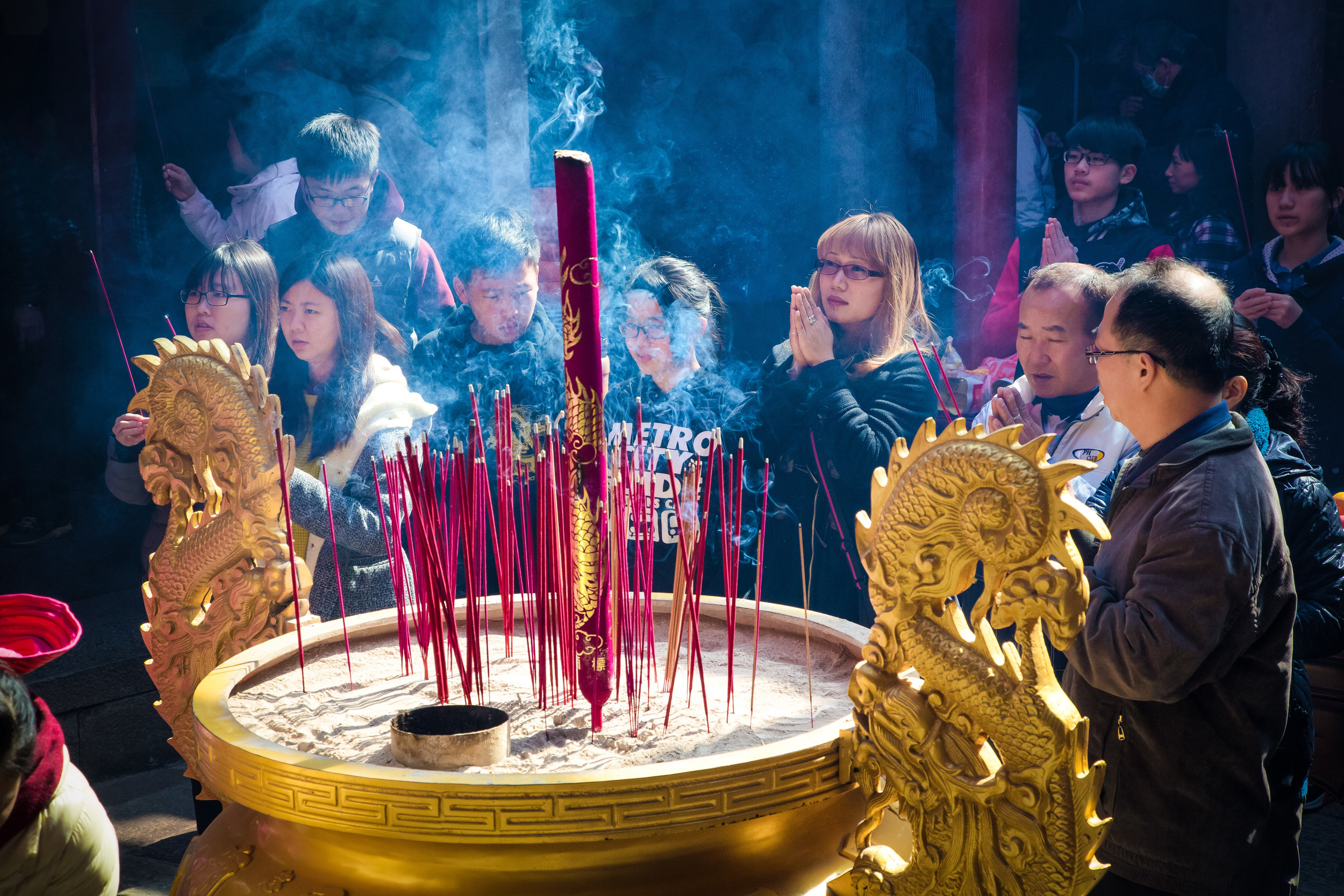
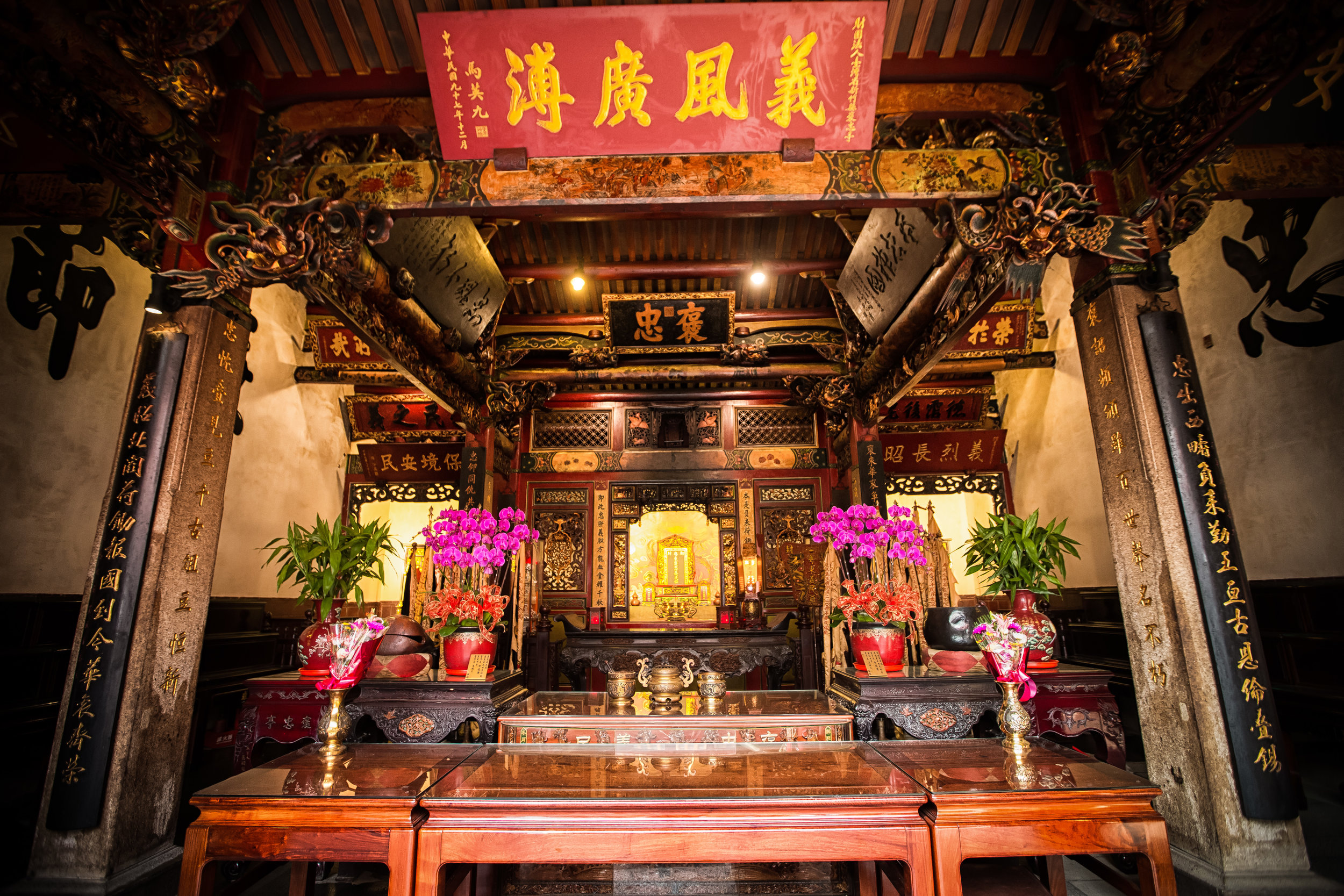
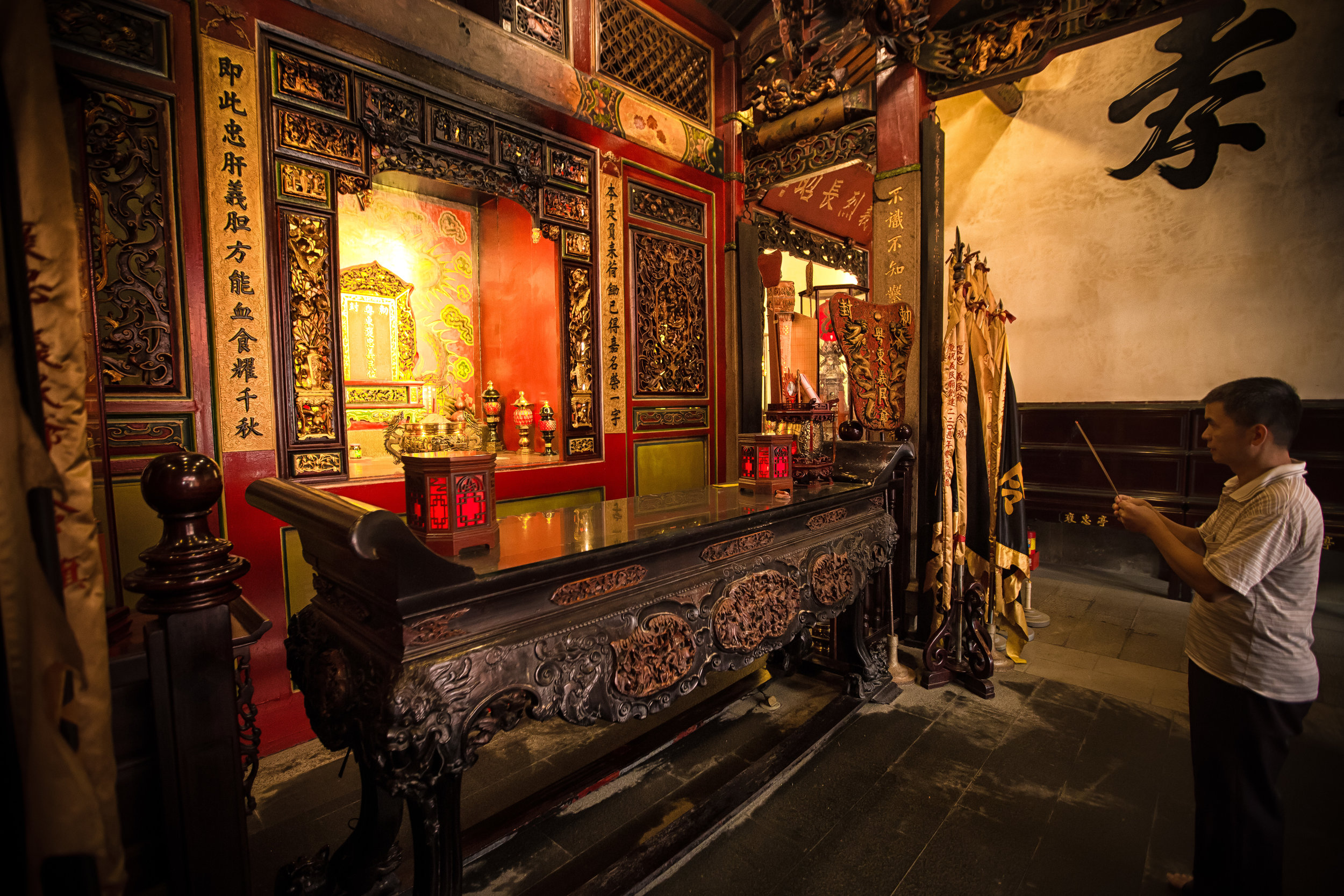
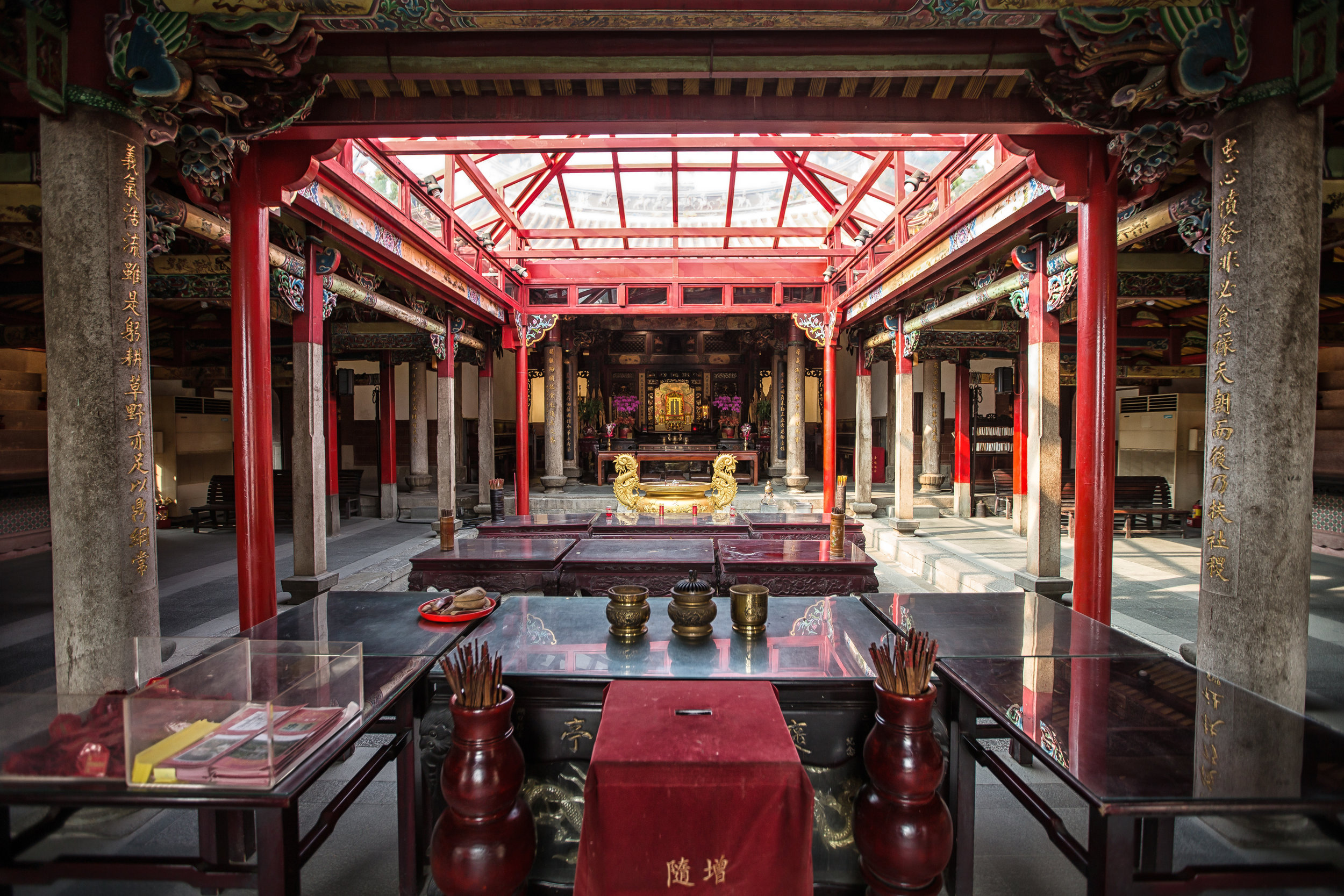
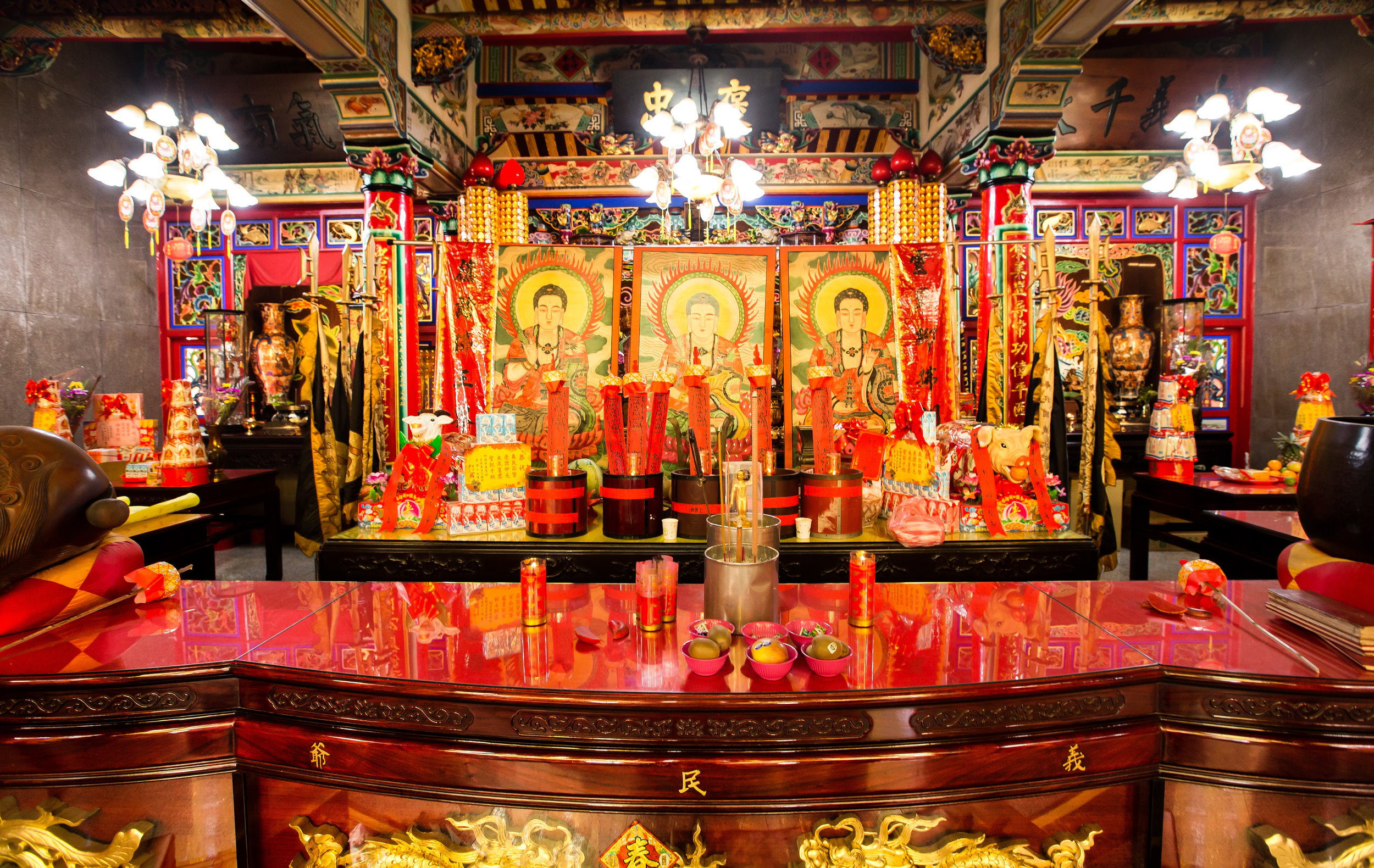
At this point I figured I was about to get yelled at for trespassing but instead he let me in and explained that the central portion of the building was an ancestral shrine for the Wu family (吳家) and that because it was the first day of the Lunar New Year, family members had been returning to pay their respects.
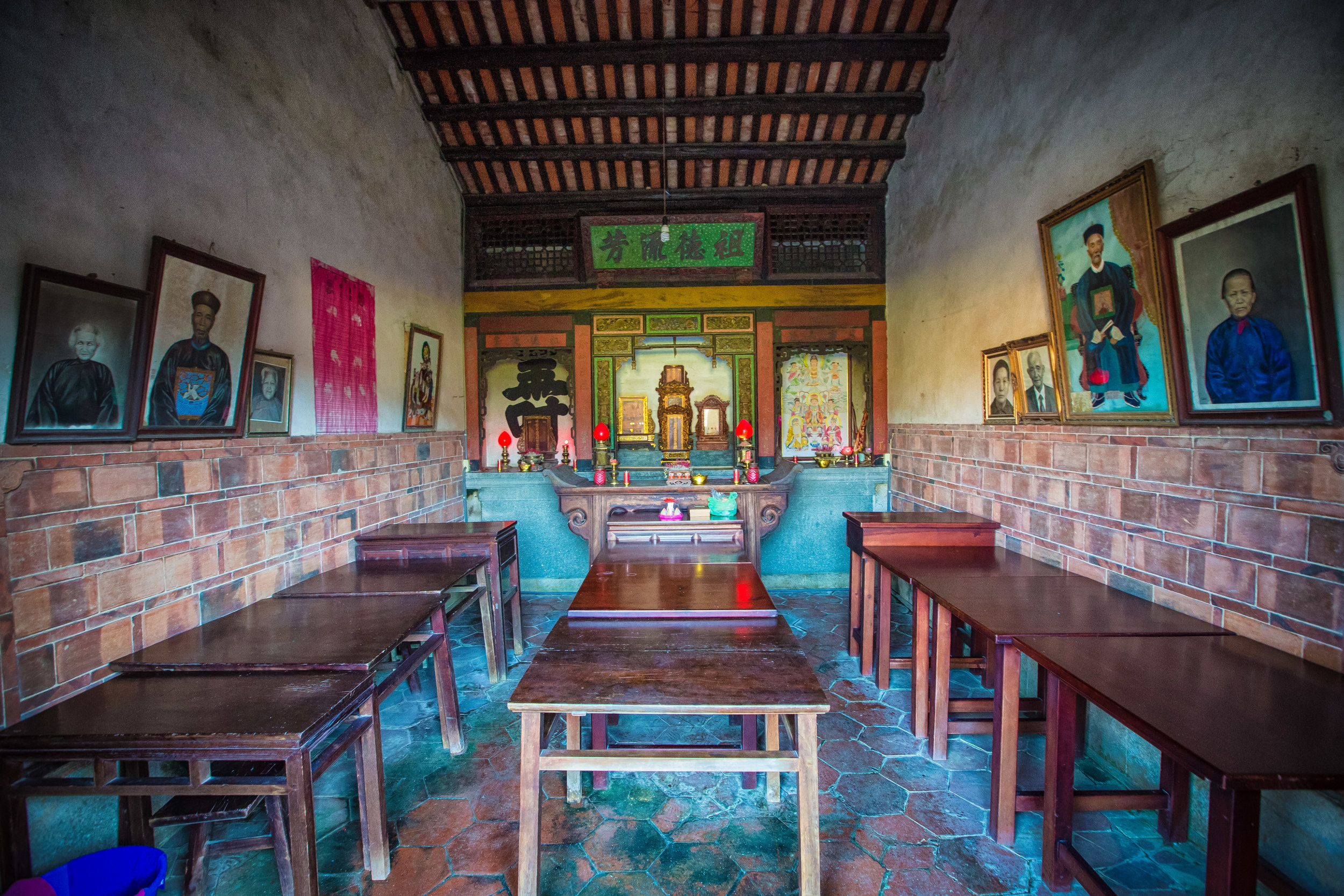
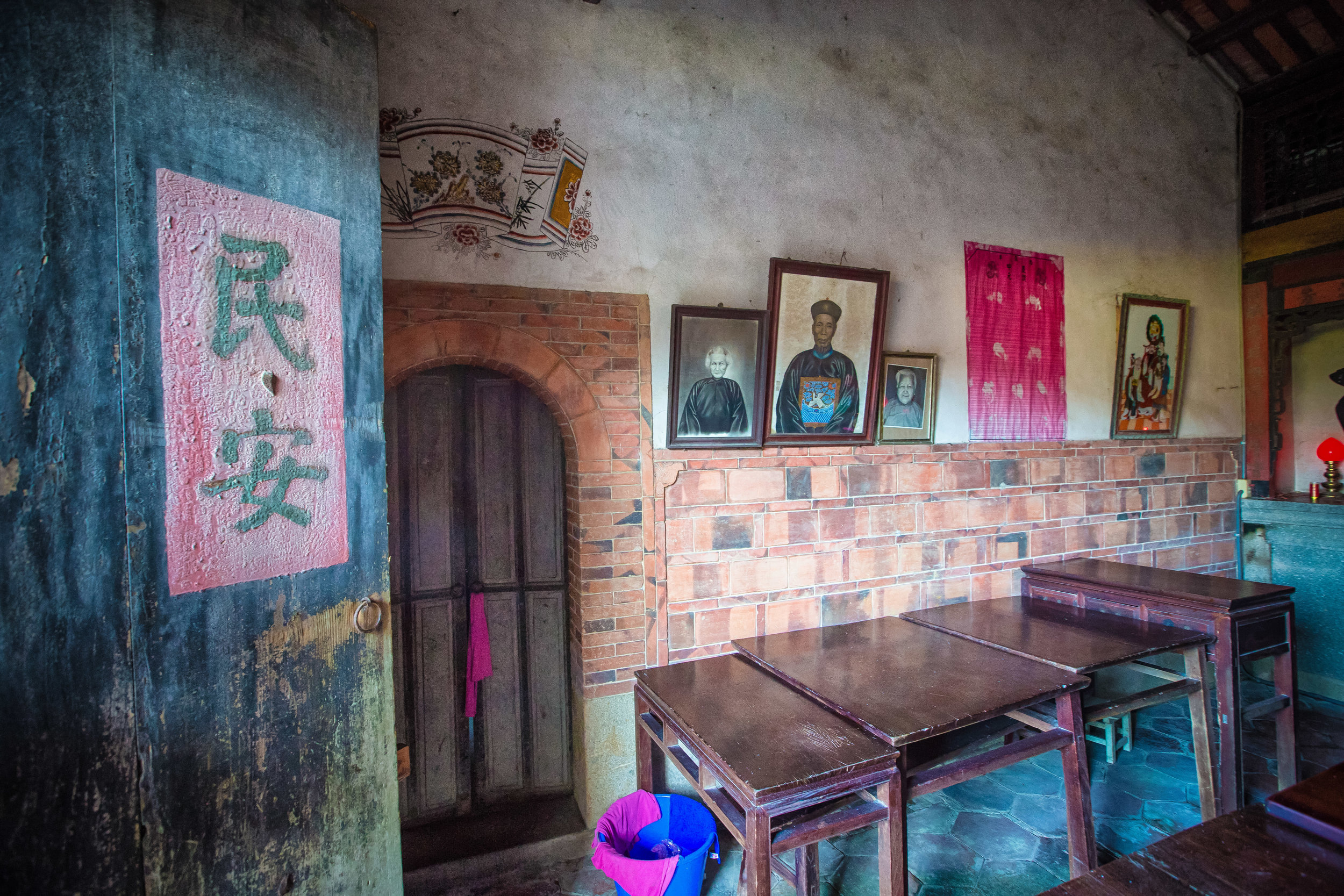
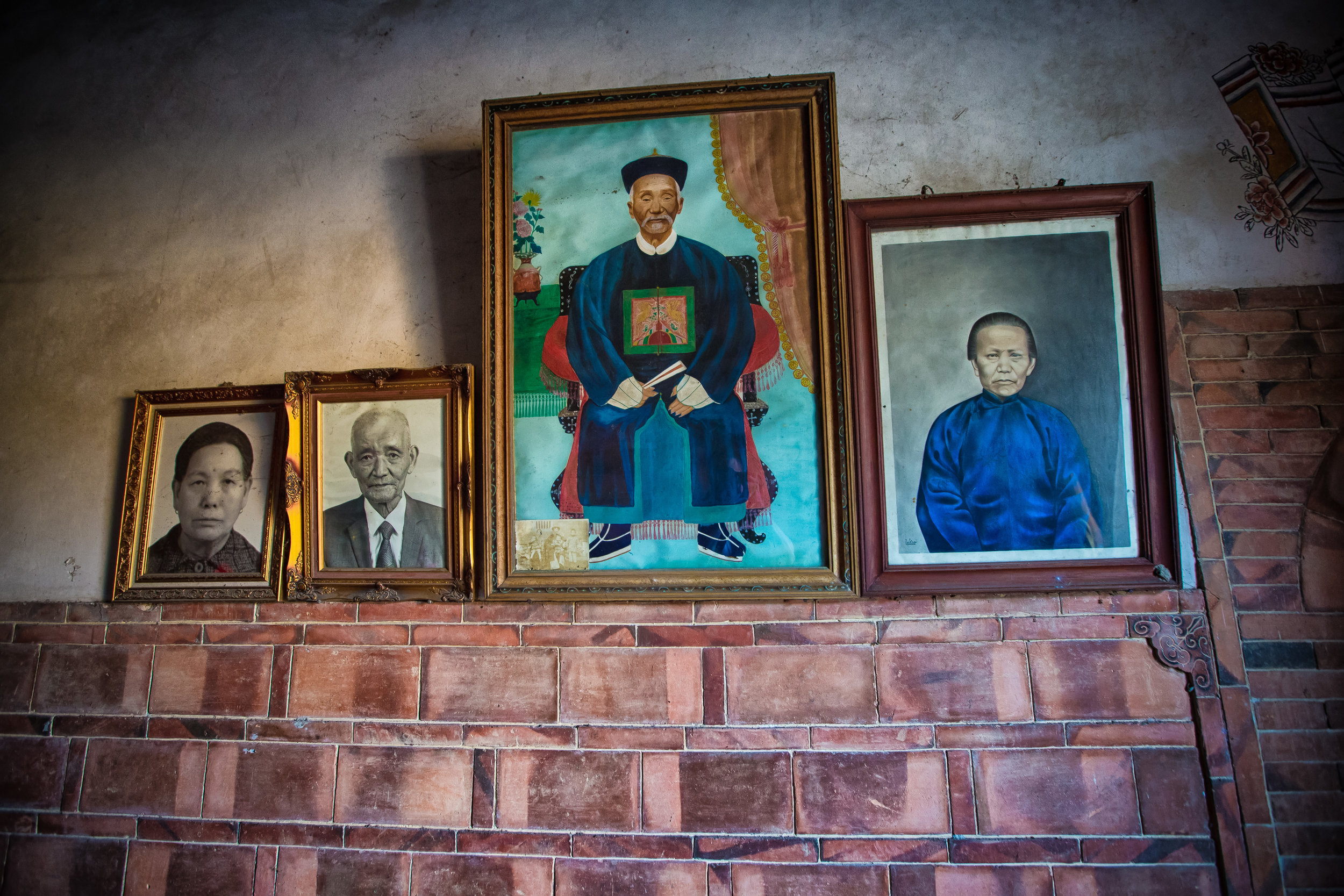
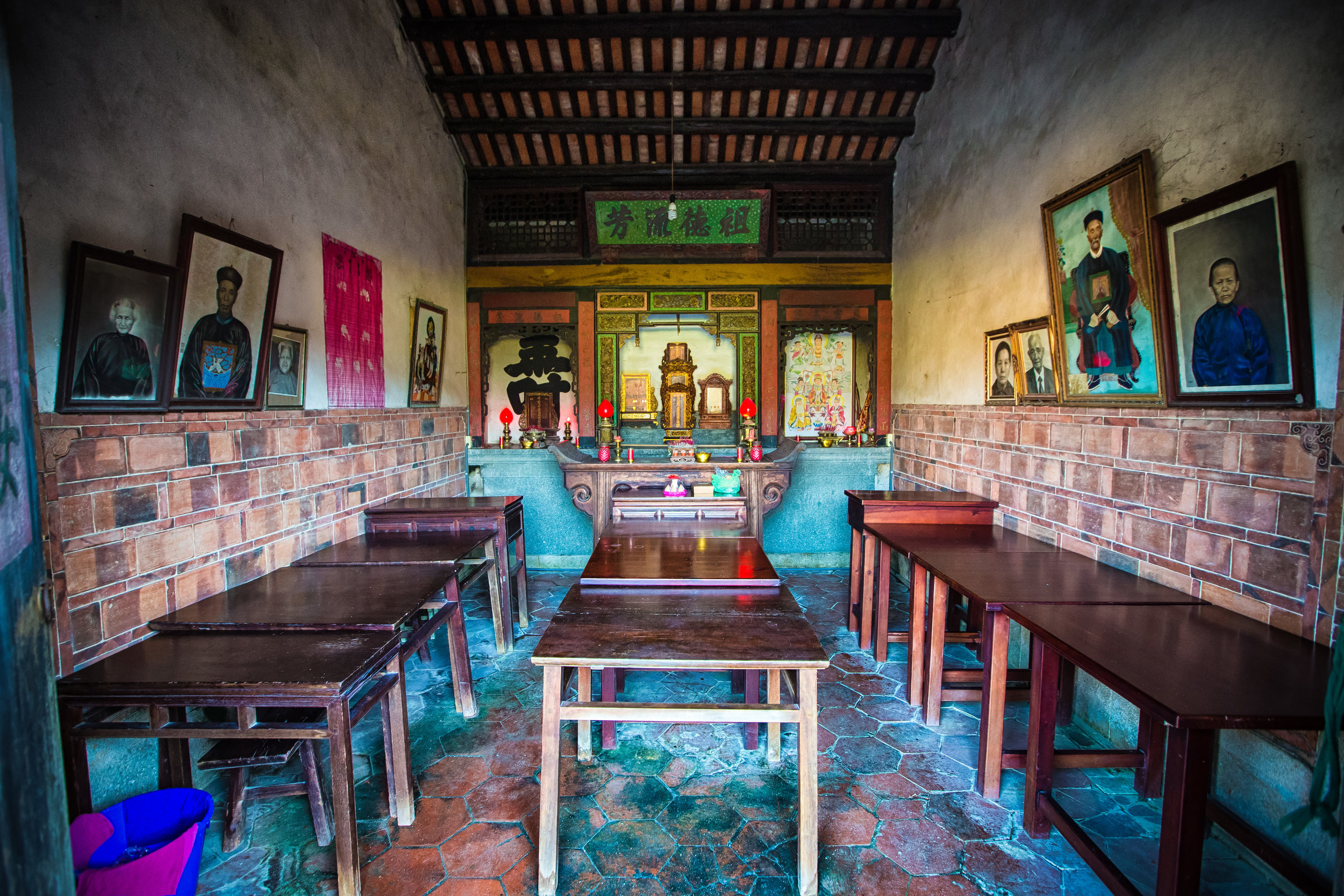
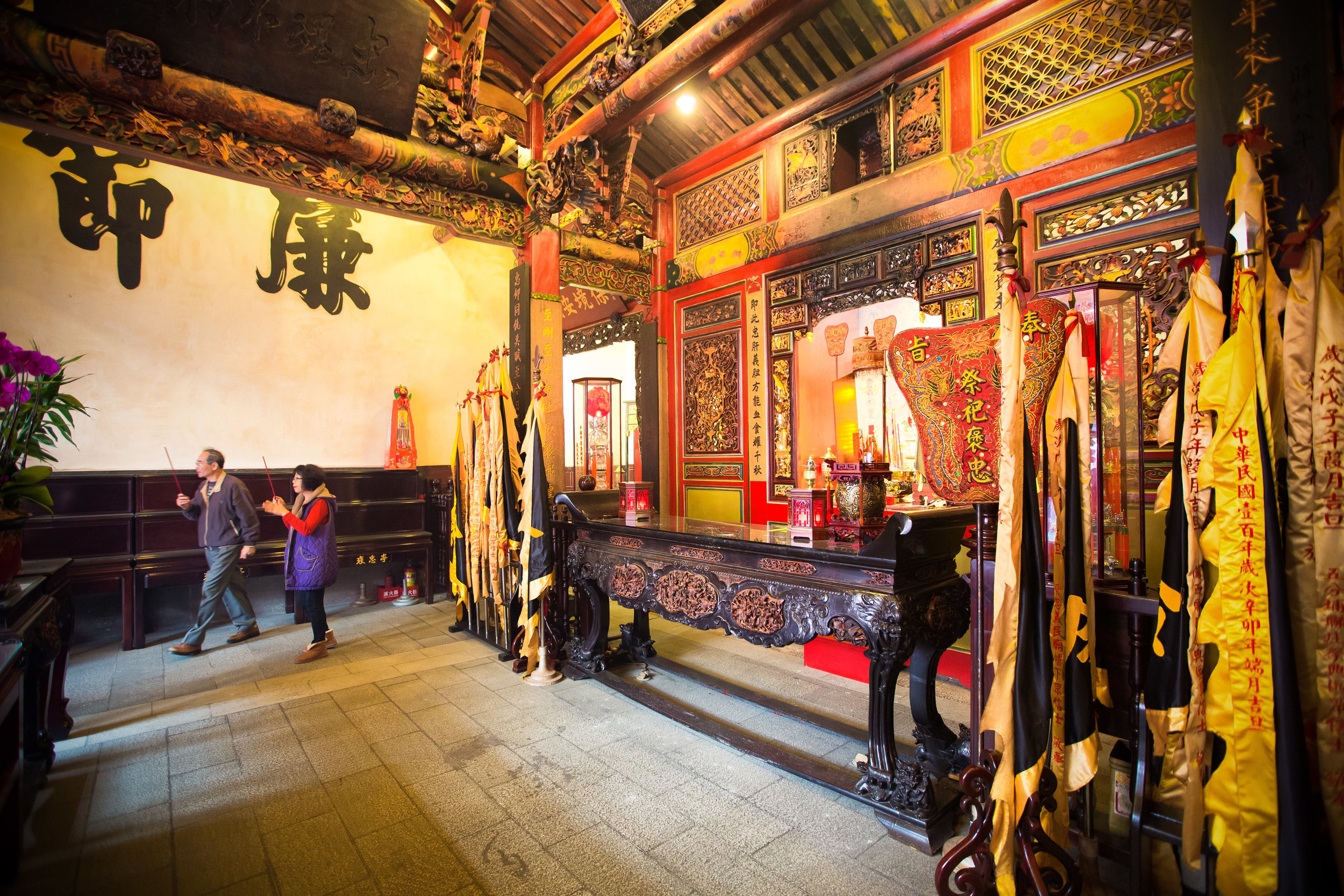
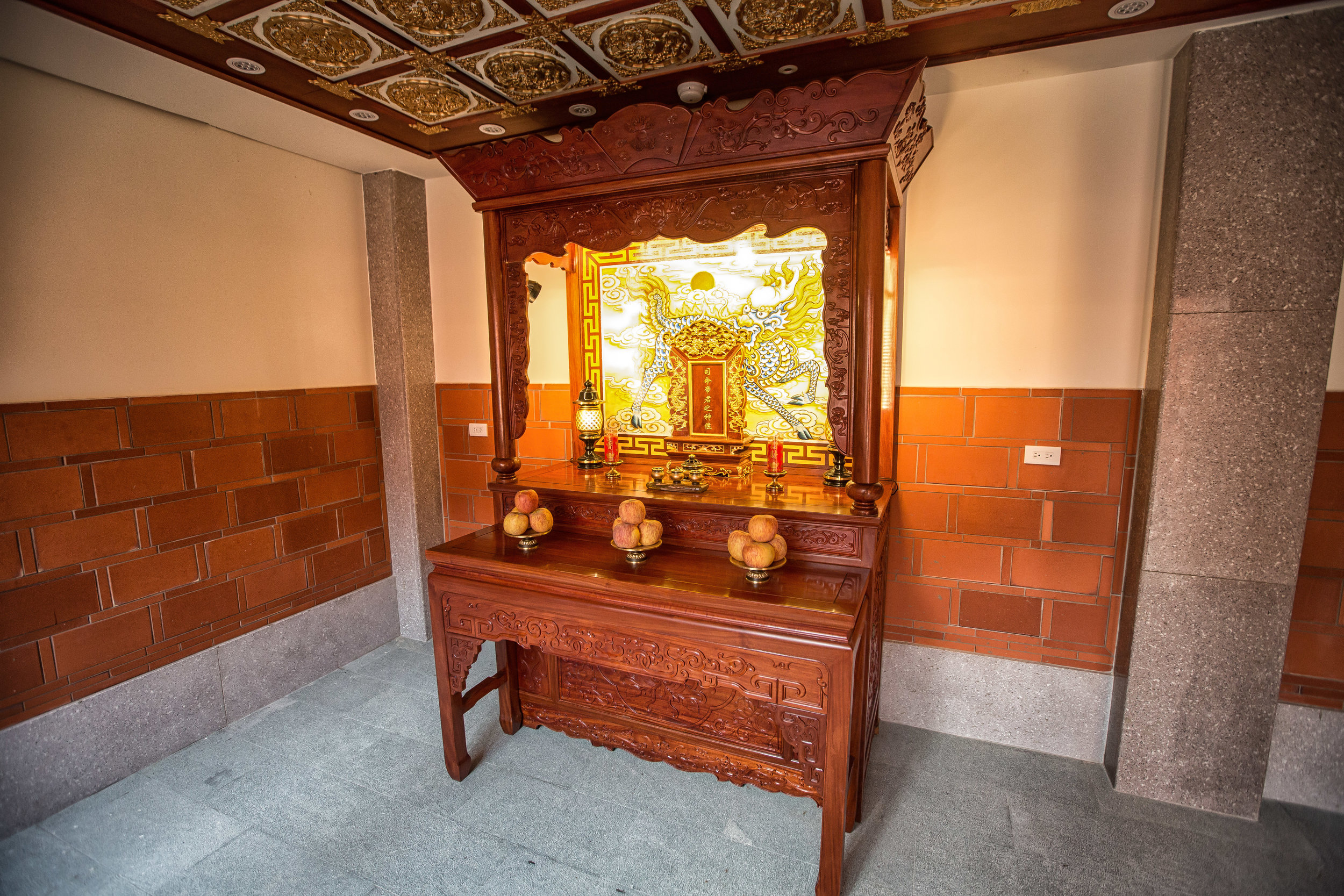
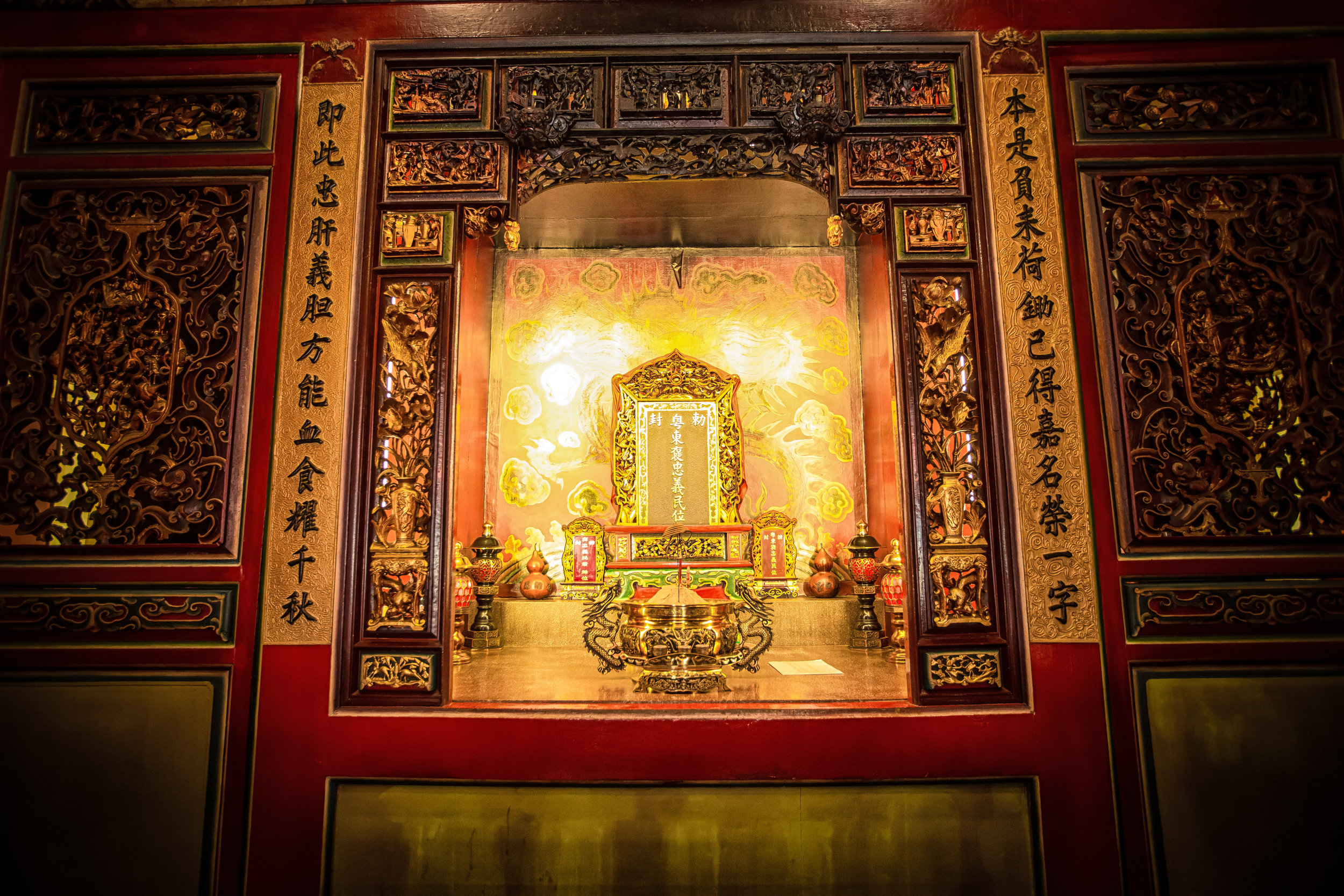
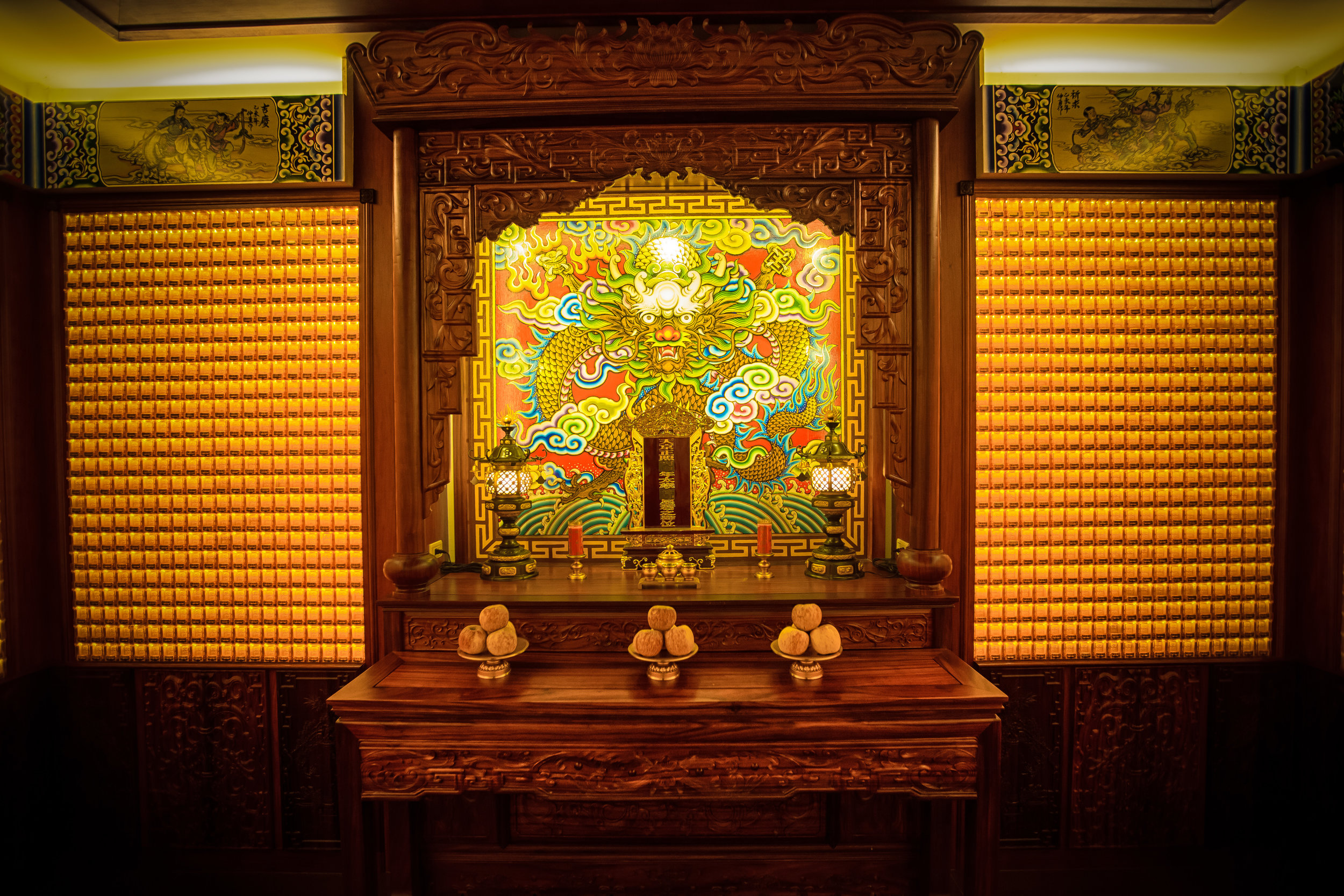
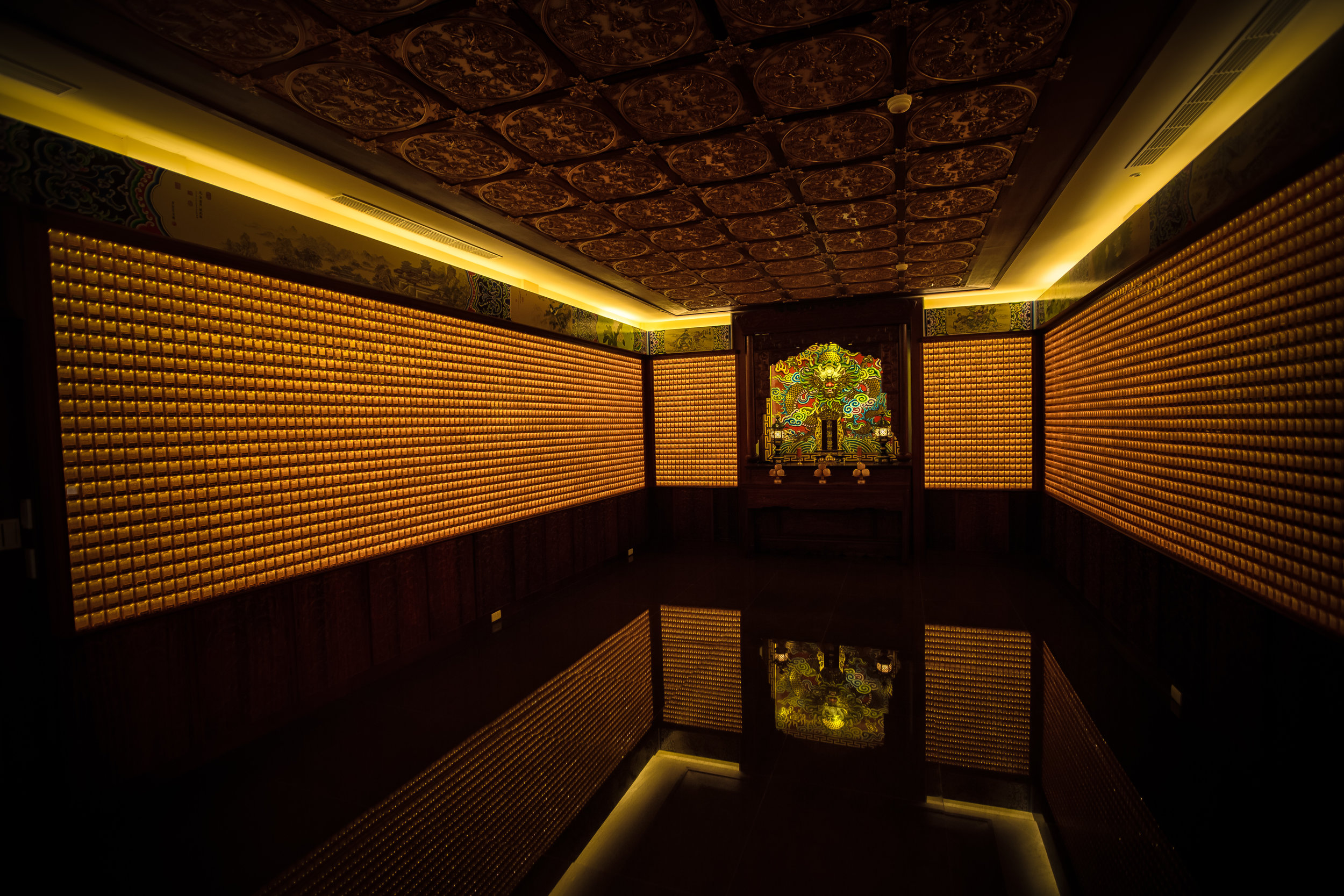
The interior of the building had some really cool hand-drawn portraits from the Qing dynasty on either side of the main shrine as well as some portraits of the family from a time when photography was just becoming a 'thing' in Taiwan. The main shrine in the front was very simple with some spirit tablets and empty space to give offerings.
The room also had several antique wooden tables in front of the main shrine which would have been used for family dinners in the main courtyard when the family was celebrating a special occasion.
The sad thing is that the person who allowed me to go in (who I assume was a member of the Wu family) and check it out told me that the old building had structural issues and was prone to leaking. The leaking was causing a lot of water damage in the old wooden building which meant that the main frame was likely to collapse and the inside was also unfortunately rotting and the smell was evidence of that.
To the right of the main entrance were several red pieces of paper stuck to the wall. Each piece of paper was recognition of a member of the family who donated to tear down the existing building and replace it with a new one.
Unfortunately these beautiful buildings are starting to disappear at an alarming rate and I'm afraid that in the future all we'll have to remember them by is photos like these.
So, if you see one in your travels, stop by and take a minute to appreciate it.
Respect your local Sanheyuan, they won't be around forever.
Gallery / Flickr (High Res Shots)