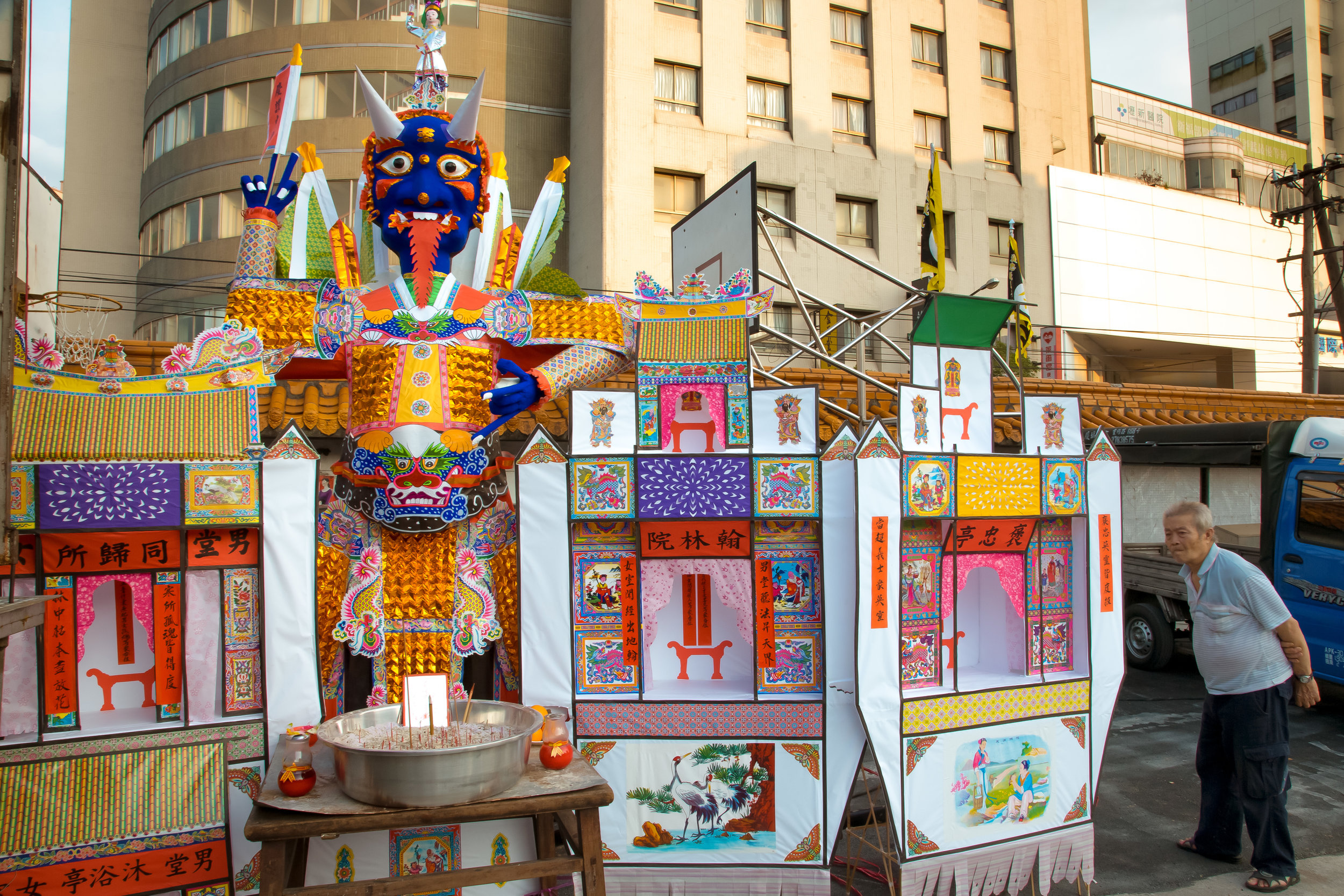
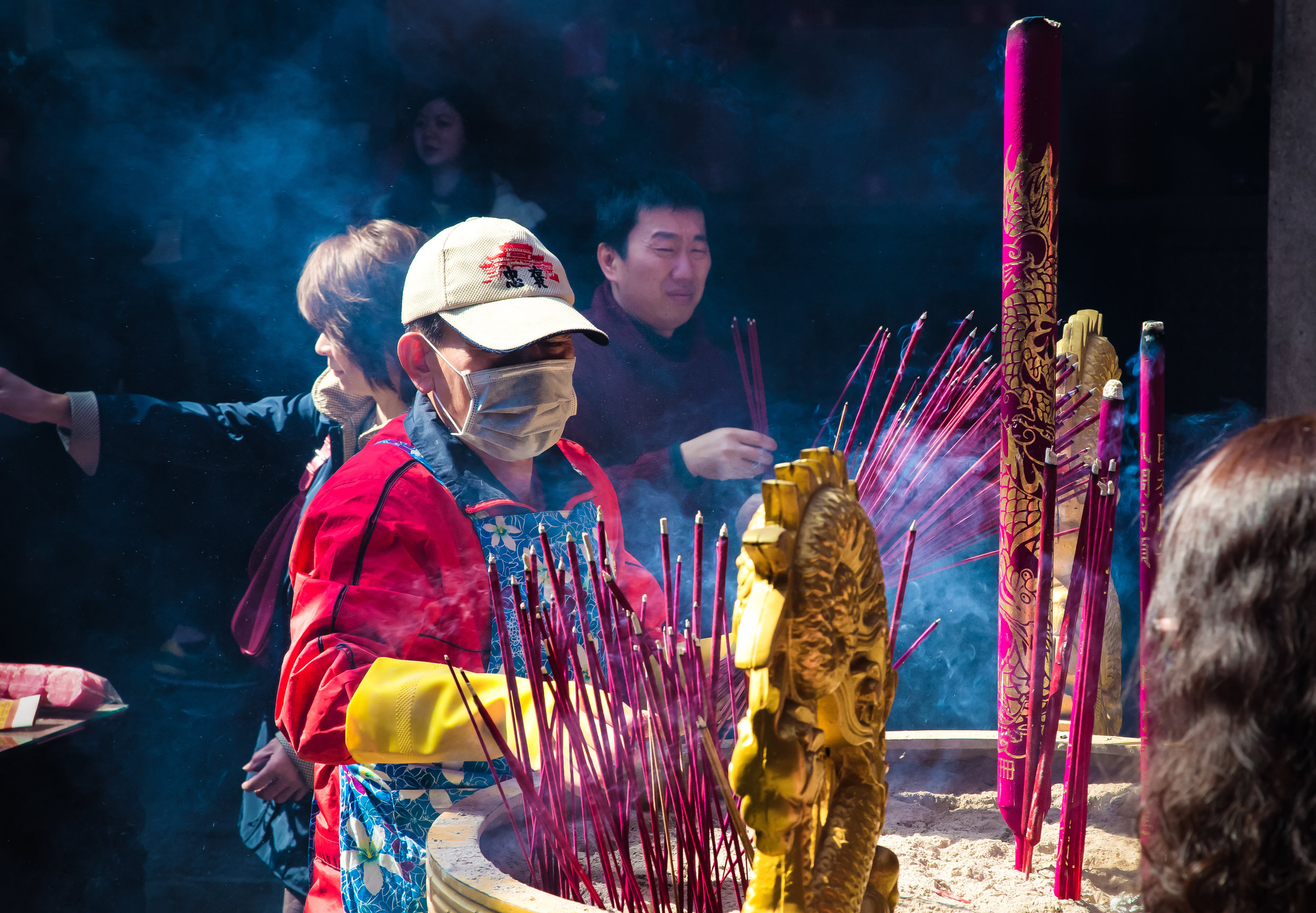
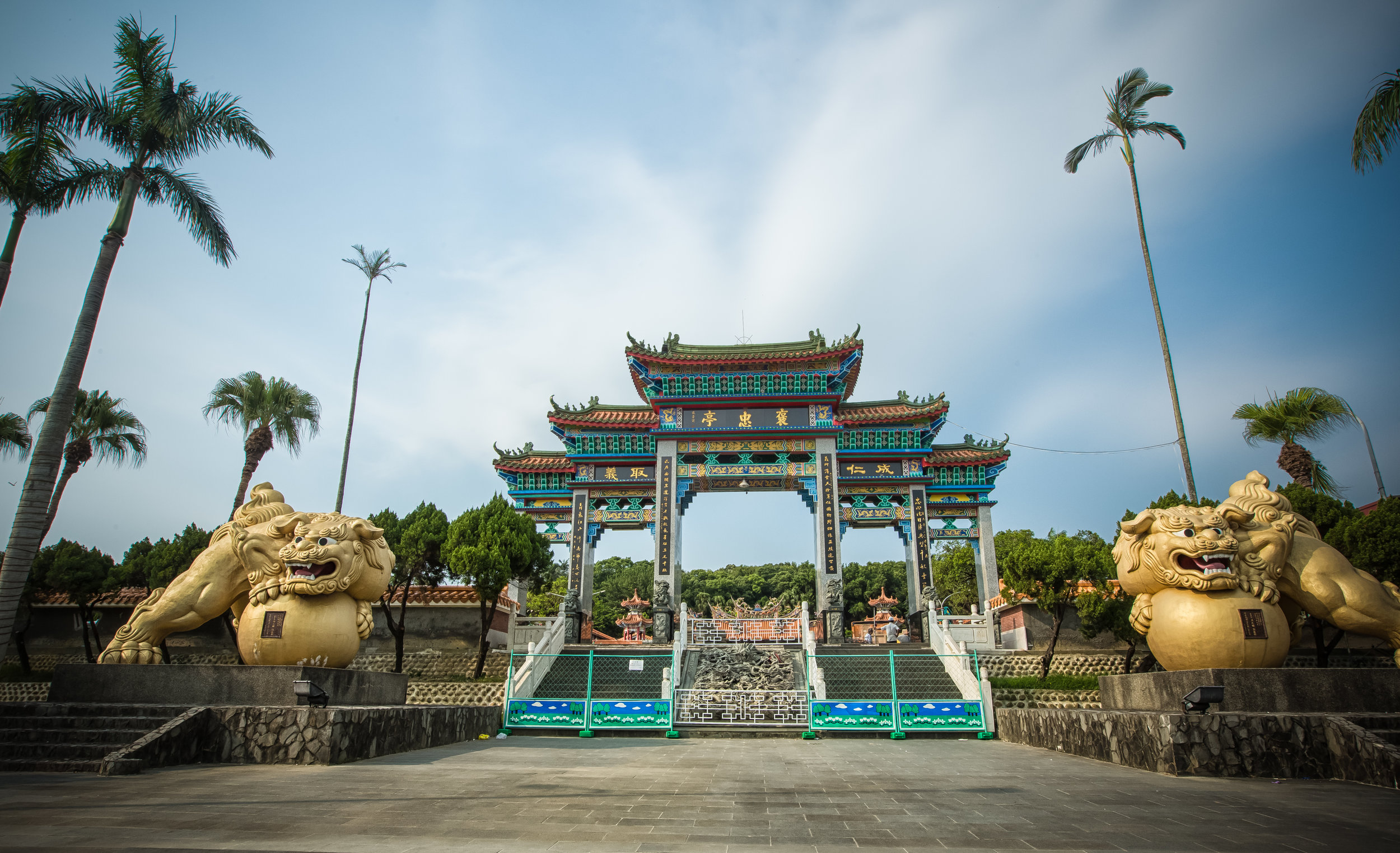
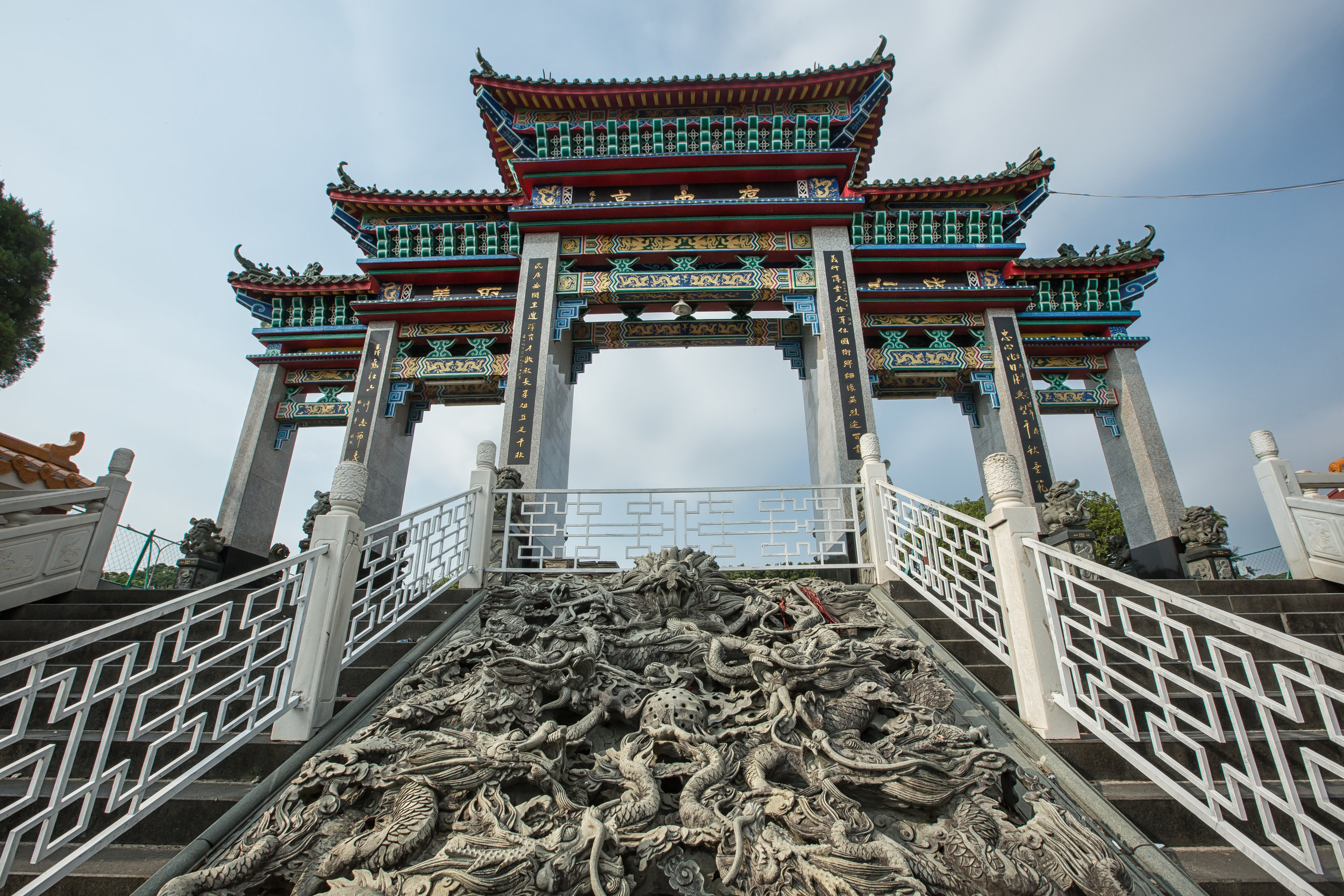
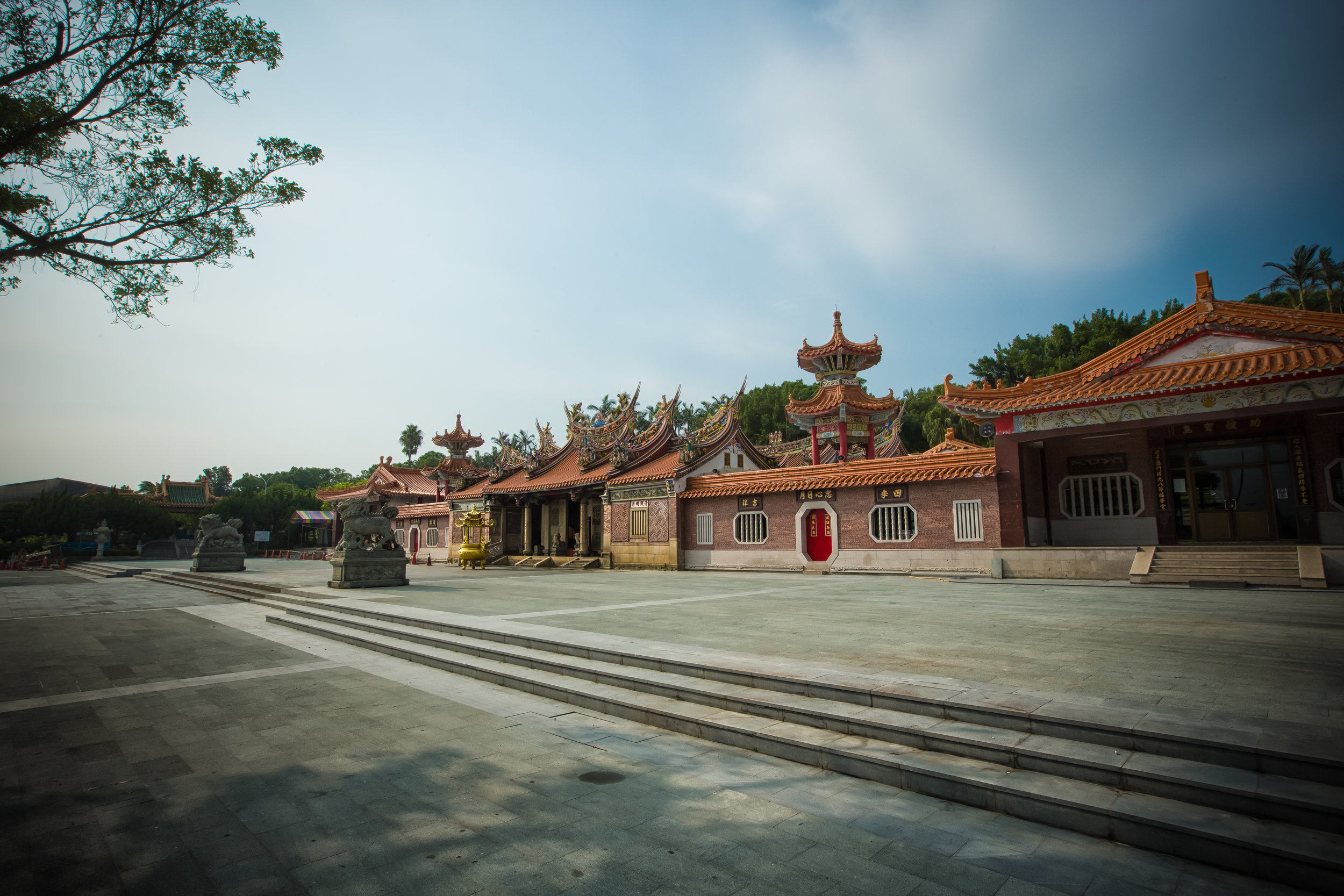
Without fail, one of the busiest times on my yearly calendar is when the annual Ghost Month (中元節) rolls around, usually in the late stages of summer, or the seventh month on the lunar calendar.
The problem I find myself faced with each and every year is that there is always so much to see and do that I need to be strategic and make sure to plan well in advance, so that I can make the most of my time.
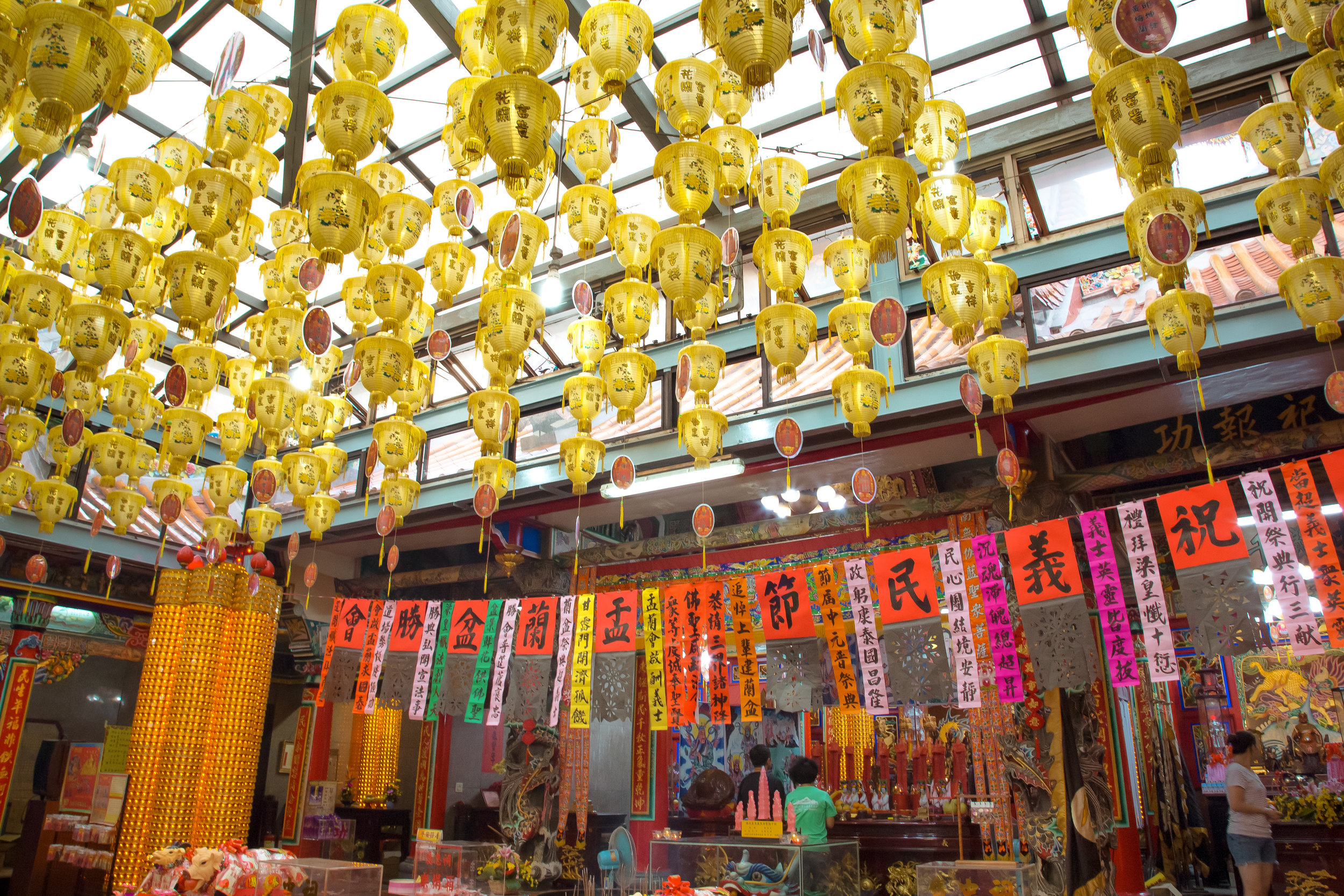
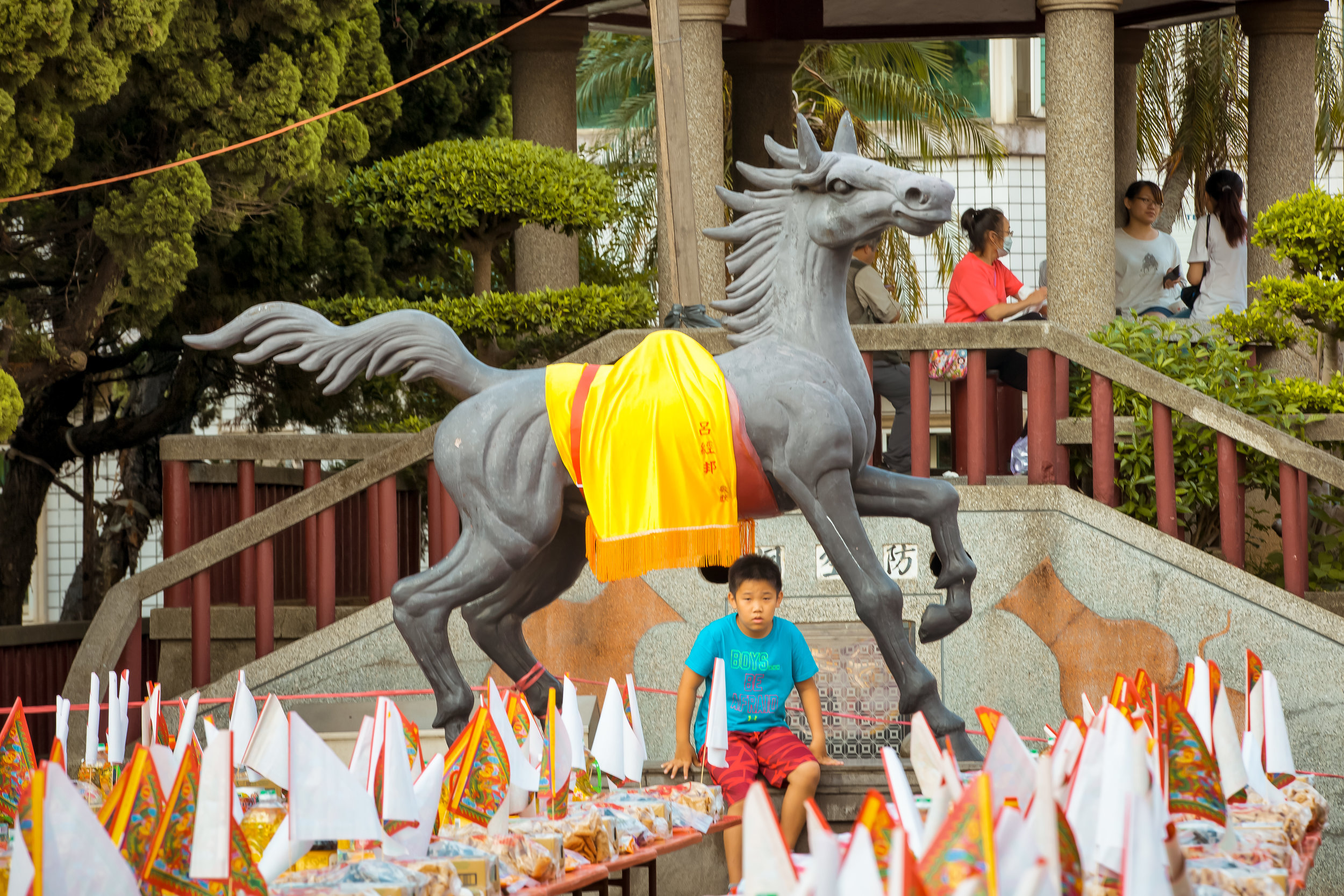
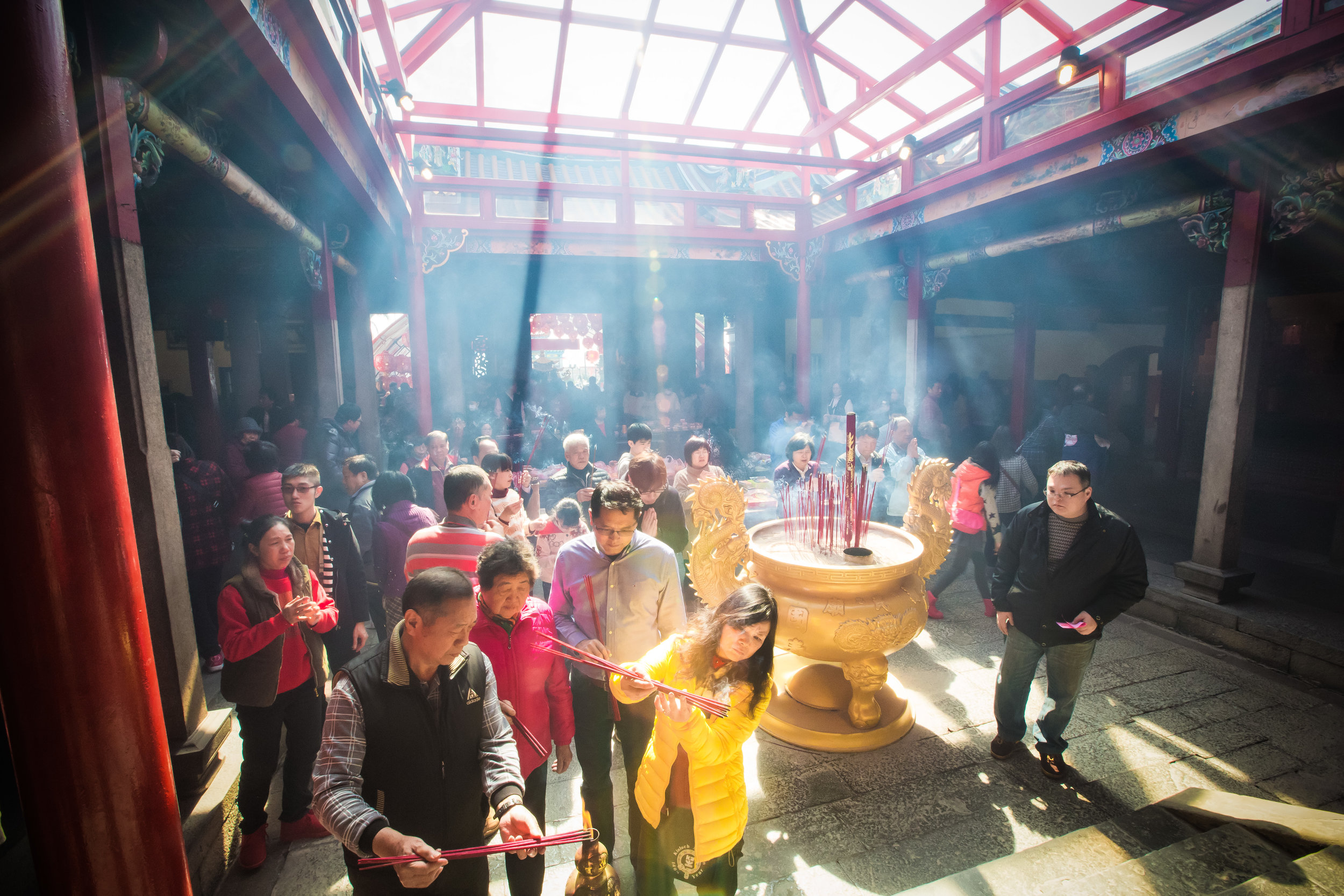
Even though there is so much to do, one of the events that I rarely ever miss is the annual celebrations that the local Hakka people in the community I live in put on for the Yimin Festival (義民祭).
One of the reasons I love this festival is that it combines Hakka culture with a carnival-like atmosphere and whenever I go, I always end up running into people that I haven’t seen in years, while also enjoying some of my favourite local dishes.
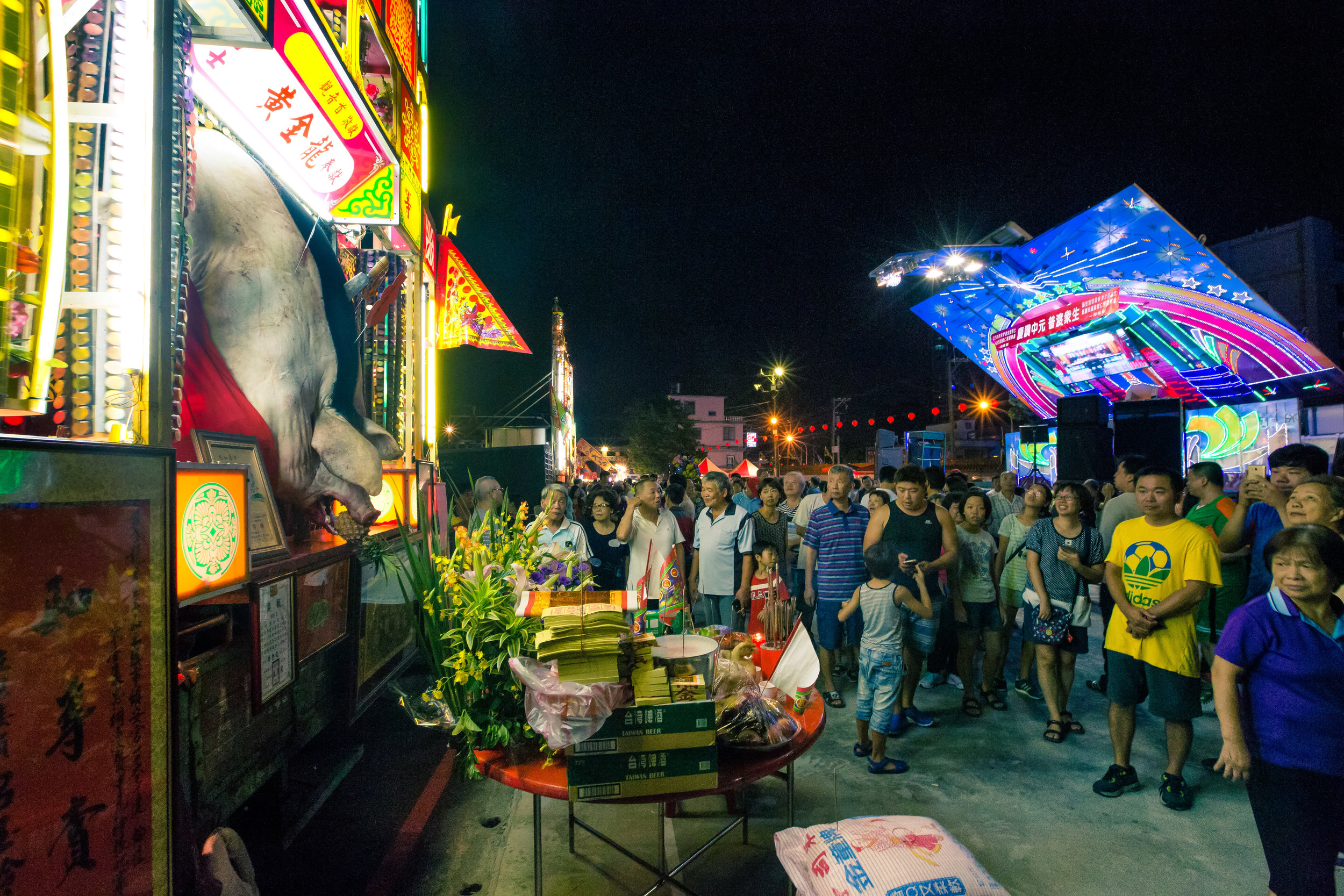
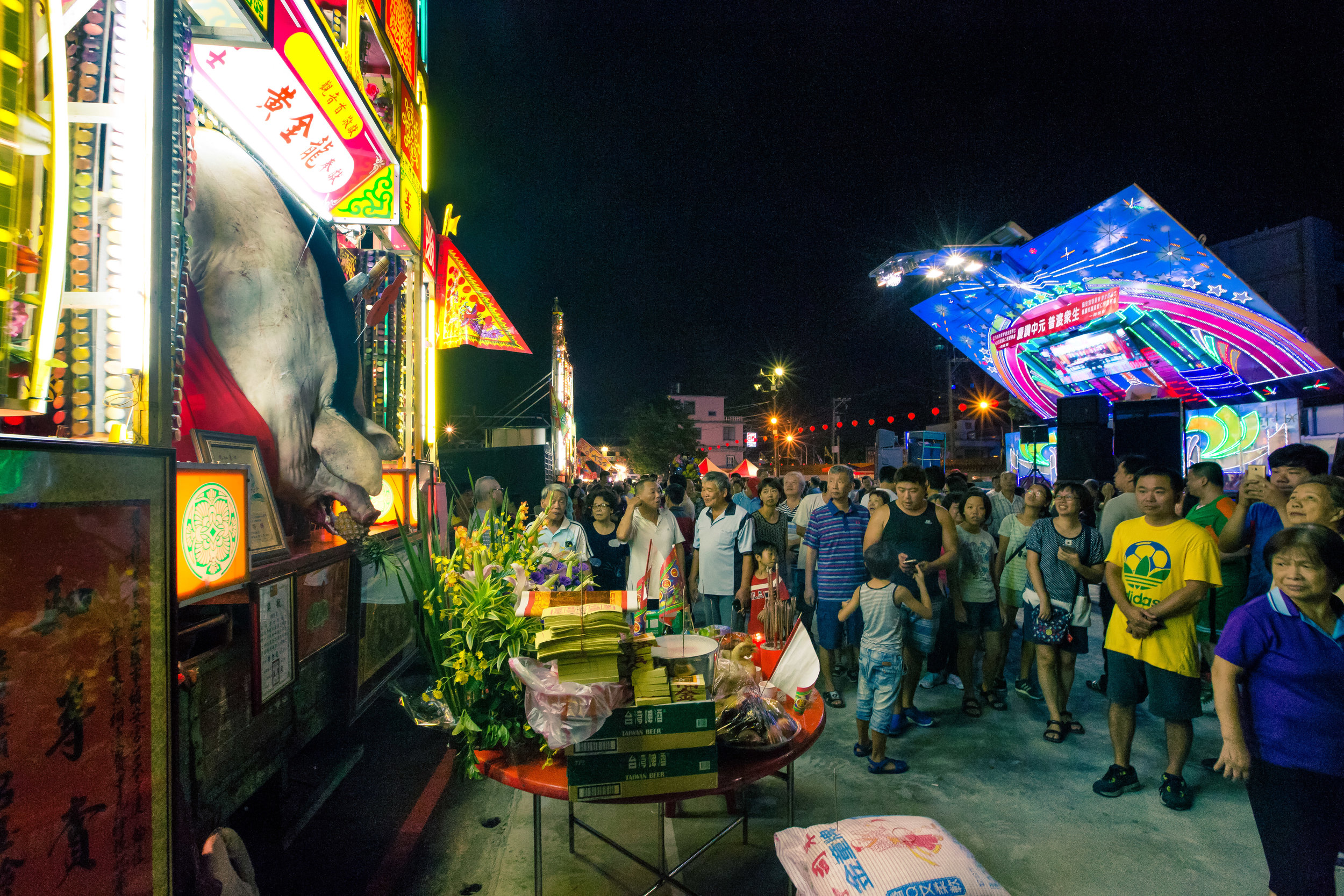
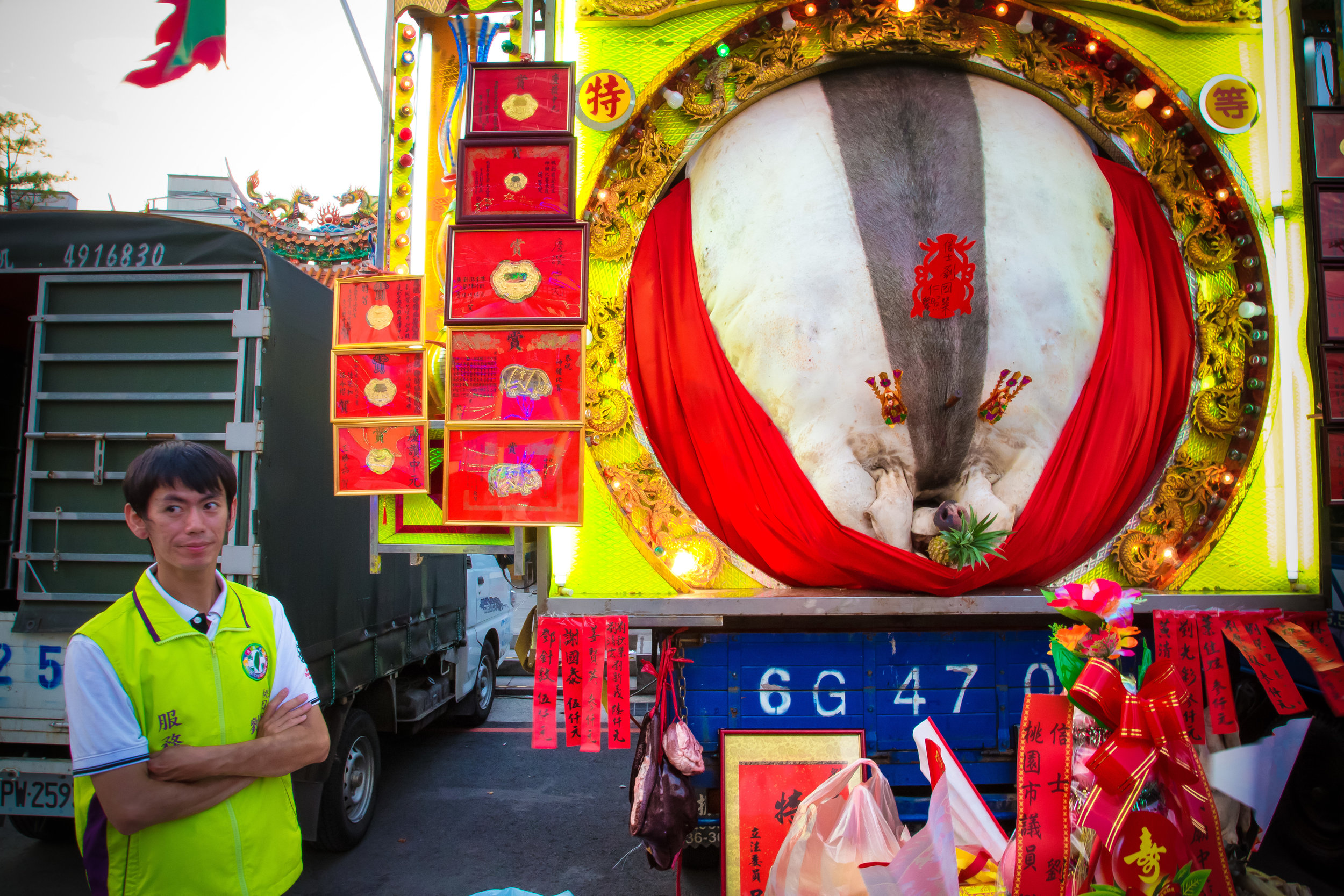
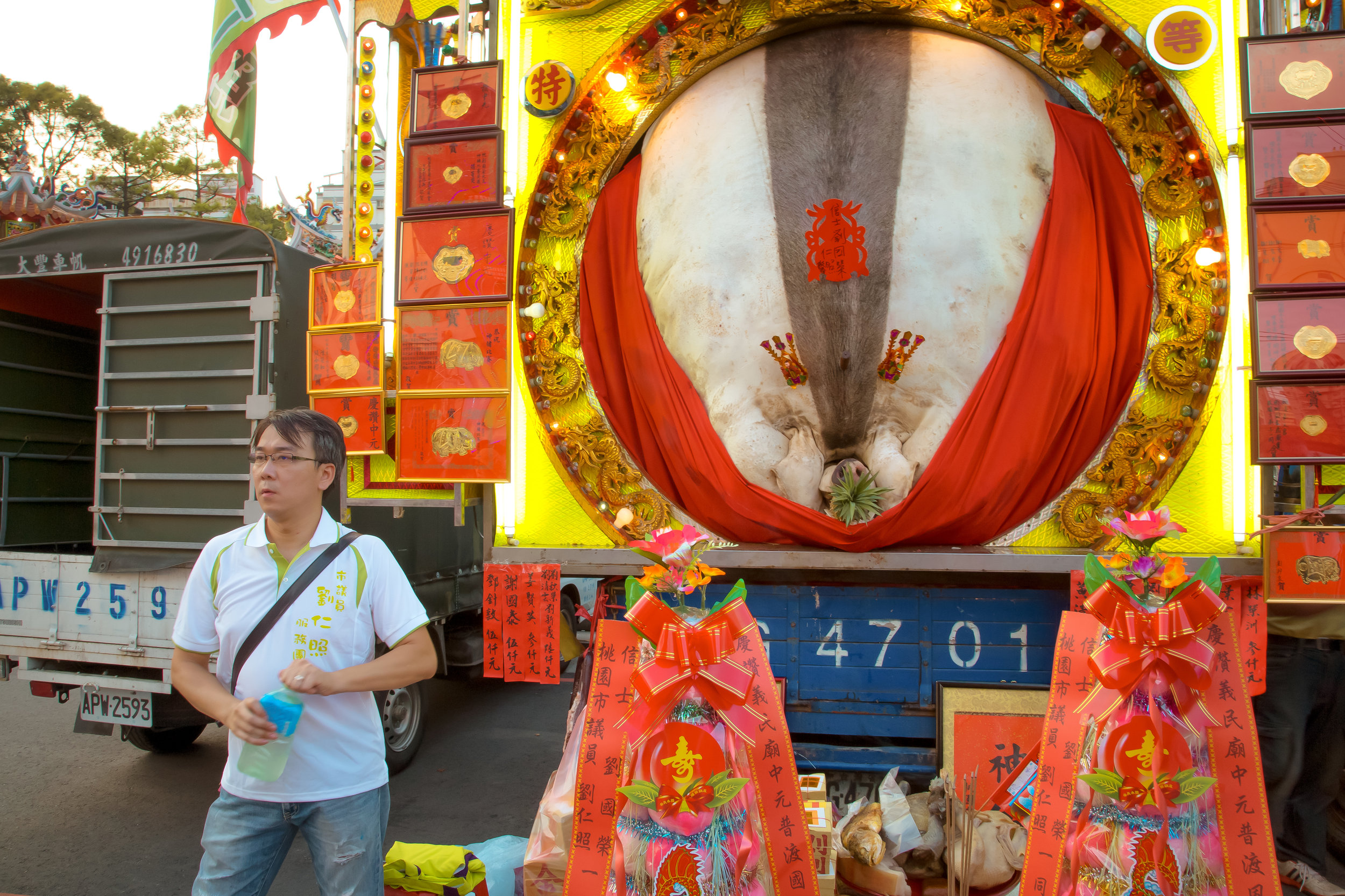
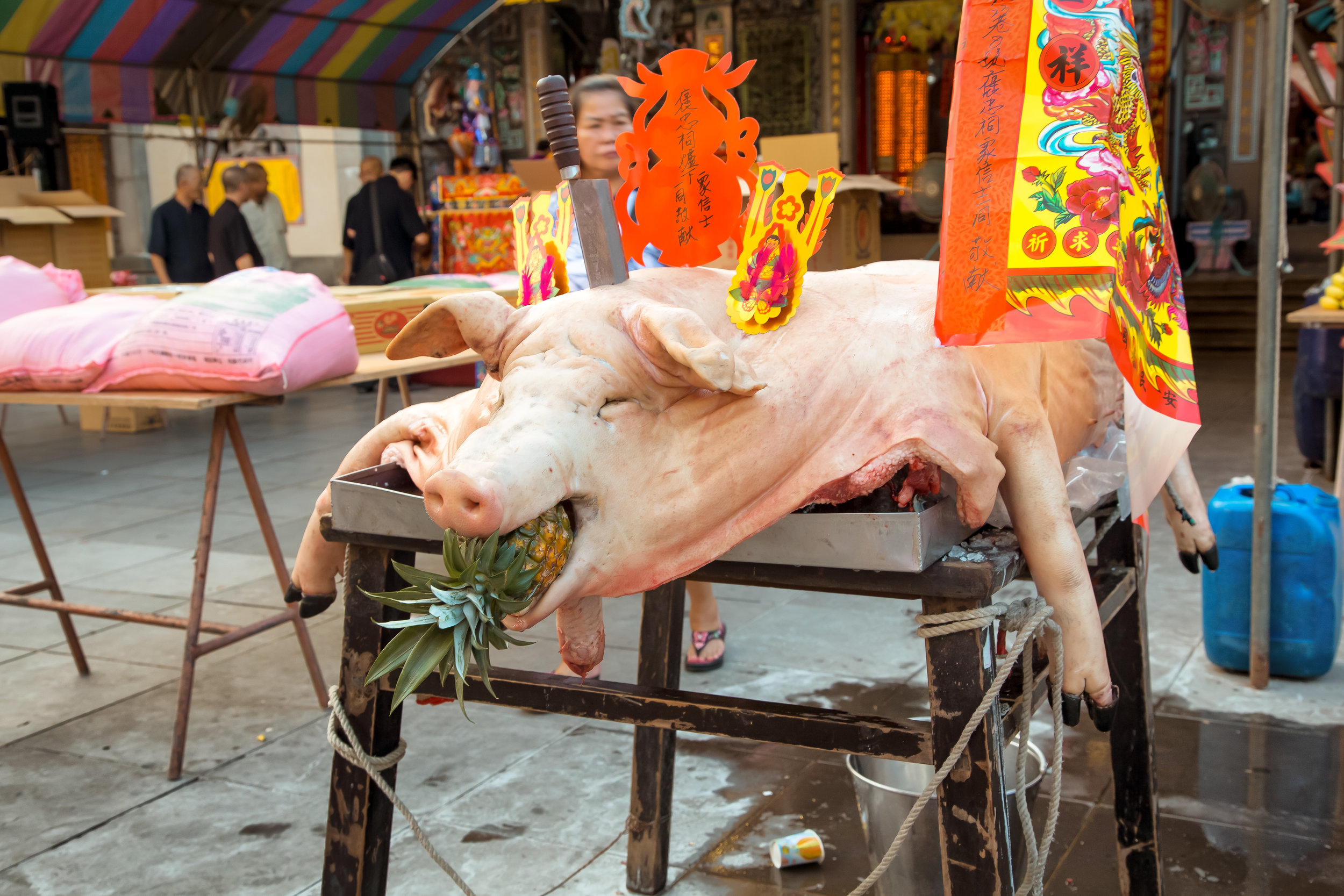
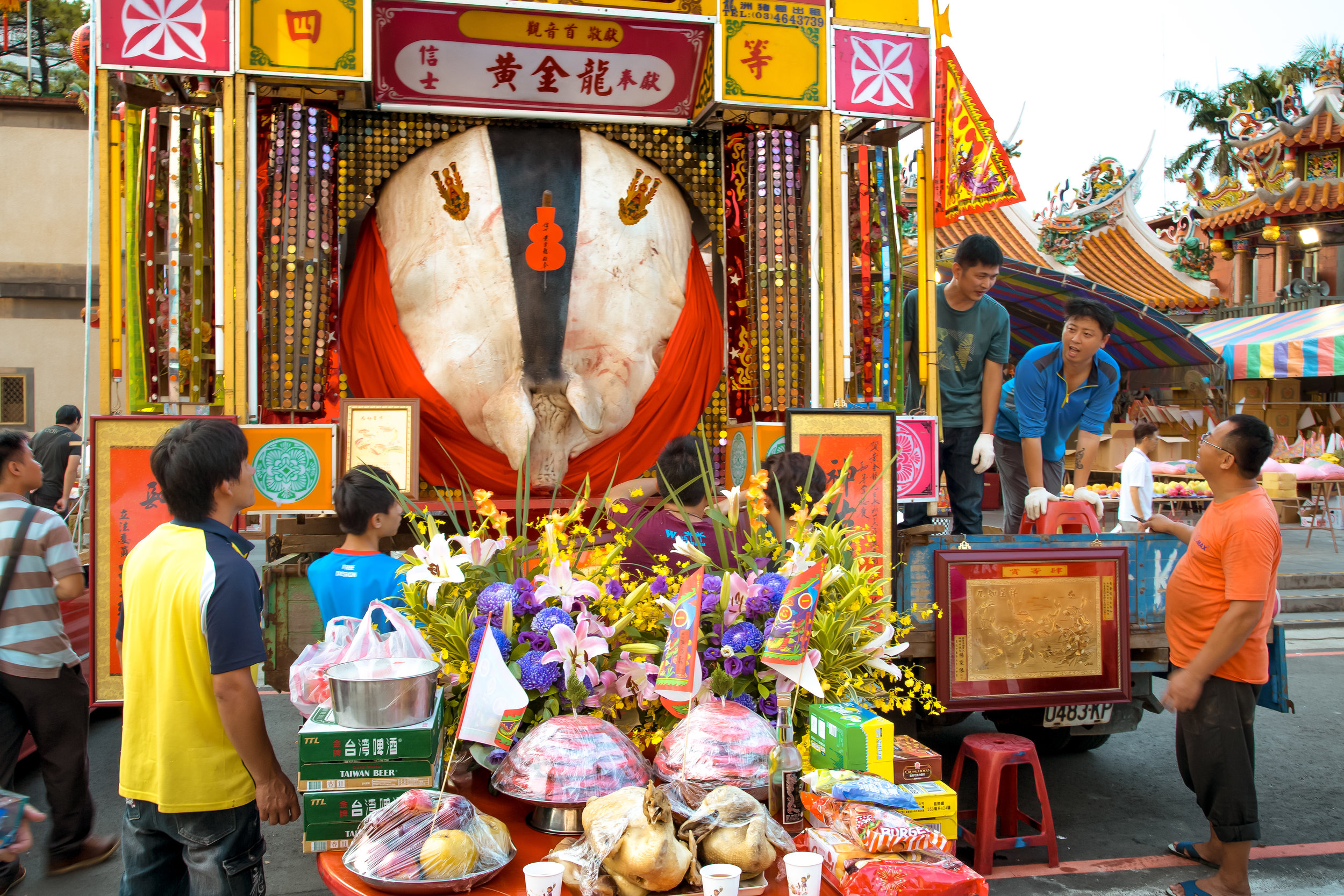
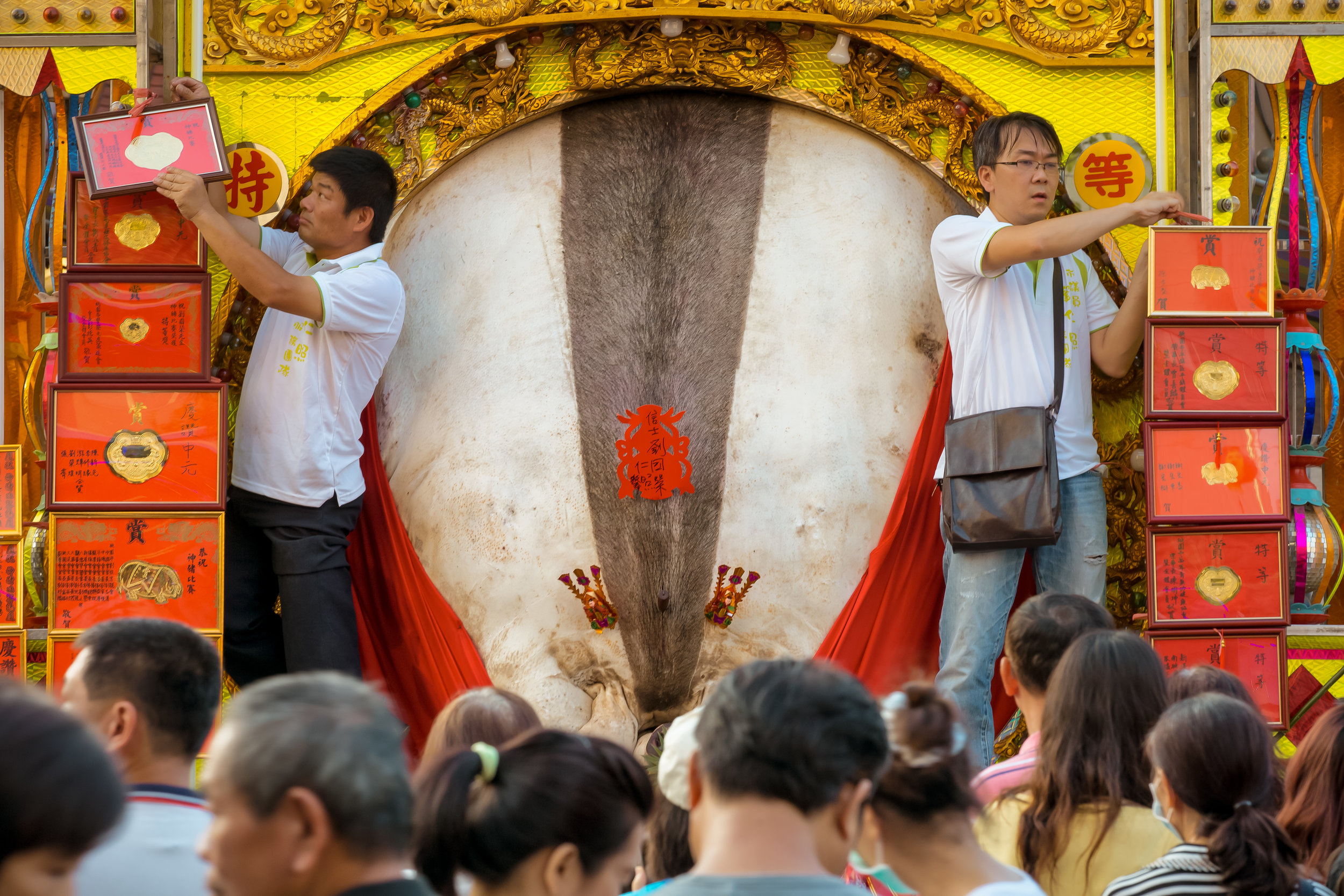
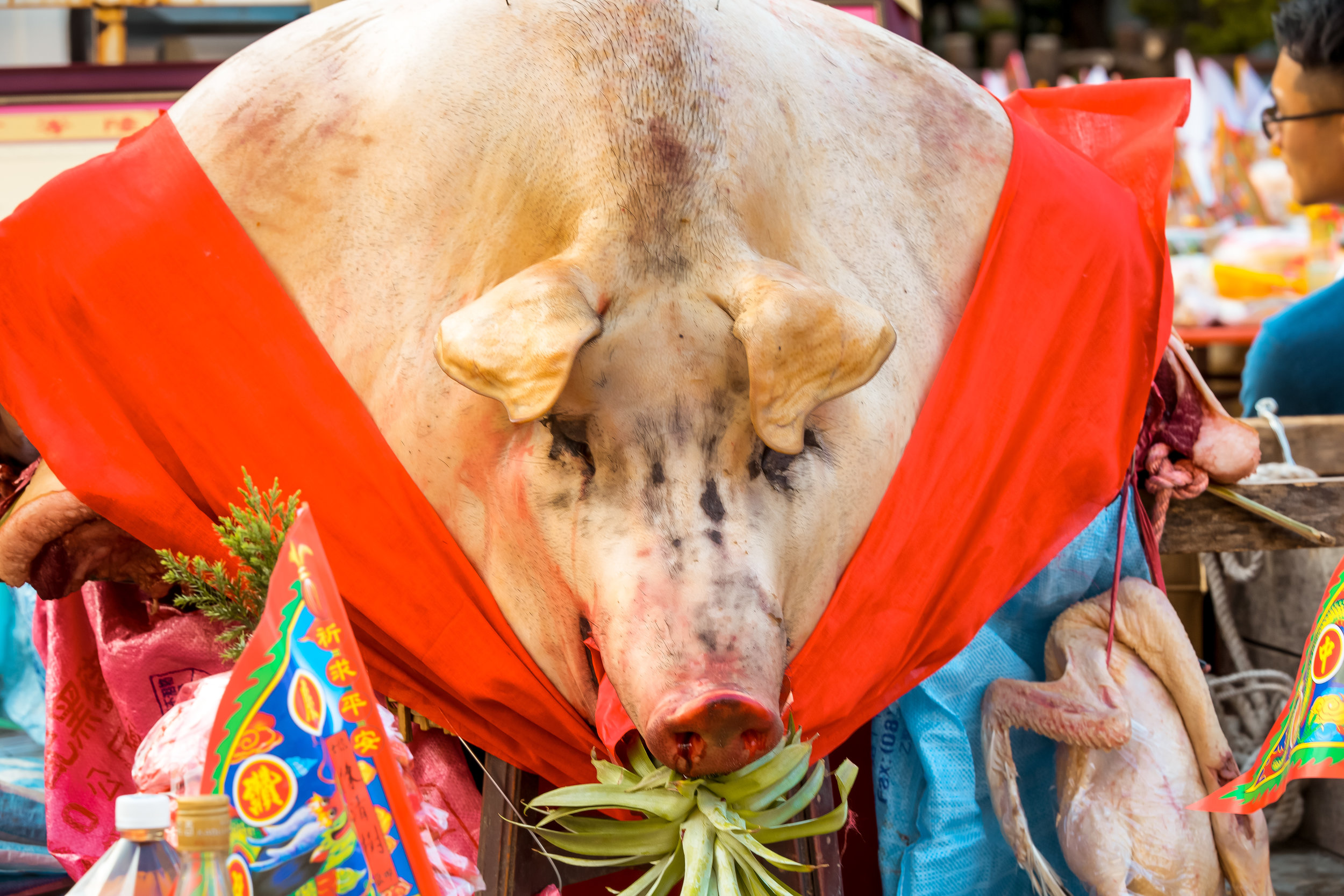
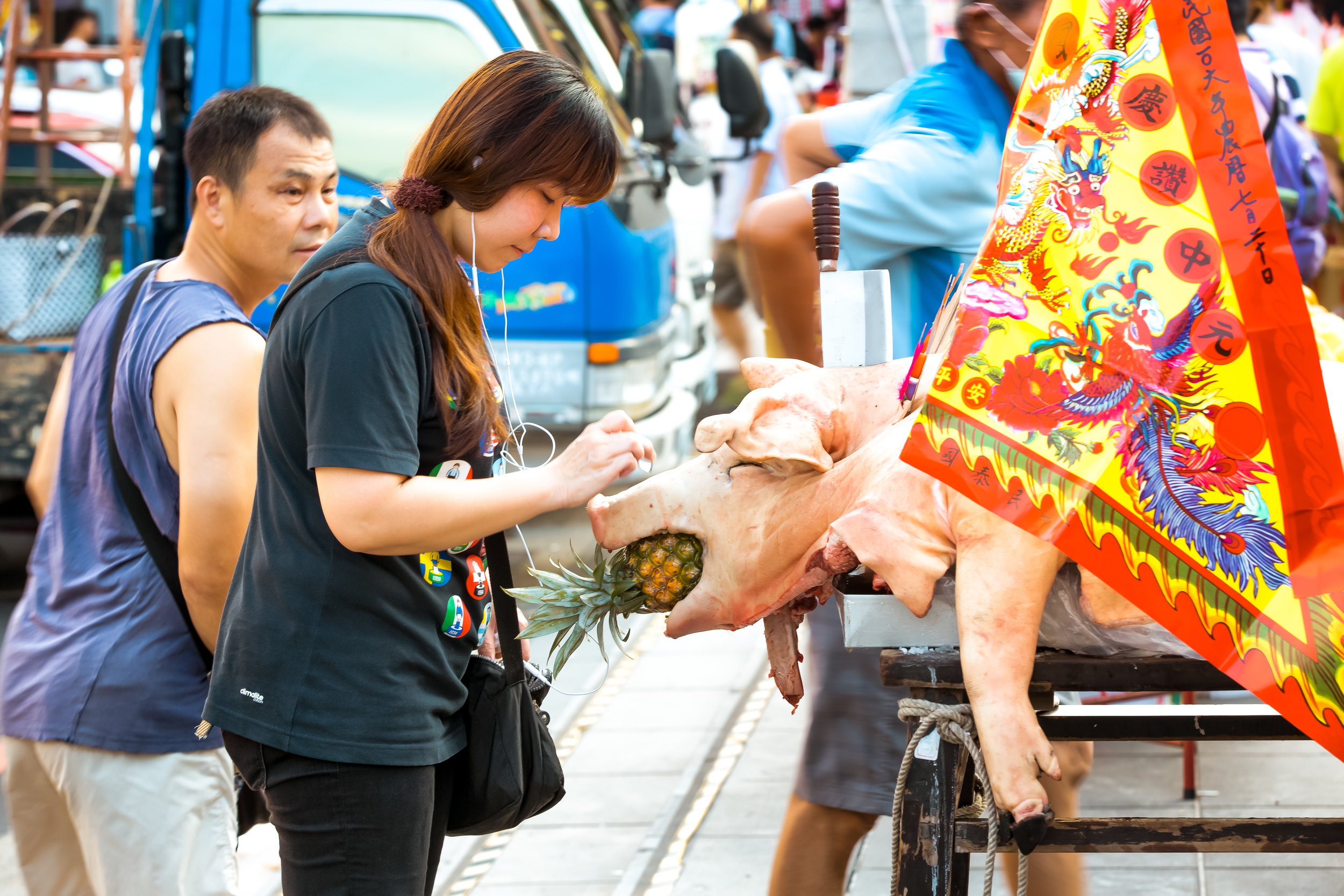
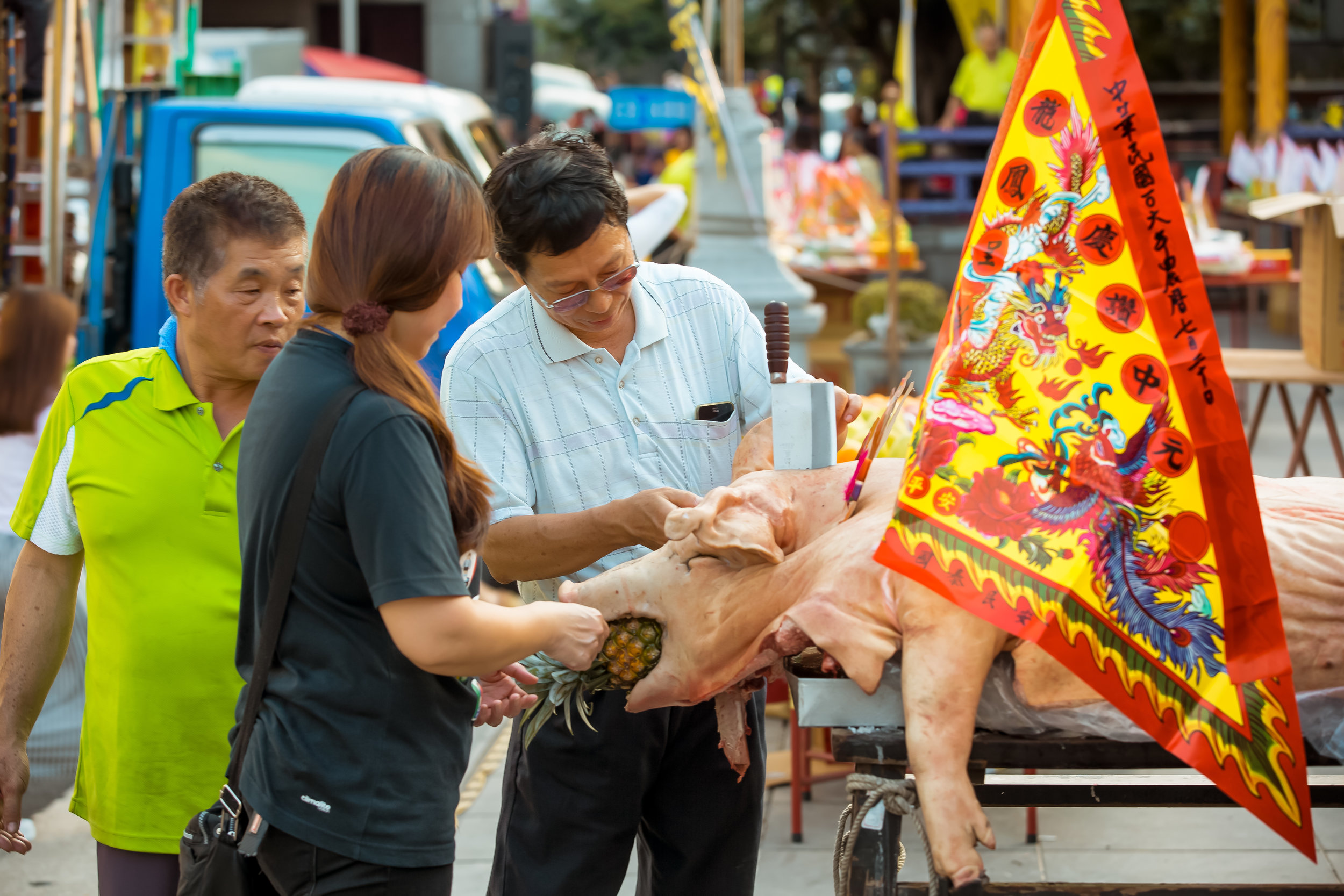
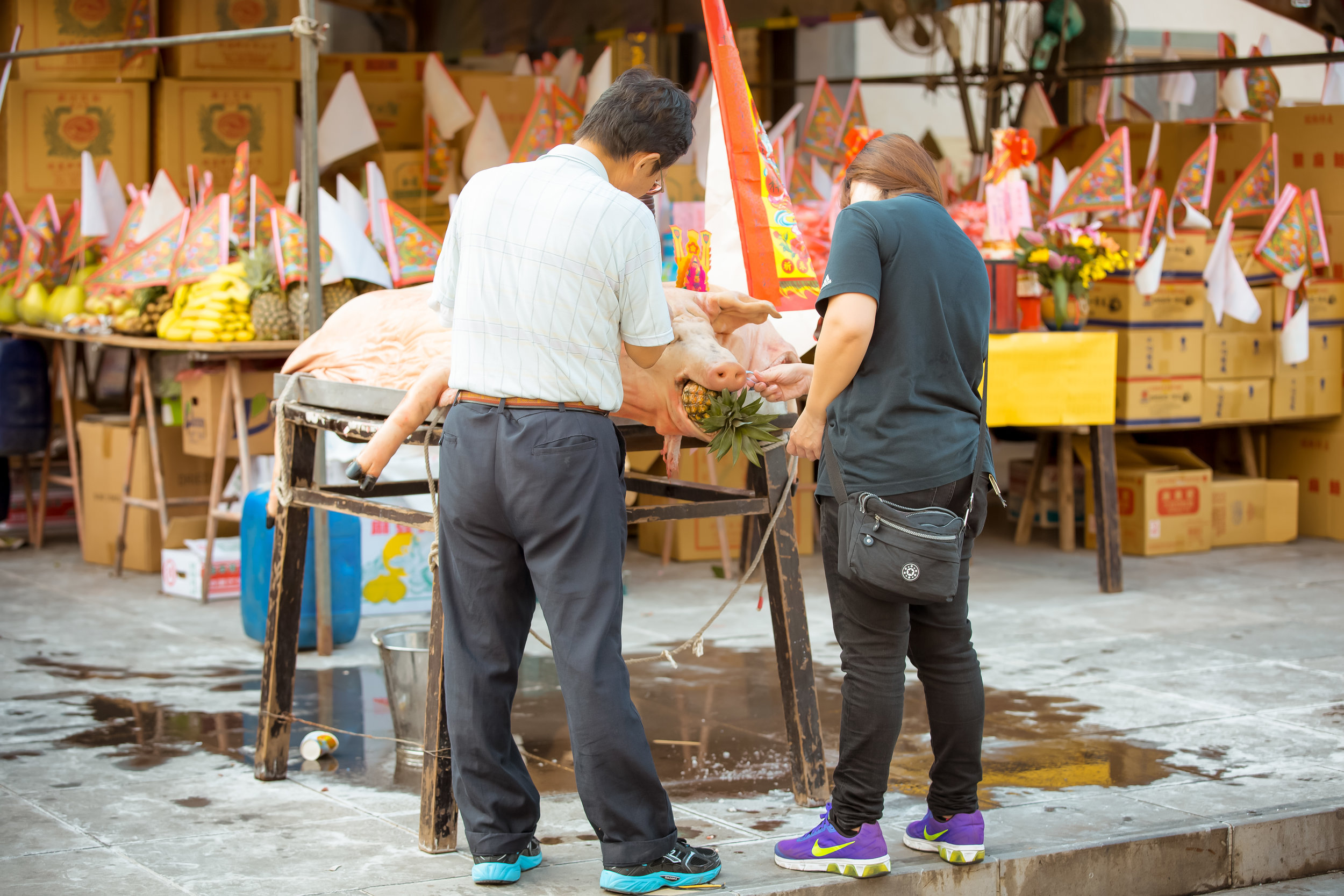
The problem with the whole thing is that there is also a dark shadow cast over the entire event thanks to the inclusion of the “Pigs of God” (神豬), a controversial element that goes hand-in-hand with the festival in the various places where it is celebrated throughout the country.
As I’ve already mentioned a few times here on my blog, the competition is controversial because its viewed by many in contemporary society as a form of unnecessary animal cruelty which clearly violates animal abuse laws, but is supported by local temples and politicians who view it as an important cultural and religious activity.
Not to sound like a hypocrite, even though I’m philosophically opposed to the practice, I also rarely miss the chance to check it out and document it.
So if I’m not a hypocrite what am I? A glutton for punishment? A masochist?
I can’t really say.
Part of me hopes that at some point in the near future all of this stuff will come to a screeching halt and the abuse of these poor animals will stop.
But on the other hand, every year I feel compelled to attend the festival to see what’s going on.
Before I get into any of my thoughts about this years event, I think it’s important to give you a bit more information about what this event actually is. I’ll explain it briefly before, but I’m not going to copy and paste what I’ve already published, so if you’d like more in-depth information about the festival, I recommend taking a look at the links below.
Yimin Temple | Pigs of God 2015 | Pigs of God 2016 | Pigs of God 2017
It’s also important that I provide a disclaimer before moving on:
As you read on, there will be photos of animal sacrifices that you may-or-may-not feel comfortable looking at. There is nothing particularly gruesome about any of it, but I’m just warning you beforehand that the photos may be unsettling for some people.
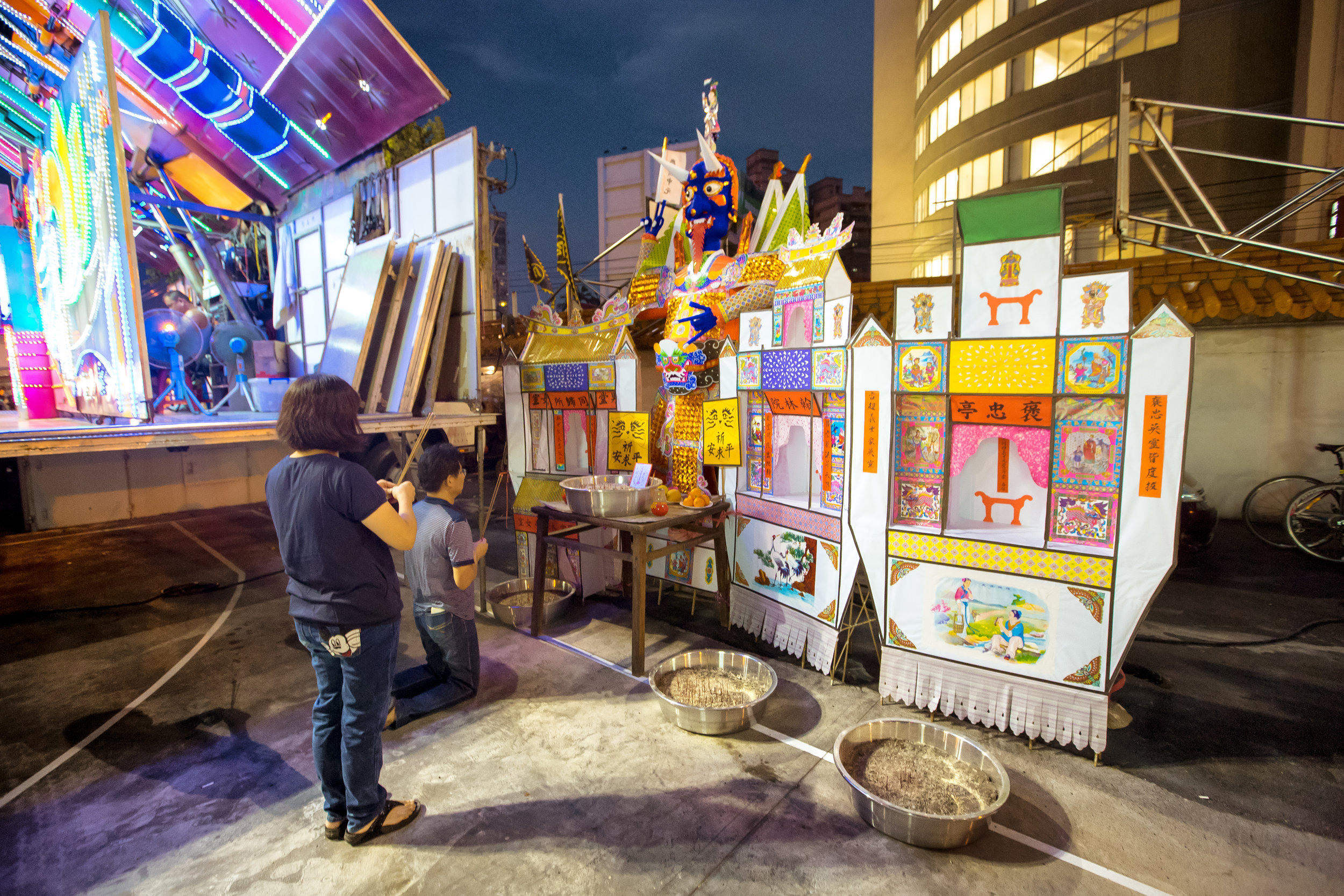
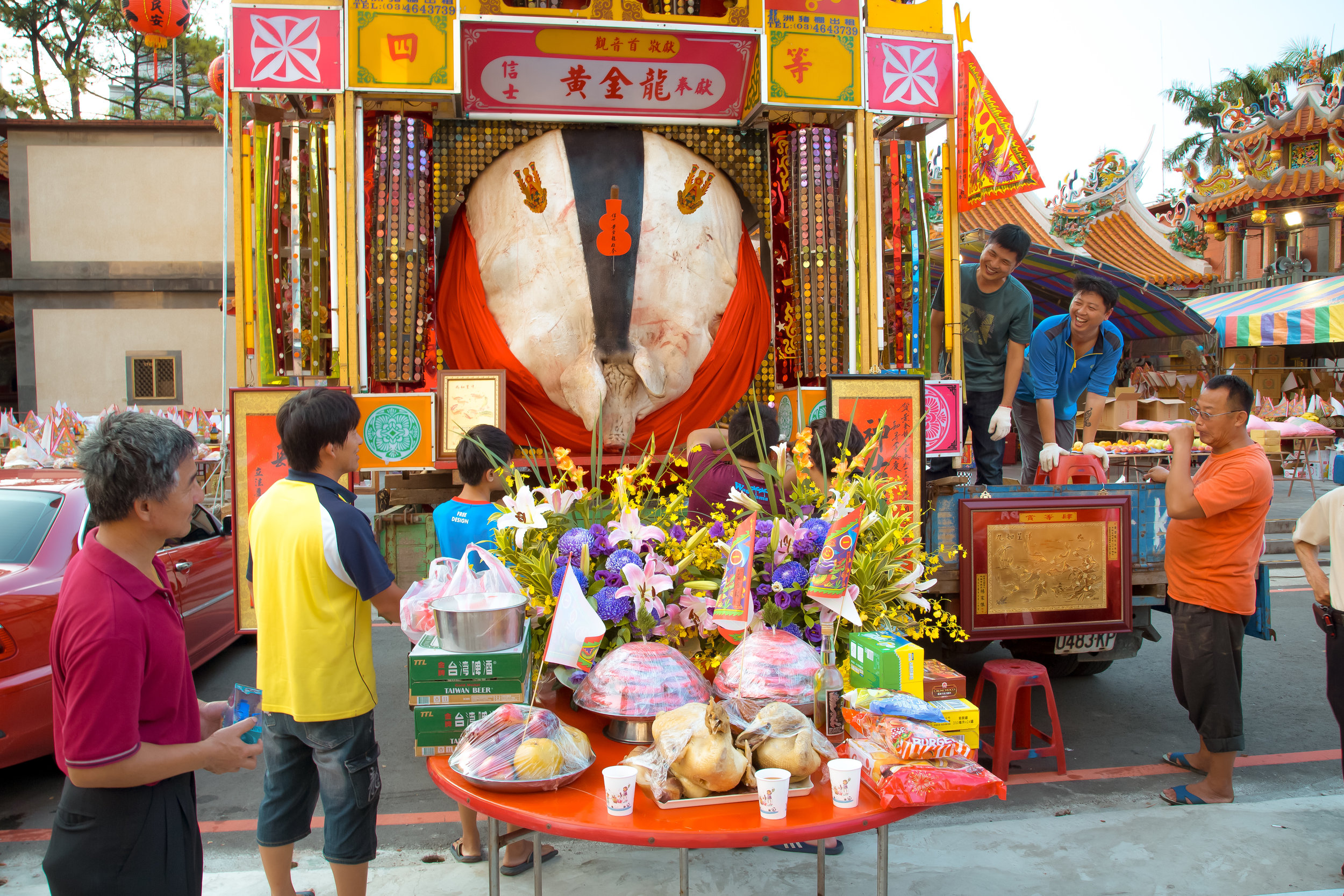
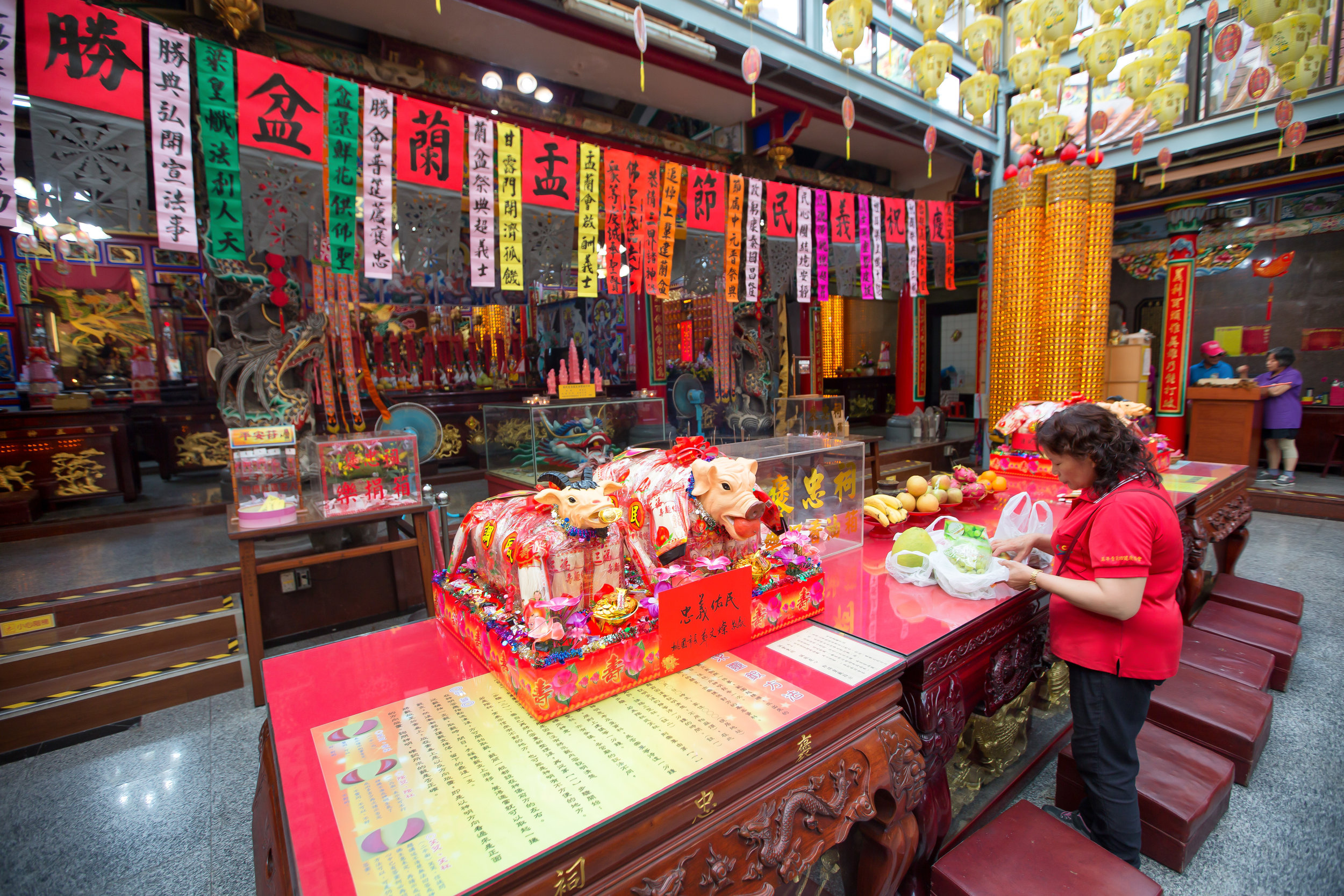
The Pigs of God (神豬/豬公)
Earlier this week, the Hakka Affairs Council, the government agency tasked with the preservation and promotion of Hakka language and culture, tweeted: “President Tsai Ying-wen attended a ceremony in observance of Hakka Yimin Festival on September 7th, a three-day event that aims to promote the spirit of Yimin, a collective phrase for Hakka Martyrs who sacrificed their lives to defend their homeland in the past. Under the collaboration between the central and local governments, Taiwan’s Hakka Yimin Festival has become one of the biggest national festivals.”
And then without a hint of irony, Channel News Asia published a report titled: “Taiwan’s Polarising Pig Festival Draws Smaller Sacrifices” which proudly explained that this year the sacrifices were smaller and so too were the crowds who came to see them.
So which one is closer to the truth?
Given that I’ve attended this event every year for well over a decade, I’m probably able to explain this stuff a little bit better than government propaganda or foreign news reports.
First though, I realize that few people will actually click the links I’ve provided above, so let me briefly talk about what the Yimin Festival is.
Way back when people in China regarded Taiwan as nothing but a worthless pile of dirt, the Hakka’s were one of the first groups brave enough to immigrate to the island.
Having settled here for hundreds of years, the Hakka people have a long and interesting history in Taiwan and are highly regarded for their loyalty, hard work and contributions to developing the country into the place we know and love today.
That being said, life for the Hakka’s was never easy and throughout history they have constantly had to face persecution and discrimination.
Nevertheless, when duty calls, the Hakka people have always been on the front lines in order to protect their homes and families. Notably in 1786, a massive uprising against the Qing took place in central Taiwan and in order to protect their way of life, the Hakka formed a volunteer militia to help quell the uprising.
Quickly putting together a force of over 1,300, the Hakka militia was victorious in quelling the uprising and saving their homes, but they also suffered tremendous losses.
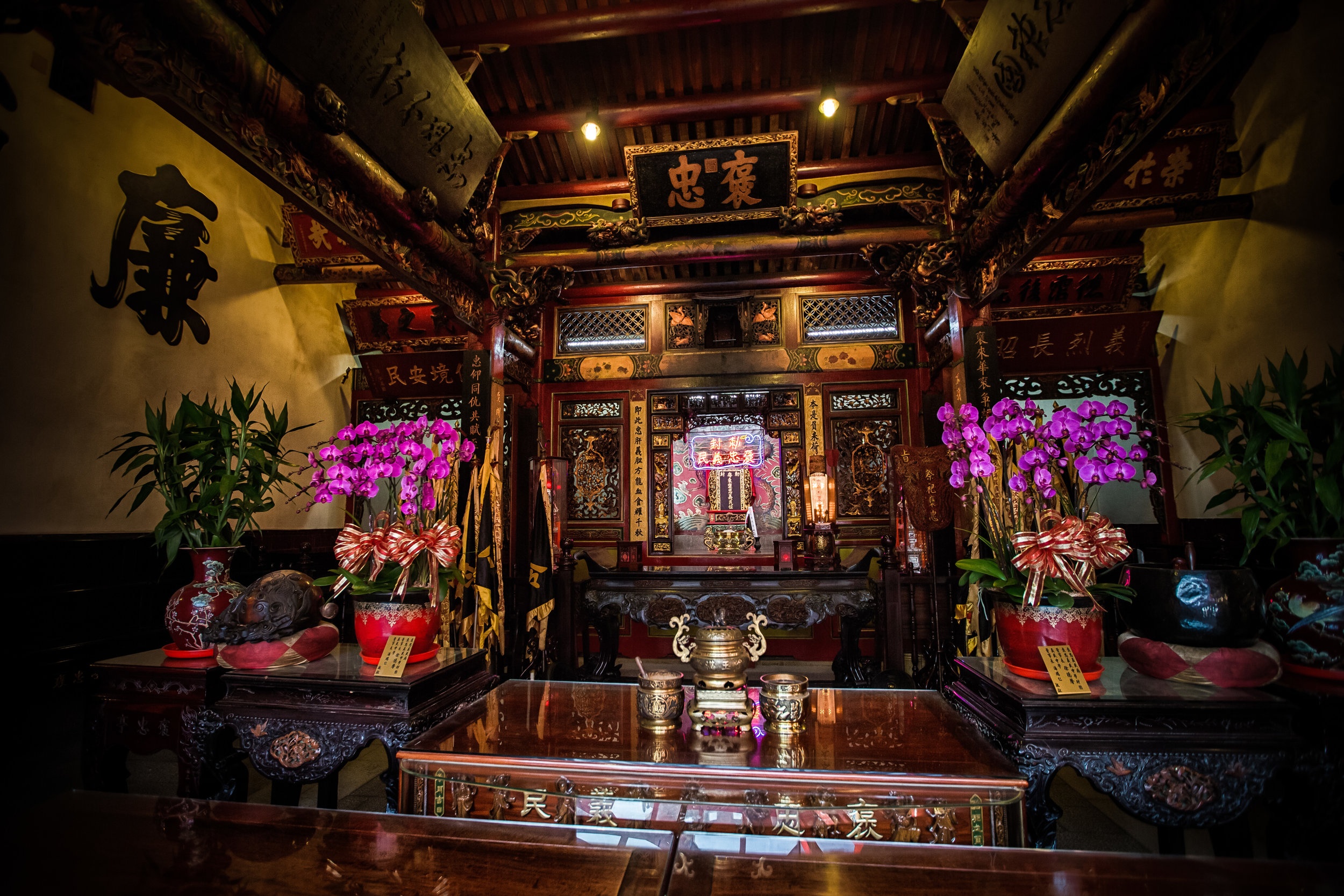
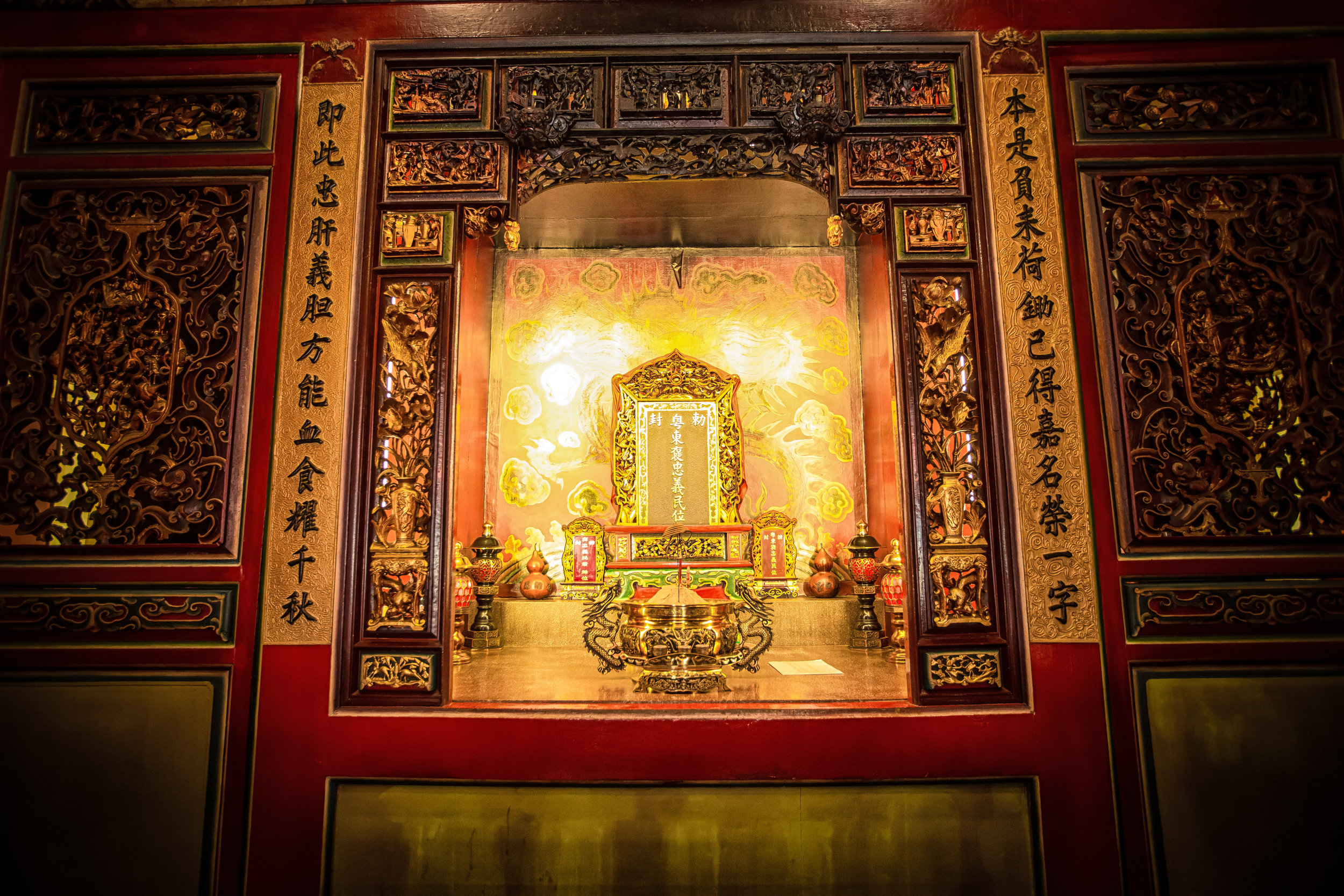
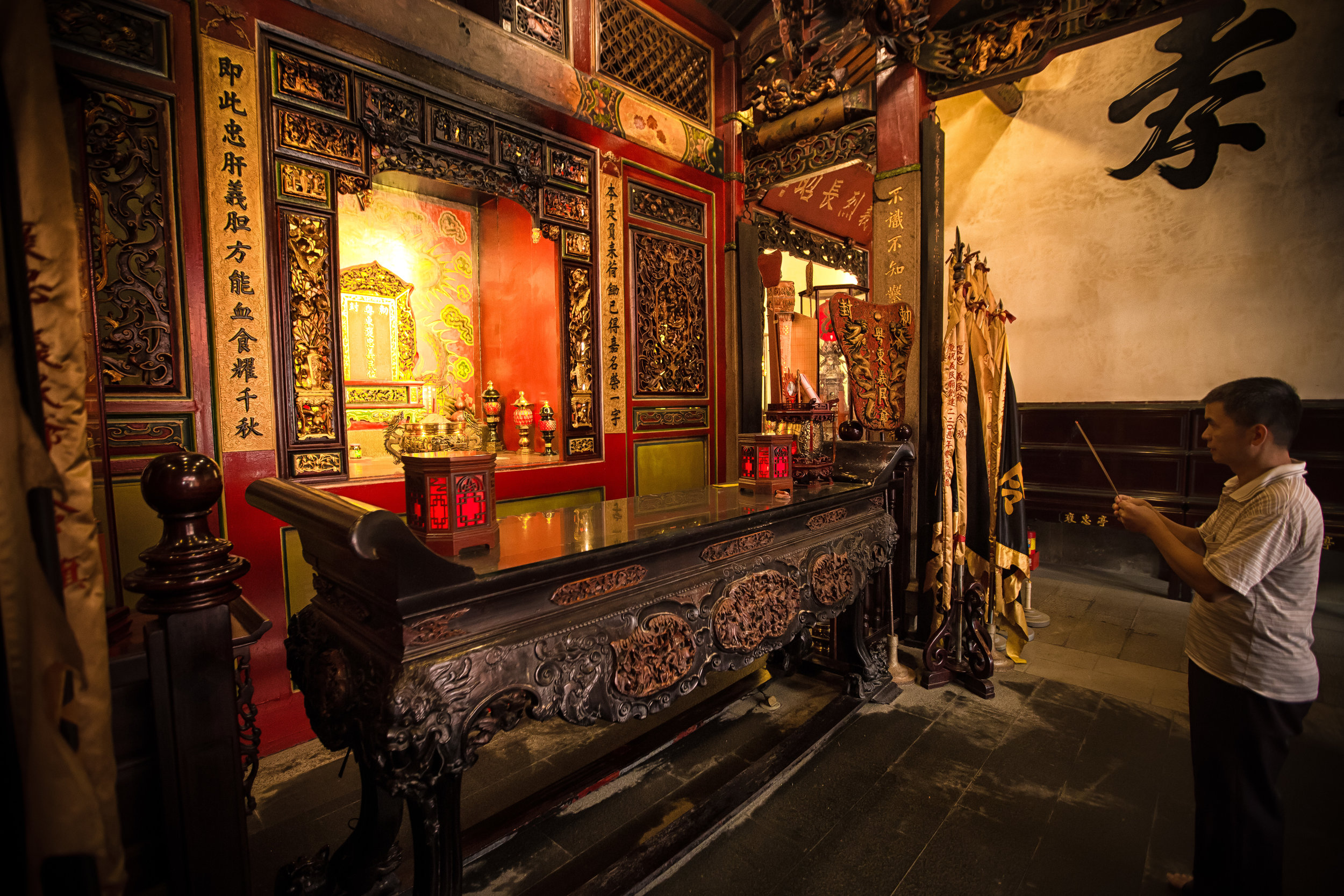
Due to the large number of casualties, it was decided that the dead would be buried together in a large tomb and honored as heroes, which became the foundation for “Yimin” (義民) worship and the Yimin Temple.
How do the Pigs of God factor into any of this?
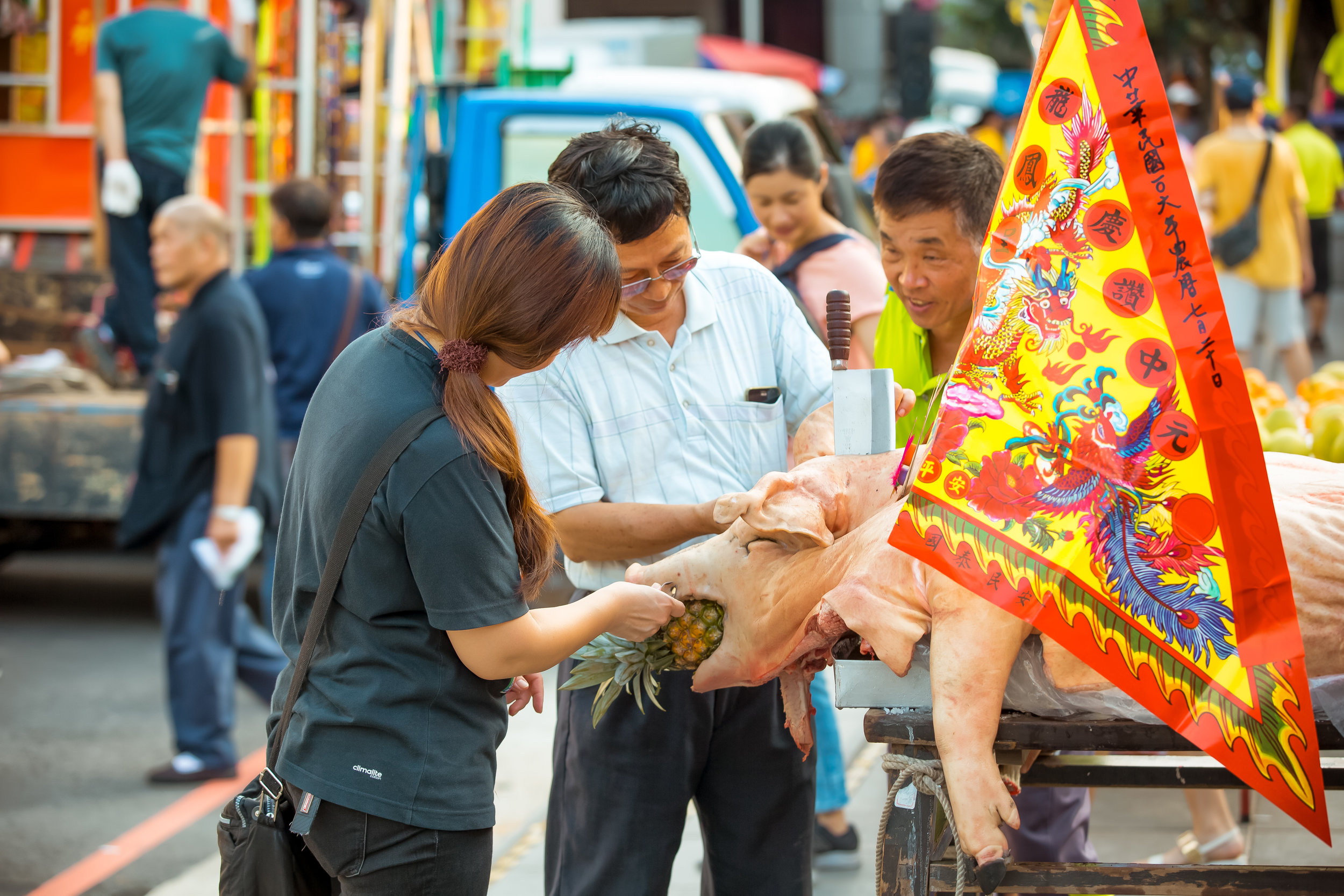
In what became a long-standing tradition, each year during the Yimin Festival, families would pool together to contribute food for a large festival. It was also decided that one of the major families would be responsible for sacrificing a pig to the ancestors as a show of respect.
Link: Hsinpu Ancestral Shrines
This rotation went on for quite some time but soon a competition (of sorts) started between families as the pigs raised for the festival started becoming larger and larger.
Ultimately the size of the pig that was offered up each year symbolized the wealth and power of a family which meant that as the years went by, the size of the pigs became a show of “face” and local power.
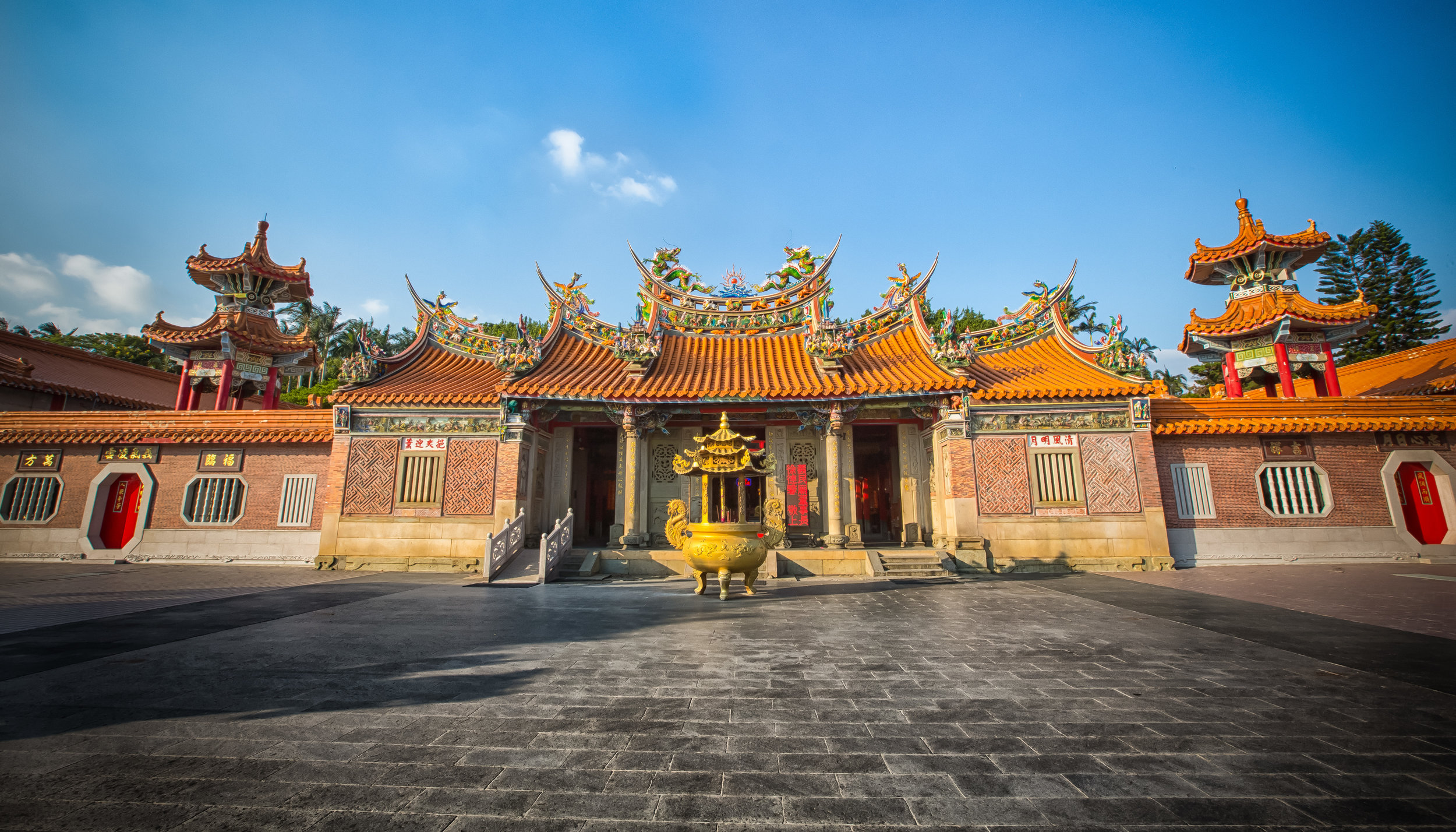
Today the Yimin Festival is celebrated all over Taiwan, but it is a much larger occasion in the Taoyuan, Hsinchu, Miaoli (桃竹苗) areas, which is where you’ll find the largest concentration of Hakka people in Northern Taiwan.
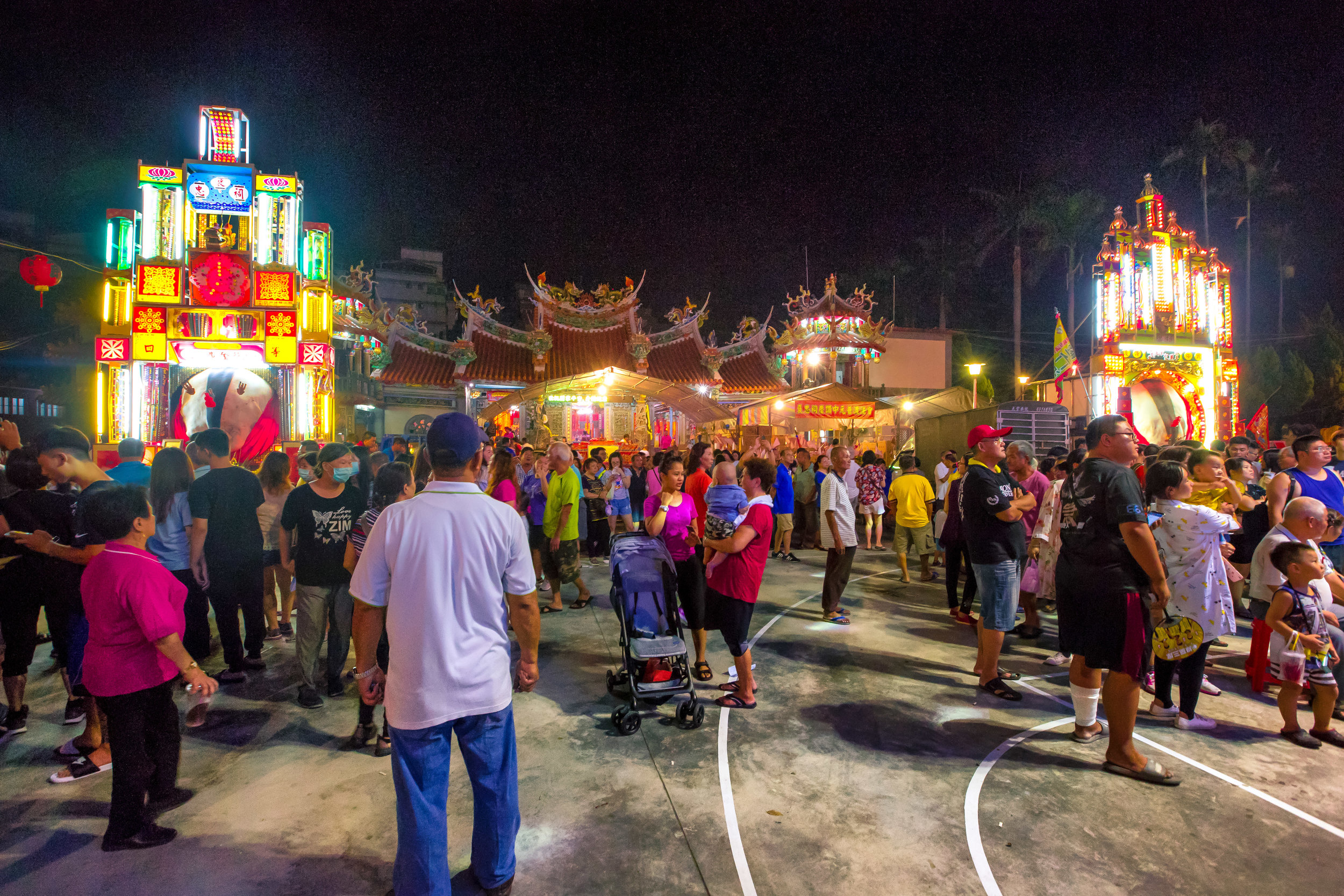
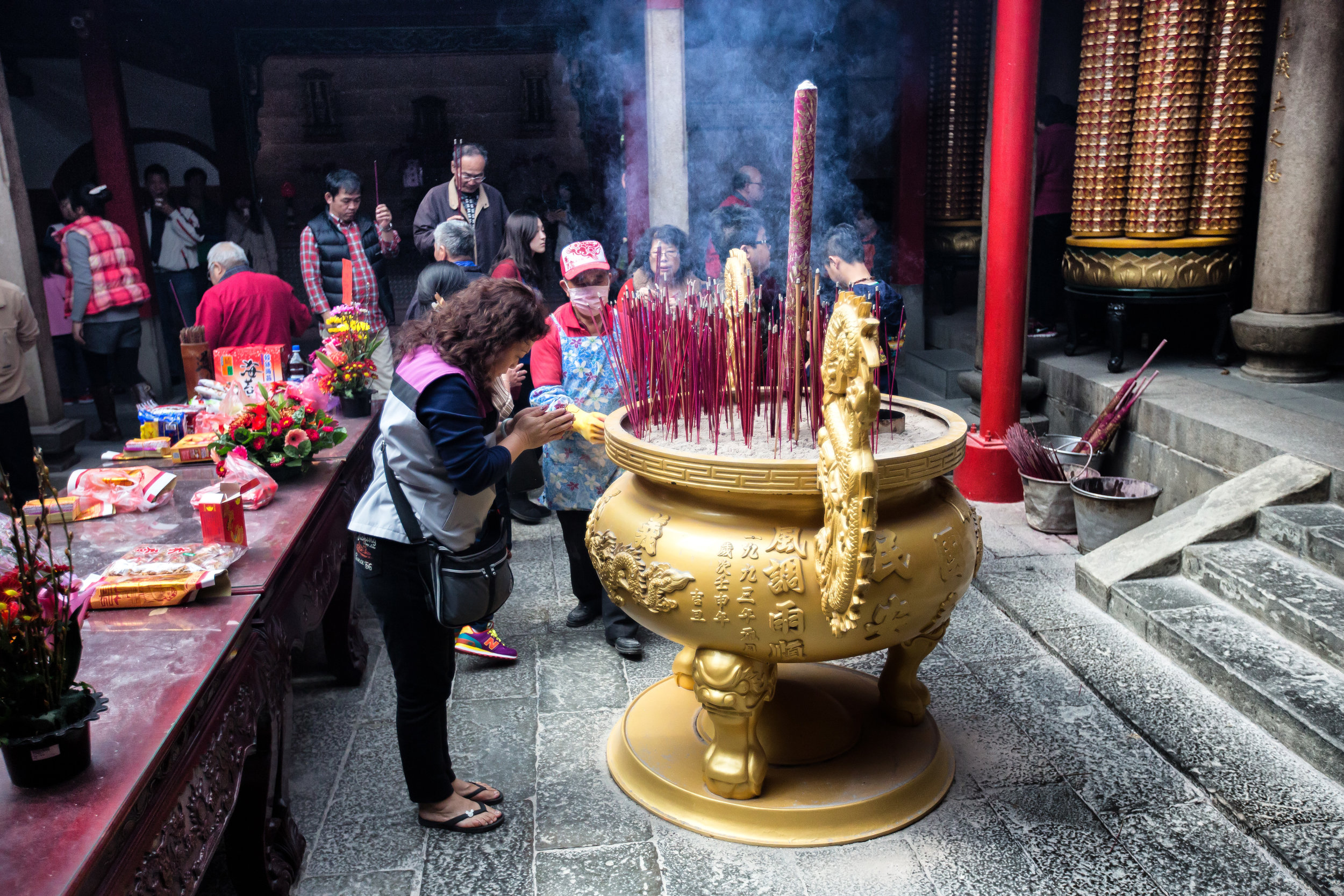
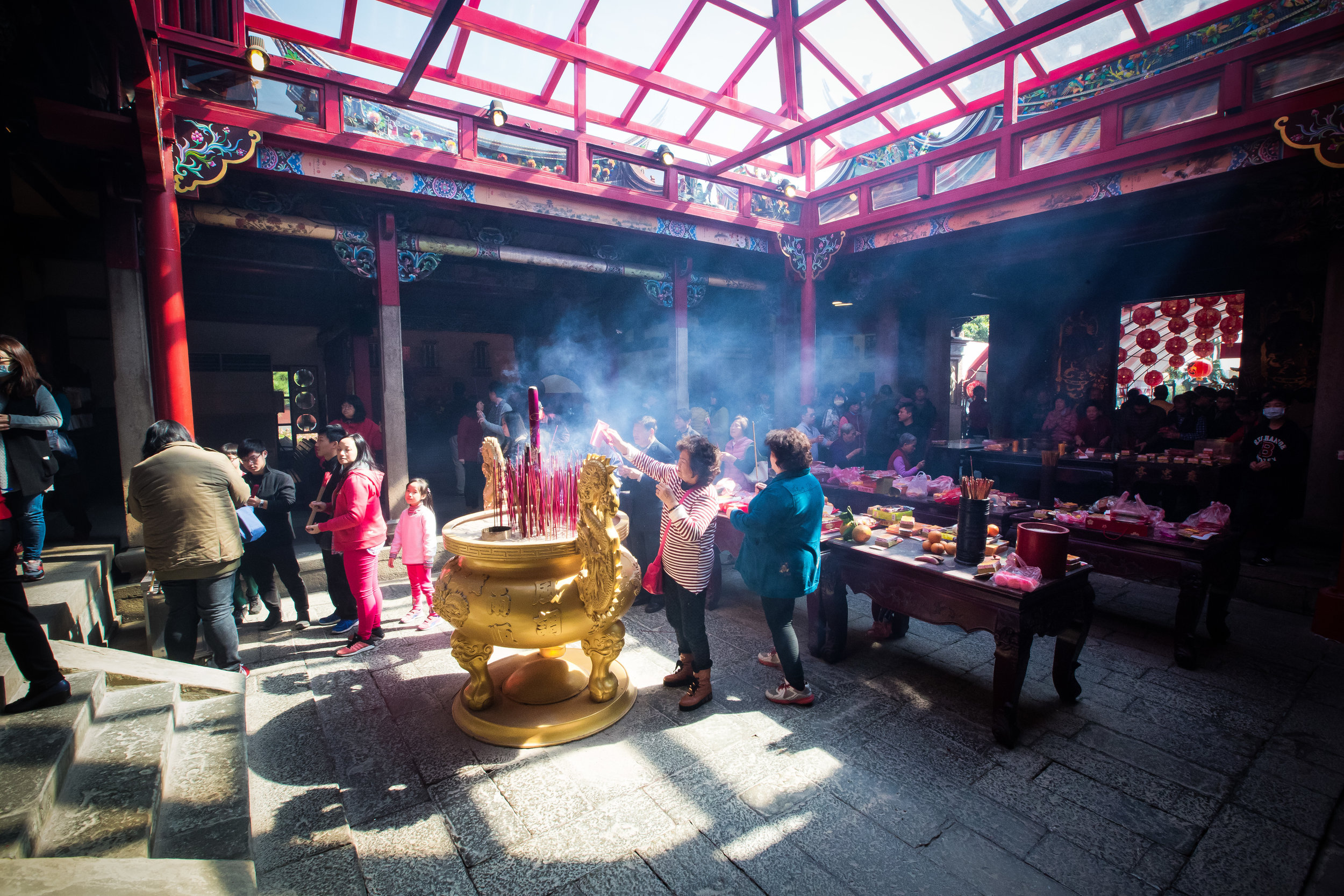
The majority of the festivities are held at the Baozhong Yimin Temple (褒忠義民廟) in Hsinpu (新埔), but wherever the festival takes place, the Pigs of God are also likely to make an appearance.
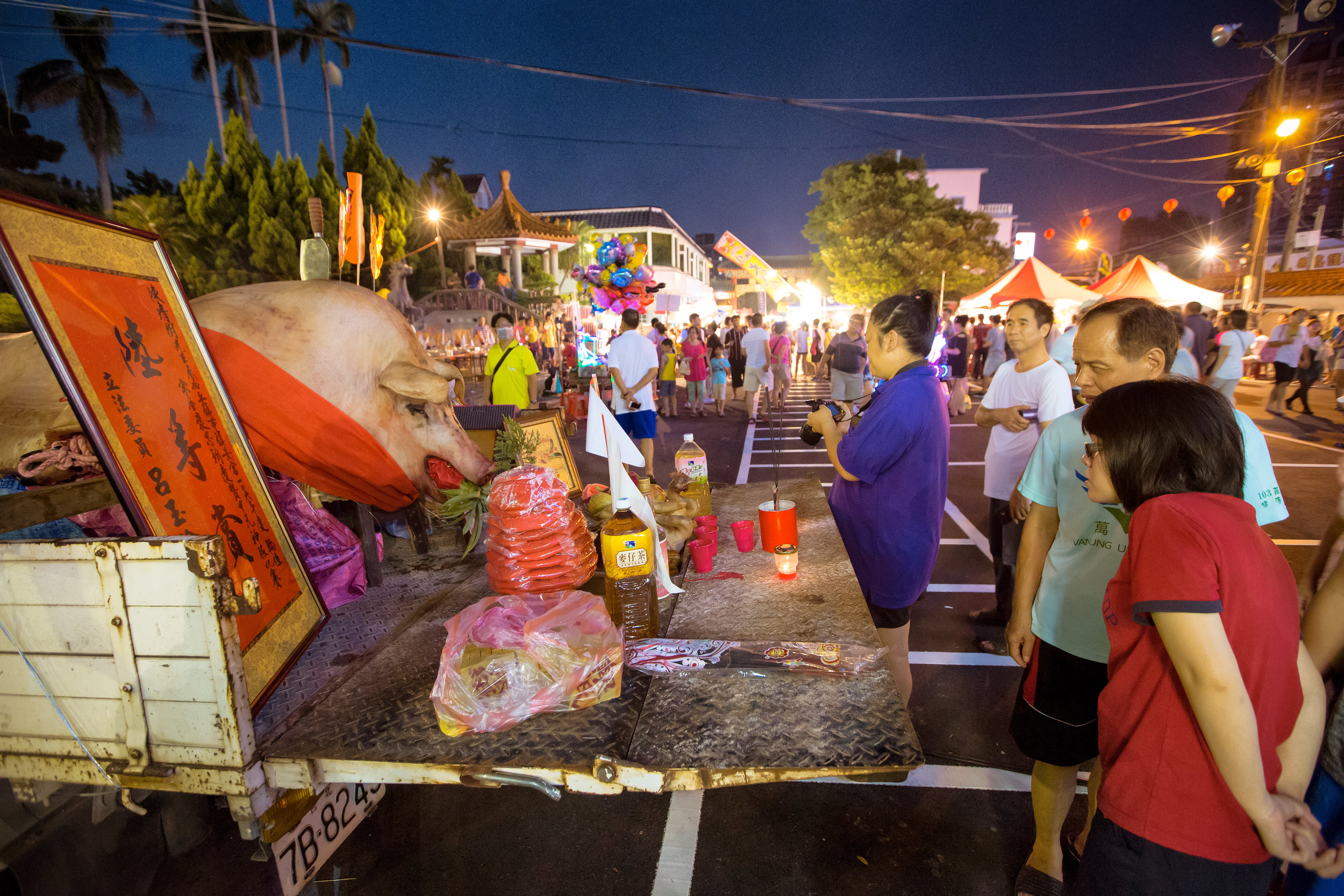
Just for a bit of clarity - market sized hogs sell when they are at about 250 - 270 pounds (113-122kg).
This means that a Pig of God candidate has to grow to at least 5-6 times the size of a normal pig.
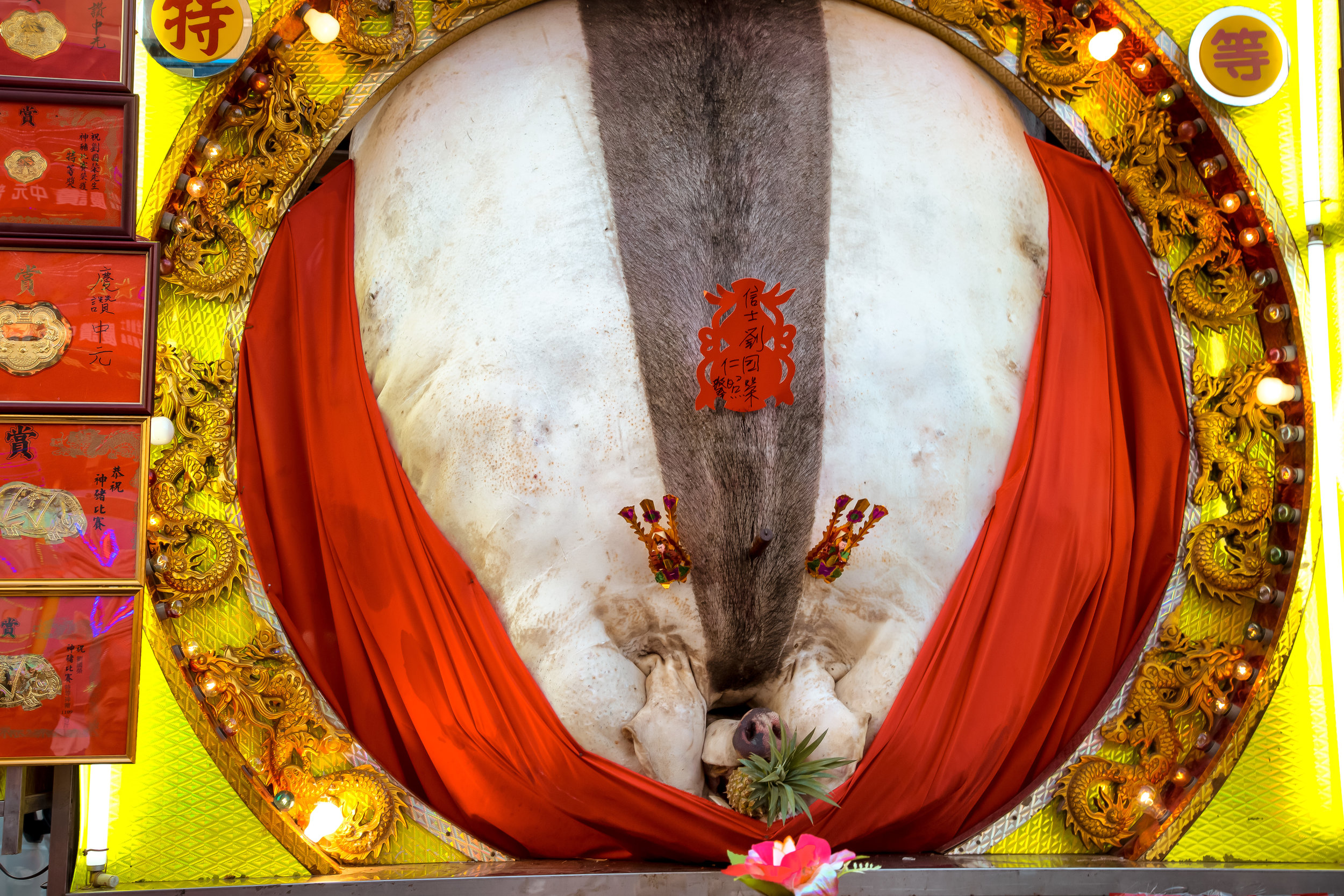
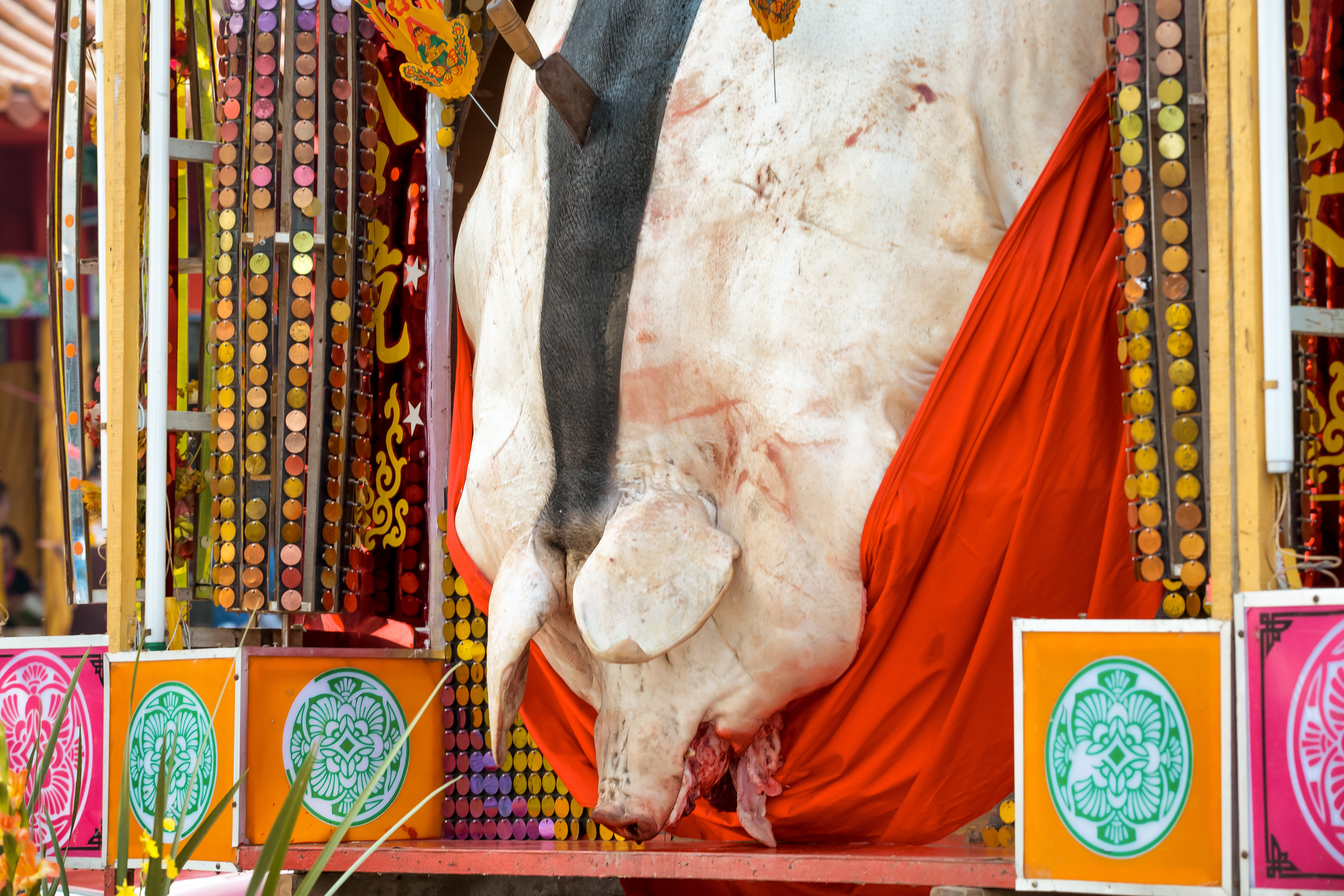
Winning pigs in the past have reached anywhere between 800-900 kilograms, making them almost ten times the size of a normal healthy pig.
To achieve such a result, the pigs are raised for anywhere between two and four years and are constantly overfed and placed in a confined space, which ultimately forces them to become immobile.
This lifestyle is extremely unhealthy for the animals as they develop painful bed sores, suffer from organ failure, developmental deformities and various other ailments.
Adding to the problem, animal rights groups have accused farmers of force-feeding the pigs heavy-metals or stones days before the contest takes place, in order to achieve a higher final weight.
As criticism of the competition has grown, proponents for the event have argued that there is no cruelty involved and farmers have even opened up their farms for animal rights groups to come and check out the process. They’ve also argued that once the pig is sacrificed, its meat is distributed to local charities so that there is no waste involved.
Link: What is Taiwan’s Pigs of God Weighing Contest? (EAST)
My only question is, if the claims are true about the illnesses these poor animals suffer, how safe is the meat to actually eat?
So, let’s talk about the 2020 Yimin festival.
The last time I blogged about the Yimin Festival, I left feeling rather optimistic.
Our current Mayor, Cheng Wen-tsan (鄭文燦), had just taken office with a progressive set of policies and things were looking good. The festival organizers were tasked with coming up with “environmentally friendly” ideas to slowly phase out the pigs - and the amount of pigs that were put on display was reduced.
Here’s a recap of my observations from the last time I blogged about this:
The Pigs of God this year were considerably smaller, which shows that a little more care was taken not to abuse the animals and overfeed them as much as in years past.
The Taoyuan City Government promoted the usage of “Environmentally Friendly Pigs of God" (環保神豬), which were art displays made to look like pigs and constructed out of recycled products and paraded around town in the same way that the real pigs would be.
The event organizers planned an alternate activity where local people as well as dignitaries as high up as President Tsai Ying-Wen would come and release water lanterns on the eve of the event.
This year, all of that progress was thrown out the window.
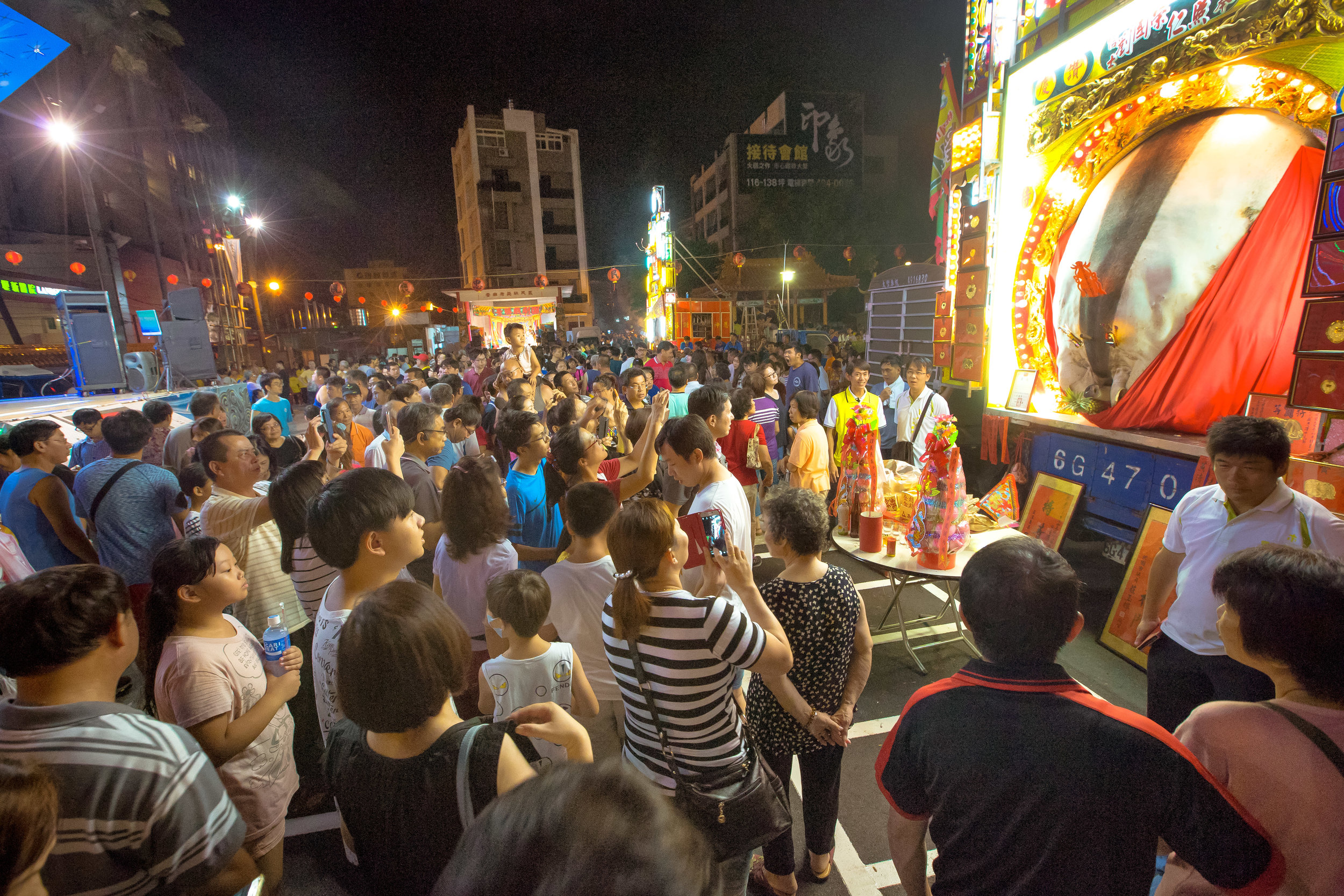
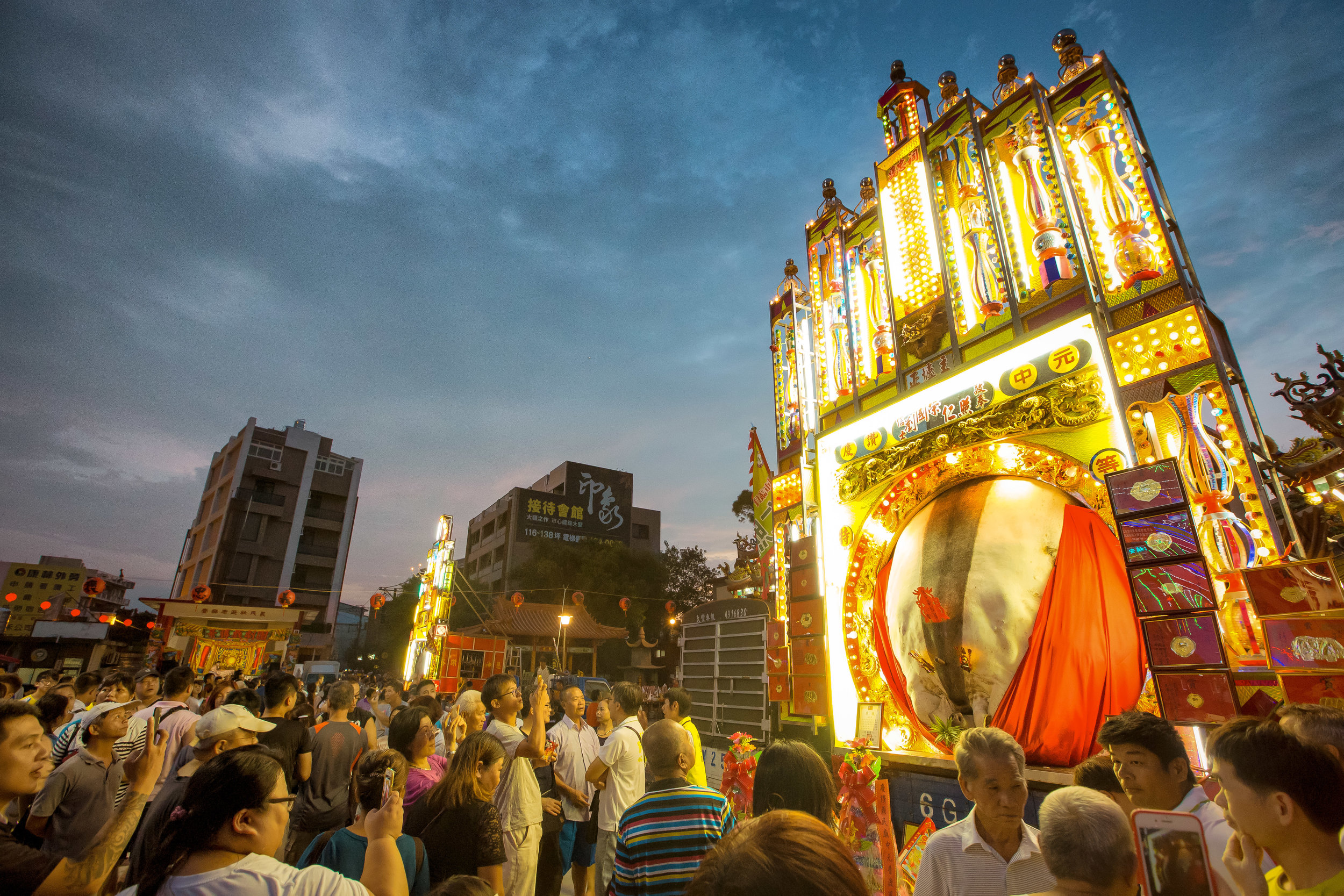
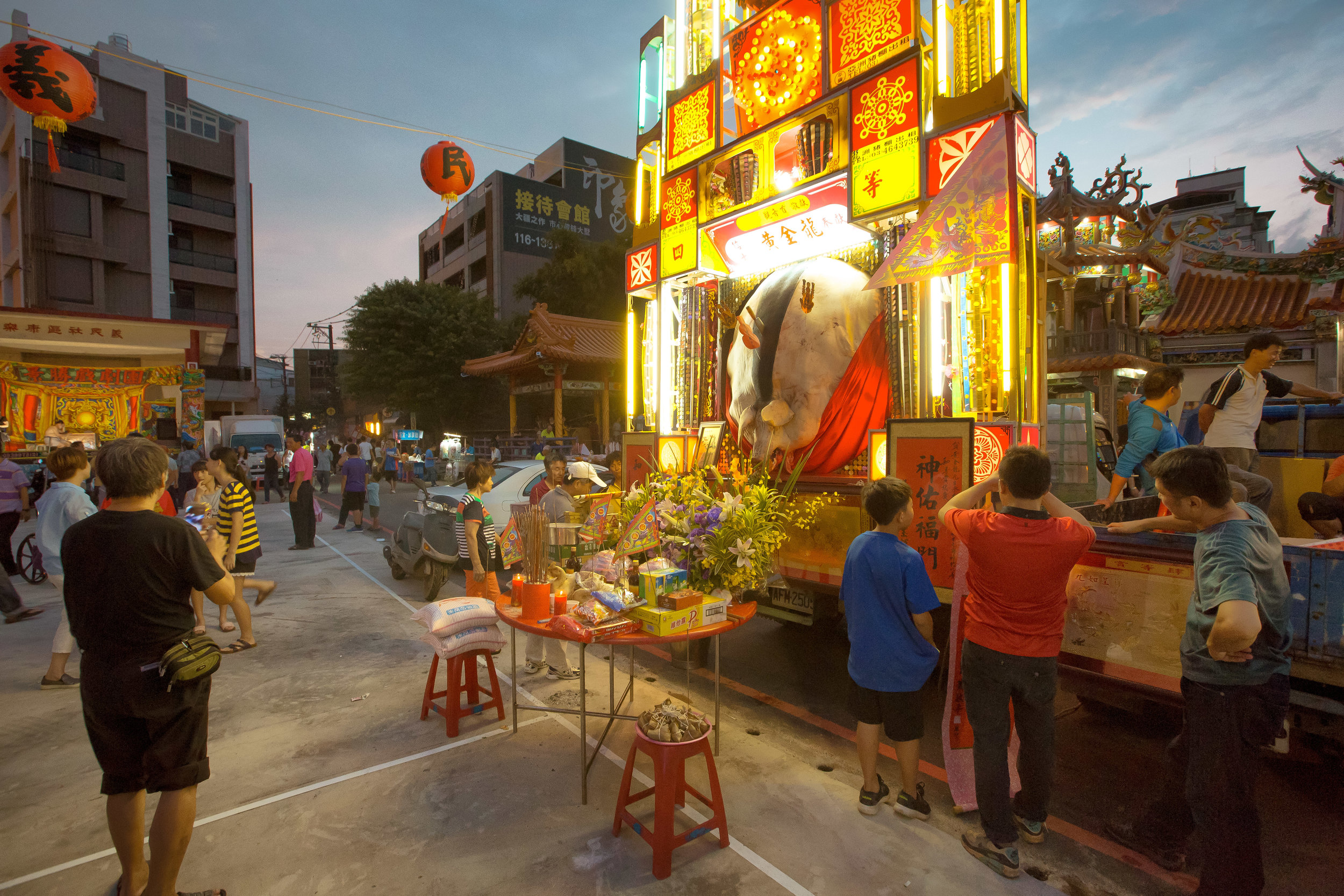
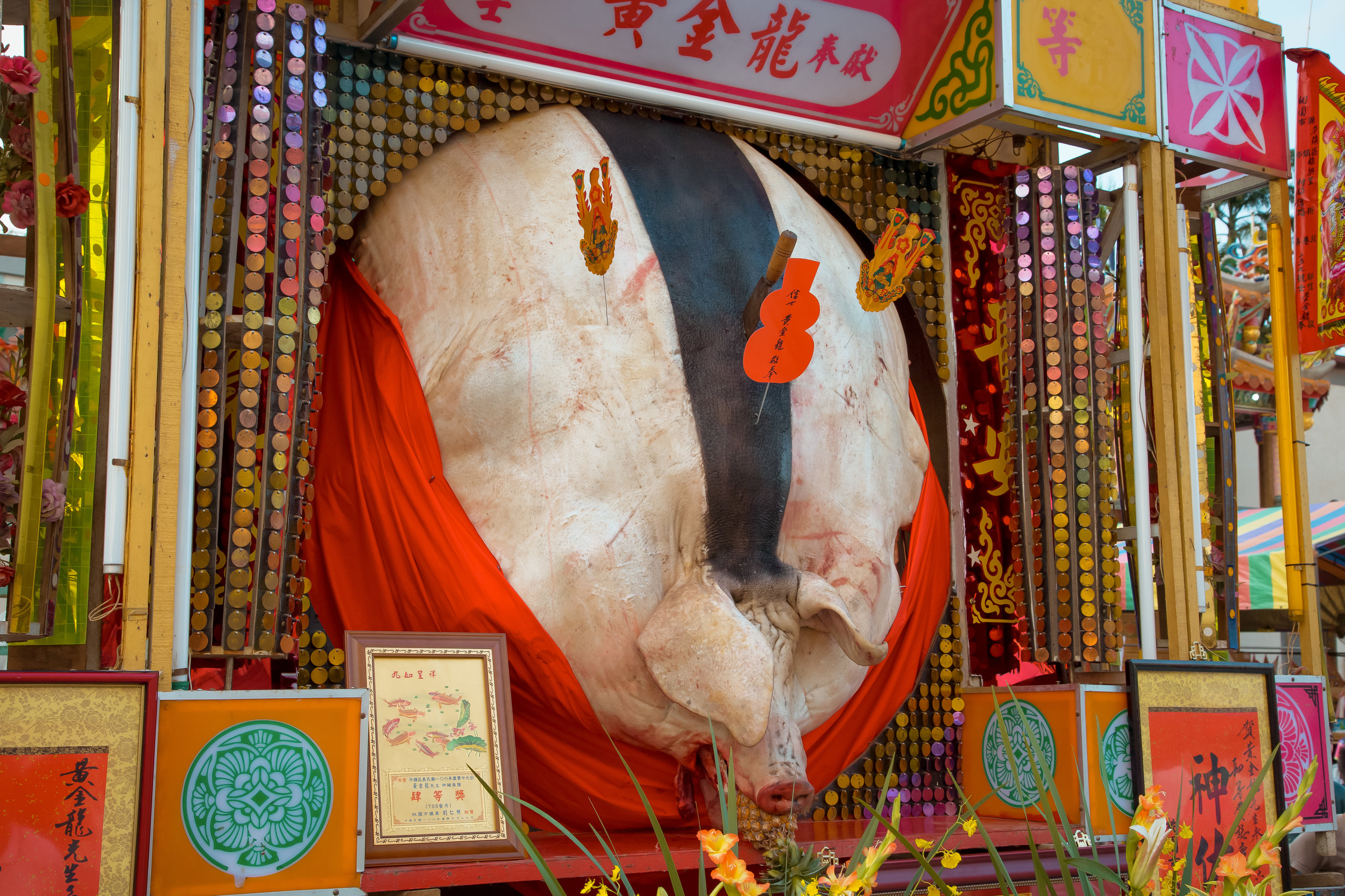
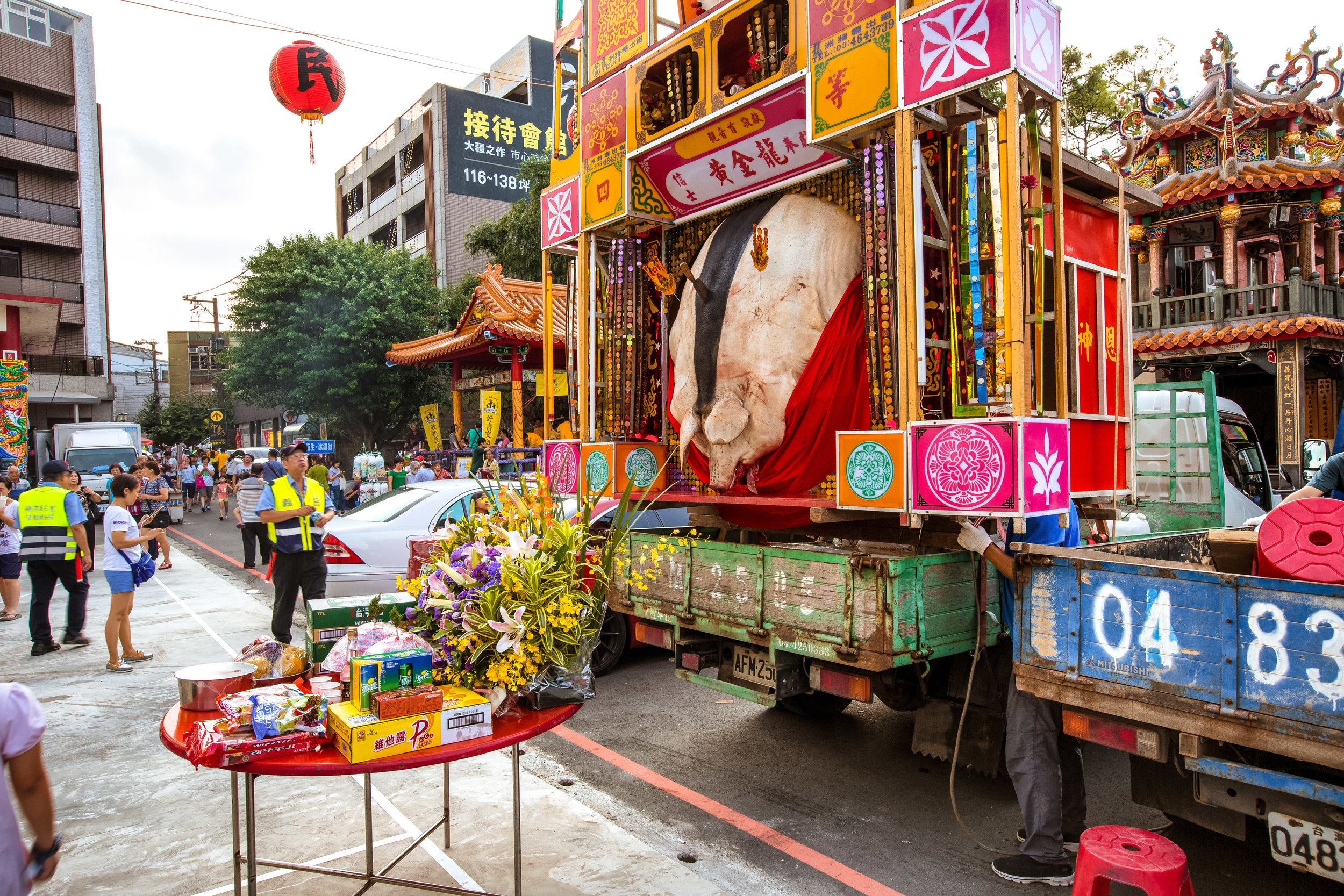
There were seven Pigs of God put on display, with a total of seventeen entering the competition.
The winning pig weighed 880 kilos with the smallest being 580 kilos.
There were no “Environmentally Friendly” pigs to be seen and they went all-out with ostentatious displays of firecrackers, fireworks and pole dancers.
And this was only at the Yimin Temple closest to where I live.
Link: The Pigs of God: Force-Fed then slaughtered for spectacle (We Animals)
There were several other temples, including one that was only a ten minute drive away, where similar events were taking place and the Pigs of God were put on display at almost all of them.
I was hoping that the efforts being made to phase this event out would have continued, but it seems like despite people’s objections, the political clout of some of these temples far greater exceeds the calls for change and modernization.
I’d also note that the last few times I’ve attended the festival, there were protesters who were also there trying their best to get people to pay attention to the plight of the pigs.
This year, they didn’t bother showing up.
The fact that politicians as far up the political ladder as the President and Taoyuan’s mayor took part in the activities just goes to show that the political will to actually do something probably isn’t really there, which is unfortunate.
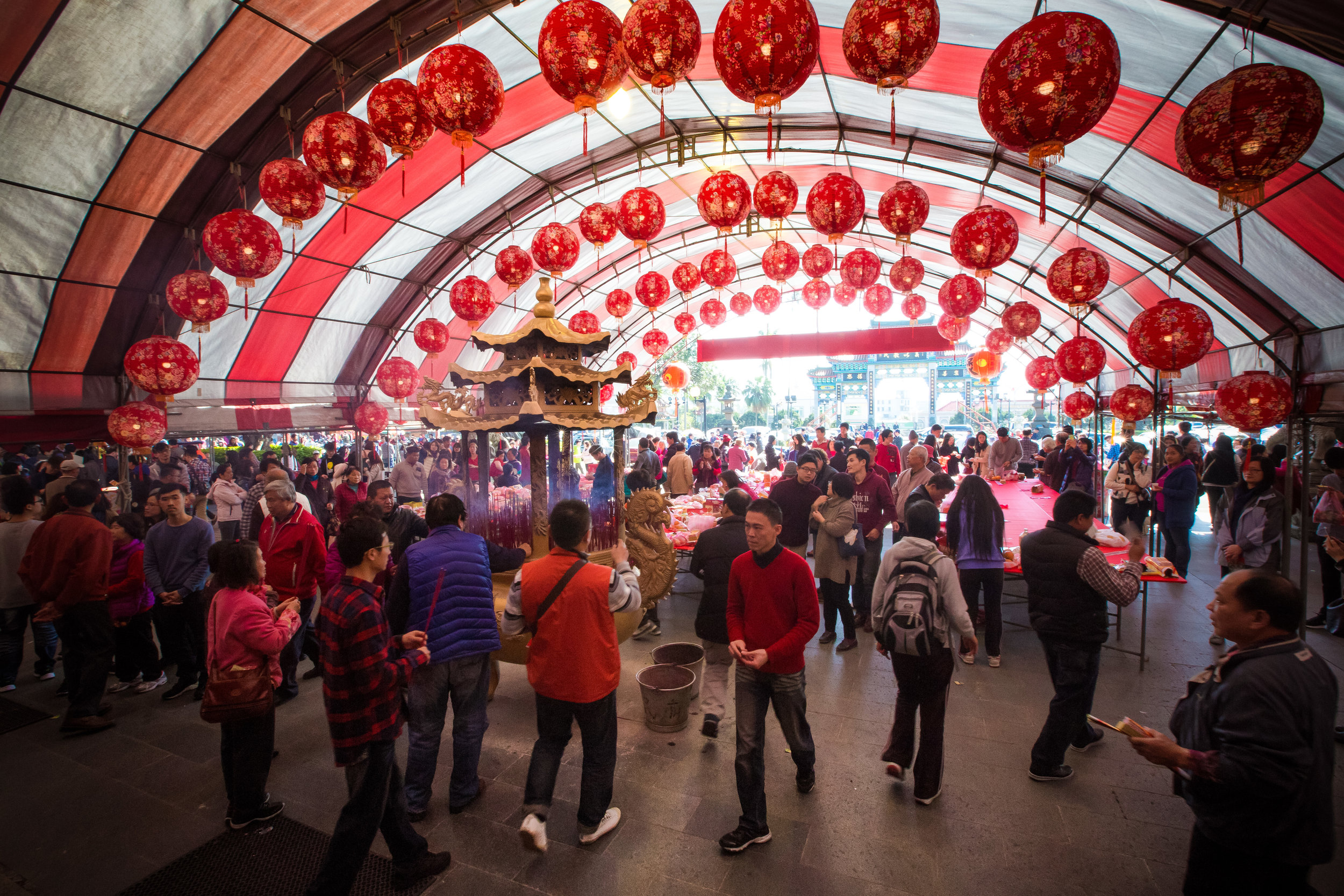
The Yimin Festival continues to be a popular event and attracts crowds of thousands - I’m not sure where Channel News Asia (in the article linked above) got their numbers, but they were way off.
I haven’t seen any official figures, but from what I saw, not even a global pandemic could keep the crowds from attending this year.
I’m sad to say that the Pigs of God aspect of this festival are going to be phased out any time soon, so I guess you’ll probably be seeing future Pigs of God posts from me in the future.
*sigh*