I’m a bit of a weirdo when it comes to organization, so when it comes to places that I want to visit, I have a map that I’m constantly updating, and, as I’ve mentioned on numerous occasions, the majority of spots that I have on my list are located somewhere in the south of Taiwan. Over the years, I’ve added so many places to visit on the map that I’d probably need months to visit all of them, but all that means is that whenever I do find the time to make my way down south, I always have a tight schedule of things to see and do with the little time that I have.
That being said, when I do find the time, my plans often end up being far too ambitious, and although I always try my best to get a lot of work done, something I’ve come to realize is that the pace of life down there is a lot more chill than it is up here in the north. Instead of running around trying to visit as many places as possible, a better idea might be to, instead, visit a few destinations while also remembering to spend time relaxing, enjoying the weather, eating great food, and enjoying some really cool coffee shops.
These decisions are, admittedly, made a lot easier when your trip is interrupted by a tropical storm that brings with it days of torrential rain. so, with few other options with such weather, a lot of the time during my most recent trip south was spent hanging out in some of the Tainan’s hip coffeeshops, where I enjoyed the tropical fruit-inspired coffee that the city has become known for. When the weather did clear up, I set off to check out some places on my list, but when the rain came back, I was off again in search of another seat at a coffee shop.
Even though I wasn’t as productive on this trip as I have been on others, I made the most of my time, despite the weather, and got to see a few places that I had on my list. Without a hint of irony, though, on the day that I was scheduled to head home, I woke up for breakfast, packed my bags, checked out of my hotel, and walked out into the kind of beautiful weather that Tainan is known for. With a few hours before my train was scheduled to depart, I decided to make the most of the little time I had and made my way to the historic Bao-An Station (保安車站), one of the locations that was pretty high up on my list.
If you’ve been following my blog for any period of time, you’re probably well-aware that one of my ongoing projects has been documenting Taiwan’s historic railway stations, especially those that date back to the Japanese-era, so this was one of the places on my list that I was really looking forward to visiting, and fortunately, I was able to check it out as it was on my way to the High Speed Rail Station that would eventually take me home.
Hopping on the train at Tainan Station and heading south on the commuter train, I couldn’t help but feel like I was back in Japan riding through the countryside. The scenery outside of the train, the bright natural light inside the carriage, and only the sound of the train seemed very Japan-like, but that’s probably because I’m more familiar with the trains up here in north where people are always chatting, playing on their phones and watching noisy videos. When the train stopped at Bao-an Station and I got off, that feeling of being in Japan became even stronger, because just across the platform was the small wooden station, which is architecturally identical to many of the older stations you’ll see in the countryside of Japan.
Amazingly, despite being one of the oldest of Taiwan’s remaining wooden train stations, and the amount of traffic that passes through on a daily basis, Bao-an Station remains in pretty good shape. Over the past century, a lot has changed in Taiwan, and the railway itself has been in a constant flux of modernization, but Bao-an Station has stayed the same, which I suppose you could say is credit to the architectural design that has allowed it to remain standing for so long. However, as an actively used heritage building, at some point it’s probably going to have to get a little love in the form of restoration in order to ensure that we’re able to enjoy it for many years to come.
As I usually do with these articles, I’ll start by introducing the history of the train station, its architectural design, and then give readers information about how to visit if they’re interested in checking out this little piece of Taiwanese history.
Shiyaroken Station (車路墘驛 / しやろけんえき)
To start, I suppose I should talk about the name of the station, because, you might be a little confused with the discrepancy between with the title of the article and the name of the station provided above. Admittedly, this is something that I was quite confused about myself as well until I dug into my research process for this article.
Suffice to say, the name of the station was changed to ‘Bao-an’ (保安) in the 1960s, nearly two decades after the end of the Japanese-era. For the six decades prior, the station was named ‘Shiyaroken' Station in Japanese, which came from the Taiwanese word “Tshia-loo-kinn” (車路墘). The interesting thing about this specific name, and the reason why I was confused, is that there were several areas in Taiwan in the early years of the Japanese-era with this name, but the Chinese character ‘qian’ (墘) is an older word that is rarely used these days in Mandarin, and pretty much non-existent in Japanese.
In addition to Tainan, you could also find places named ‘Tshia-loo-kinn’ in both Taichung and Pingtung as well, and in each case, the names date back to the Qing Dynasty, and (although I haven’t found any credible source regarding the origin of the name) likely referred to ‘road-side stops’ that were once located along the safe trading routes of the time.
To better understand the name, I’ll break it down for you:
車 (Tshia) - vehicle; car;
路 (loo) - road; path;
墘 (kinn) - Taiwanese word for ‘beside’ (旁邊) or ‘nearby’ (附近)
Take from that what you will - The important thing is that after the arrival of the Japanese, the name stayed the same, but it was pronounced “Shiyaroken” (しやろけんえき / シヤロケンエキ) in Japanese, which is actually quite similar to the Taiwanese pronunciation.
Staying on the subject of the station’s name, when it was changed from ‘Shiyaroken’ (or Tshia-loo-kinn) to ‘Bao’an’ in the 1960s, the reason for doing so, if you’re asking me, was a little strange. The official reason for the name change isn’t well-documented, but they changed it to ‘Bao’an’ in honor of the local Bao’an Temple (車路墘保安宮). The reason why I’d argue that this was a bit odd was because the temple wasn't actually all that close to the station, and was in fact much closer to Rende Station (仁德車站), the next stop south. It’s possible that they just changed the name to something that was easier for the ‘newer’ residents of Taiwan, who had trouble speaking Taiwanese, or possibly because the ticket-making system that was used at the time wasn’t actually compatible with the characters.
If you read my article about Taichung’s Zhuifen Train Station (追分車站), the original name of the station in Japanese was ‘Oiwake Railway Station’ (追分驛 / おいわけえき), but given that the Chinese characters for “Oiwake” (追分) are an abbreviation for a much more auspicious meaning in Mandarin, which translates as “chasing your dreams” or “pursuing your destiny” (追到緣分), they made a similar name change to another station nearby. In that case, the next station over, originally named ‘Oda Station’ (王田驛) was officially renamed ‘Chenggong Station’ (成功車站) in the 1960s. This became a hit with the locals, who collected tickets with the stations ‘Zhuifen - Chenggong’ (追分 - 成功) as together the stations translate almost literally as “make your dreams come true” (zhui fen cheng gong / 追分成功).
Given the time frame of that particular name change, I figured the distance from the temple ultimately didn’t really make much of a difference to the Taiwan Rail Corporation at the time because a ticket from the newly re-named ‘Bao’an Station’ (保安車站) to the nearby ‘Yongkang Station’ (永康車站) became an instant hit with locals. The reason for this was similar to the situation above as the tickets employed a homophonic pun in Mandarin that read in a clockwise manner became ‘Yongbao Ankang’ (永保安康), or literally, ‘Peace and health forever!’
Even though my article about Zhuifen Station predates this one, it was only until I started my research for my article did I realize that the ‘auspicious ticket’ thing was initiated at Bao’an Station. I had always assumed it was a result of the name change between Zhuifen and Chenggong.
This is why I enjoy doing all this research for these articles. I learn a lot in the process!
Link: Auspicious train ticket | 吉祥語車票 (Wiki)
With regard to the history of this station, it actually got its start quite early. As I mentioned before in my article about Taiwan’s Remaining Japanese-era Train Stations (台鐵現存日治時期車站), the Jukan Tetsudo Project (ゅうかんてつどう / 縱貫鐵道), known in English as the ‘Taiwan Trunk Railway Project,’ quickly got underway shortly after the Japanese took control of Taiwan. The project, which sought to have a railway constructed from Keelung in the north and Kaohsiung in the south (and beyond), was constructed in different phases, and the southern phase that connected Tainan to Takao (Kaohsiung) was completed quite early.
Amazingly, it would take just over a decade to have the entire west coast railway completed, but by the time the entire system was connected, Shiyaroken Station had already been in operation for about eight years on the southern stretch of the railway between Tainan and the port station in Kaohsiung.
When most people introduce the history of the station, resources will point to a specific date to when it was established, but I have to note that there is a bit of a caveat to those claims - Originally opening for service on November 29th, 1900 (明治33年) as ‘Shiyaroken Parking Lot’ (車路墘停車場), it would only be upgraded into a ‘station’ (驛) a few years later after the opening of the Shiyaroken Sugar Factory (車路墘製糖所), which was located a short distance away from the station. That being said, when the Sugar Factory opened, the station was moved about 1.5 kilometers north of its original location for the benefit of the staff at the factory, officially opening on November 10th, 1909 (明治42年).
Oh, and remember when I mentioned above that the local Bao’an Temple was much closer to Rende Station? Well, that station, which opened in 2014, sits on the same location as the original Shiyaroken Station.
Note: That ‘Parking Lot’ reference above was a very literal translation - Today, the word most commonly used in Mandarin for ‘parking lot’ is ‘停車場’, which is literally: ’Stop Car Space’, but a long time ago in Japanese, the same characters were used to identify a minor train station. The term, ‘Teishajo’ (停車場 / ていしゃじょう) was a designation that was mostly used for smaller train stations, as opposed to the larger stations, known in Japanese as ‘eki’ (驛 / えき), which is another word that isn’t used in Mandarin.
Although Bao-an Station opened in its current location in 1909, another aspect of the station’s history that isn’t so well-advertised is that it likely wasn’t upgraded into an ‘eki’ (驛 / えき) type of station until 1928 (昭和3年), when the currently used station house was constructed. So, if we’re being strict with these things, the station might have been established well-over a century ago, but the building that we can pass through today is just a few years short of a century old.
Interestingly, though, the history of this station is one that goes in spurts where there’s a flurry of activity, and then some downtime when not much happens for a few years, which then repeats itself. The little station has pretty much remained the same for over a century, but the world around it has changed considerably, and the number of people passing through its turnstiles have been reflected by these changes. Obviously, the number of people passing though the station was consistent while the nearby Sugar Factory was in operation between 1909 (明治42年) and 2003 (民國92年) as the station was only a stop away from the downtown core of Tainan.
Link: Ten Drum Rende Creative Park (Wiki) | Ten Drum Tainan (Taiwan Everything)
In 2001, though, daily traffic at the station increased by about 500% due to the popularity of the 'Yongkang - Bao-an’ auspicious ticket. By the time that craze settled down, though, the number of passengers started to decrease due to fewer trains stopping at the station. Most recently, thanks to the construction of the High Speed Rail Station and the new Shalun Branch Line (沙崙線), the number of arrivals at the station has once again started to increase, and this was helped out even more by the opening of the beautiful Chimei Museum, which is within walking distance of the station.
During my visit to the station, on a beautiful sunny Monday morning, it was quite busy with a number of passengers coming and going as well as a number of tourists who had come to check out the station prior to walking over to the Chimei Museum (奇美博物館).
With all of the tourist traffic passing through the station, it remains relatively attractive, and nostalgic for a lot of people, but looking at it through my telephoto lens, its obvious that it is in need of some urgent reparations and restoration. Sections of the roof have begun to sink in, and the city government has cited termite damage on the wooden exterior.
As a Protected Heritage Property, eventually they’ll have to restore the building, but unlike many of Taiwan’s other older railway stations, its highly unlikely that it's in any danger of being torn down or replaced any time soon.
In the drop-down box below, I’ll offer a concise timeline of the stations history and then I’ll introduce its architectural design:
-
1896 (明治29年) - The Colonial Government puts a team of engineers in place to plan for a railway network on the newly acquired island.
1900 (明治33年) - Shiyaroken Station (車路墘停車場) opens for service on a limited track running between Tainan Station (臺南停車場) and Takao Port Station (打狗停車場).
1902 (明治35年) - After years of planning and surveying, the government formally approves the Jukan Tetsudo Project (縱貫鐵道 / ゅうかんてつどう), a railway plan to be constructed along the western and eastern coasts of the island.
1908 (明治41年) - The 400 kilometer Taiwan Western Line (西部幹線) is completed with a ceremony held within Taichung Park (台中公園) on October 24th. For the first time, the major settlements along the western coast of the island are connected by rail from Kirin (Keelung 基隆) to Takao (Kaohsiung 高雄).
1909 (明治42年) - Shiyaroken Station is relocated 1.5 kilometers north of its original location for the benefit of staff of the newly established Shiyaroken Sugar Factory (車路墘製糖所).
1920 (大正9年) - In a major administrative restructuring policy, Tainan Prefecture (臺南州) is officially established, stretching from Chiayi to just south of Bao-an Station.
1928 (昭和3年) - The current station house, constructed entirely of cypress from Alishan (阿里山) is completed and opens for service.
1945 (昭和20年) - The Second World War comes to an end and the Japanese surrender control of Taiwan to the Chinese Nationalists.
1962 (民國51年) - Shiyaroken Station is officially renamed ‘Bao’an Station’ (保安車站).
2001 (民國90年) - Bao’an Station is recognized as a Tainan City Heritage Building (臺南市市定古蹟)
2001 (民國90年) - Bao’an Station experiences a massive surge in traffic due to the popularity of the Yongkang - Bao’an tickets. Daily ridership increases by at least 500% for the year.
2008 (民國97年) - A second platform is constructed at Bao’an Station, creating the first expansion.
2011 (民國100年) - The Shalun Branch Line (沙崙線) running from Tainan Station to Shalun Station, next to the Tainan High Speed Rail Station opens for service. The number of commuter trains departing Tainan Station is increased, which means that the number of daily departures and arrivals at Bao’an Station increases.
2014 (民國103年) - In order to prepare for the construction of the future Tainan City subway system, the Taiwan Railway Corporation established Rende Station (仁德車站), about 1.5 kilometers south of Bao’an Station on the site of the Shiyaroken Station that was established in 1900.
2015 (民國104年) - The Chimei Museum (奇美博物館) opens in new location within walking distance of the station, which creates an increased amount of daily traffic.
Architectural Design
Whenever it’s time to start detailing the architectural design specifics of the historic Japanese-era buildings that I write about, it’s often where I end up spending the majority of my time researching and writing, but, fortunately, in this case, I won’t need that much time. I’ve already written a number of articles about Taiwan’s historic train stations, each of which was constructed in an almost identical architectural design. If you’ve read any of my articles about the Coastal Five Treasures (海線五寶), Xiangshan Station (香山車站) or Qidu Station (七堵車站), you’re likely to notice that most of these stations all appear relatively similar,, save for some minor differences.
The reason for this uniform style of design is because during the late Taisho (大正) and early Showa (昭和) eras, prior to the Second World War, many of the (smaller) train stations constructed in not only Taiwan, but Japan as well, were built in what would become a generic style of station design that offered all the functionality that a train station of the era required, were earthquake proofed in design, and most importantly were cost-effective.
Even though the number of stations constructed in this design have deceased in the post-war era, its rarely ever due to the quality of their design, but the changing demographics of the community that they serve. So, even though you can still find quite a few of these stations around Taiwan and Japan, it’s mostly because they have been constructed in areas where the population hasn’t changed much, and a larger station has yet to become necessary.
Considered to be an architectural fusion of a traditional Japanese-style building with western elements, what I personally find surprising about the design of these stations is that there doesn’t seem to be a specific term in the Japanese language used to describe it. Something I’ve had to learn the hard way during my time researching these things, though, is that it is often difficult to come across these specifics from Japanese sources. In the Chinese language, however, the design of these stations is referred to literally as a ‘Hiraya Kirizuma Western Style Wooden Station House” (木造平家切妻洋小屋), which probably doesn’t tell you much, but does offer a pretty good idea of what to expect from the design of the station if you’re familiar with the terms.
To help you better understand, what it basically means is that these buildings are a ‘single-story’ (平家) station ‘constructed of wood’ (木造), which makes use of the traditional Japanese ‘kirizuma’ style (切妻) of architectural design with 'western fusion elements’ (洋小屋) mixed in. That being said, the ‘western’ aspects of the architectural design were, for the most part, inspired by the architectural design of Western Baroque (巴洛克建築), which was quite popular with the Japanese architects of the day. However, for cost-saving measures, the western elements of design were minimal, and Bao’an Station in particular featured far fewer of these western-inspired elements than its contemporaries.
Like the other stations mentioned earlier, Bao’an Station was constructed using the traditional irimoya-zukuri (入母屋造 / いりもやづくり) style, an ubiquitous style of Japanese design that is most often referred to in English as the “East Asian hip-and-gable roof,” which is a term that I don’t really think gives people a good indication about what’s actually going on with this style of design. The key thing to keep in mind about the ‘irimoya’ style is that despite the English translation, it doesn’t necessarily tell you what ‘variation’ of roof is constructed on any given building, but it does indicate that buildings constructed in this style will feature one of traditional Japanese architecture’s various styles of intricate roof design.
I probably couldn’t come up with a more appropriate English term for describe these buildings, but, for me, a name that focuses more on the ‘moya’ (母屋 / もや) aspect of “irimoya”, might offer people a better idea of what’s going on. In layman’s terms, the ‘moya’ is essentially the core, or the ‘base' of the building, and when the irimoya-style is used, the ‘moya’, (literally the “mother-house”) is usually considerably smaller than the roof, which extends well-beyond the base.
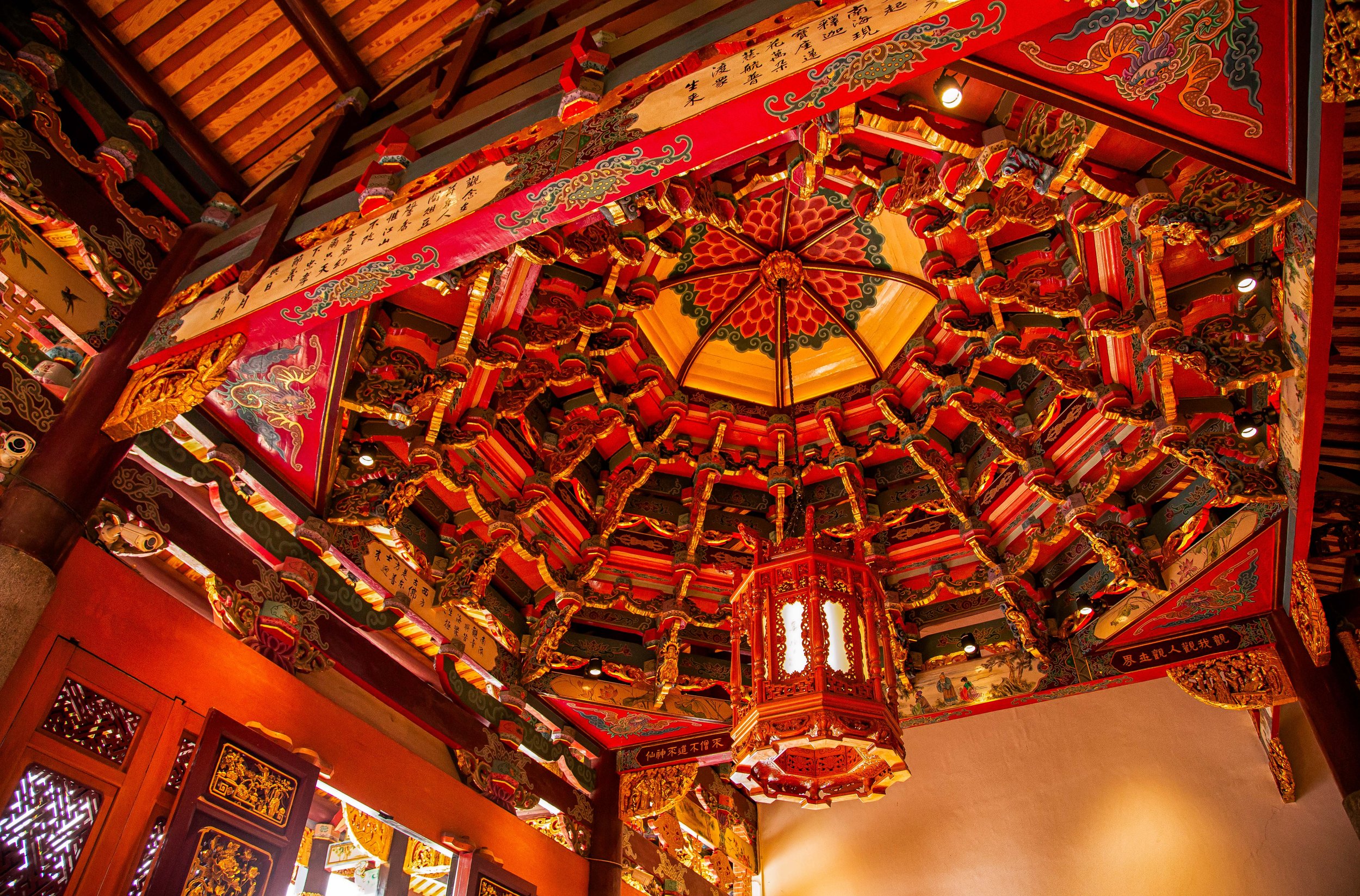
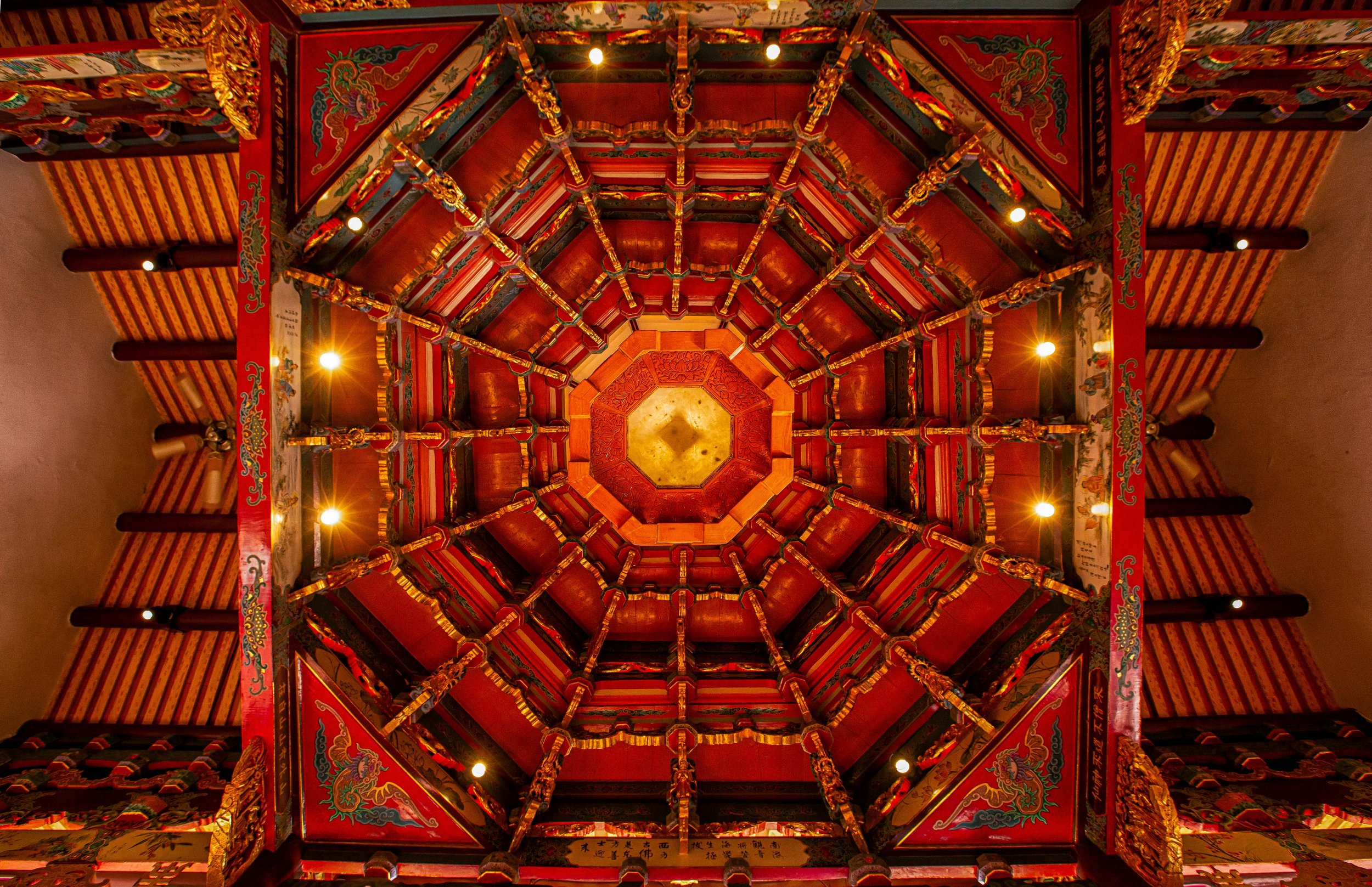
This is a style of design that is also used in much more decorative buildings, such as Shinto Shrines, Buddhist Temples, and Martial Arts Halls, but is also commonly used for anything from houses to train stations like this one. The purpose of the building, and the amount of decorative elements aren’t really all that important, what always remains the same is that as the roof eclipses the size of the base and that the building features a genius network of roof trusses and pillars both within the interior and on the exterior of the building that allow the roof to become the defining aspect of the building, as well as ensuring that its weight is evenly distributed to ensure that the whole thing doesn’t collapse.
In this case, the roof of the station was designed using the kirizuma-zukuri (妻造的樣式) style, which is one of the oldest and most commonly used roof designs in Japan. Translated simply as a “cut-out gable” roof, the kirizuma-style is regarded as one of the more ‘basic’ styles of Japan’s ‘hip-and-gable’ roof designs. To explain as briefly as I can, it is a two-sided roof that can appear simple in design from the front of the building, but as you walk around the perimeter, you’ll notice that it becomes much more complex. The roof is layered with the eaves on the lowest layer extending well beyond the base, supported by a network of pillars that surround it on three sides. The top layer is where you’ll find the ”cut-out gable” with the gable-section of the roof covering the eastern side of the building, while the longer ‘hipped' side ‘cuts’ through it. Both of the ends of the ‘hip’ section feature triangular-shaped “tsuma” (妻 / つま) or gable-ends, with rectangular windows placed in the middle that allow natural light into the interior of the building.
The upper part of the roof is covered with Japanese-style black tiles (日式黑瓦) while the lower eaves are covered with rain-boards (雨淋板) that help to direct the flow of rain water on rainy days. The black tiles that cover the roof appear to be quite old, and some of them are in pretty bad shape.
I haven’t been able to find any information regarding their age, but its possible that they could be the original tiles from the Japanese-era given that they tend to have a pretty long shelf life. They’re likely going to have to be replaced at some point in the near future, though. The original rain-boards, though, have already been replaced, and if their replacements are any indication, it might be better if those black tiles can last a little longer.
Even though the roof is somewhat basic in terms of its decorative elements, especially when compared to the hip-and-gable style roofs you’ll find on other Japanese-era buildings, there are still a number of elements to take note of, I’ll list each of those specific elements below with a diagram that should help you better understand what’s going on.
Hiragawara (平瓦 /ひらがわら) - A type of arc-shaped clay roofing tile.
Munagawara (棟瓦 /むねがわら) - Ridge tiles used to cover the apex of the roof.
Onigawara (鬼瓦/おにがわら) - Decorative roof tiles found at the ends of a main ridge.
Nokigawara (軒瓦/のきがわら) - The roof tiles placed along the eaves lines.
Noshigawara (熨斗瓦/のしがわら) - Thick rectangular tiles located under ridge tiles.
Sodegawara (袖瓦/そでがわら) - Cylindrical sleeve tiles.
Tsuma (妻/つま) - The triangular shaped parts of the gable on the roof under the ridge.
Hafu (破風板/ はふいた) - Bargeboards that lay flat against the ridge ends to finish the gable.
Moving on from the roof, starting from the main entrance to the station, you’ll find a roof-covered ‘kurumayose' (車寄/くるまよせ) porch that protrudes from the flat front of the building with a pair of pillars holding it up. The roof of the porch features a similarly designed kirizuma-style roof facing in the opposite direction of the roof above, adding to the three dimensional design of the building.
The ‘moya’ base of the building is a cube-like structure that is split into two sections, with one side reserved for passengers, and the other for the staff working at the station. One of the major differences between this station and some of the others mentioned earlier is that the passenger side is considerably larger, and features beautiful wooden benches. When you walk into the building from the front entrance, you are met with the ticket booth on the left while the right-hand side is covered on all three sides with beautiful Japanese-style paneled sliding glass windows (日式橫拉窗), which assist in providing a considerable amount of Tainan’s natural light into the interior as well as a bit of breeze on hot days.
One of the most notable aspects of the interior is the wooden gate located near the ticket booth. Gates like this were once very common in train stations during the Japanese-era as a means to help filter people in and out while waiting in line, but few of them remain these days. The gate was originally constructed to look like the Japanese word for ‘money’ (円), but was likely replaced at some point and looks a little different now.
Similarly, the entrance to the train platform features two wooden partitions that connect to a fence at the rear of the station, which date back to the Japanese-era. Now that the station has transitioned to electronic card swiping, the original turnstiles have been removed, so you can simply just walk through to get to your train.
This is the part of the station’s architectural design that I appreciate the most as the open gates transition into a fence-like structure that includes a roof-covered portico that surrounds the building on three sides. Part of an intricate network of carpentry genius, the pillars that connect to the fence assist in distributing the weight of the roof, but they also prevent people from jumping over the fence to take a free train ride. The fence, pillars, and gates combine to make an almost three-dimensional design and add complex geometric shapes to the design of the building, and are part of the western-inspired elements mentioned above.
In the past, in order to get to the train platform, you literally had to cross the train tracks and walk up a set of stairs that brought you to the island platform. Given how dangerous this is, especially since the introduction of Taiwan’s express trains that speed through without stopping at the station, an overpass has been constructed that allows passengers to safely make their way to the platform area. As I mentioned earlier, the platform area is one of the areas that has been expanded several times since the Japanese-era, which has allowed the station to keep up with the modern changes to the railway, while maintaining the same historic station house. When passengers are waiting for the train on the platform, you can enjoy a pretty good view of the rear of the station, the roof of the building, and the trees that were planted next to the building when it was originally constructed.
Finally, while not exactly part of the architectural design, I’ll conclude by mentioning the trees. One of the things that I’ve really started to appreciate about Japanese architecture, especially when it comes to the construction of buildings, is that they always plant trees next to the building as a time capsule of sorts that helps to show how old the building is. In this case, we have what has become known as the ‘Bao’an Three Treasures’ (保安三寶), which are likened to 'The Three Star’ deities (三星 / 福祿壽), Fu (福), Lu (祿), and Shou (壽), who are often found adorning the top of Taiwan’s temples. To the right of the main entrance, you’ll find an Orange Jasmine (七里香) while the much taller Palm tree (棕櫚樹) and Coastal she-oak (木麻黃) are to the left. If the memorial plaque next to trees is any indication, they date back to 1909 (明治42年) and predate the current station house, which is pretty cool.
Getting There
Address: #10, Alley 529, Wenxian Road, Rende District, Tainan City
(臺南市仁德區保安里文賢路一段529巷10號)
GPS: 22.932940, 120.231660
How is one to get to Bao’an Train Station?
You take the train, of course.
Given all the modernization that has taken place on Taiwan’s railway, the fact that you can still take a train to one of the nation’s oldest stations is pretty cool.
So you should definitely take the train. You do however have other options for getting there.
The station is located only one stop south of Tainan Train Station, and the ride take only about seven minutes to get there. So, if you find yourself the proximity of the downtown core of Tainan, you shouldn’t have much of a problem hopping on a train. Likewise, if you’ve travelled into the city by High Speed Rail, you can transfer to a commuter train from the Shalun Train Station (沙崙車站) and take the train to Bao’an Station, which is a seventeen minute ride.
As a smaller station though, Bao’an Station isn’t serviced by every train headed south rom Tainan, so if you want to visit, you’ll need to make sure that you get on one of the silver Local Commuter Trains (區間車).
Bus
In terms of buses, there are a few options that’ll help you get to the station, or the Chimei Museum (奇美博物館), which is within walking distance of the station. Located a short distance from the main entrance of the station, you’ll find a roof-covered pavilion set up where buses will come in off the main road and pick people up and drop them off. There are options that will take you to downtown Tainan, as well as others that will take you to the High Speed Rail Station, and beyond.
The following bus routes are available at the Bao’an Station stop:
Tainan City Bus (幹支線公車): Red Line #3, Red Line #4
High Speed Rail Shuttle Bus (高鐵快捷公車): #H31
I’ve linked to each of the bus routes above, but Taiwanese websites like this are notoriously unreliable, so if you click on any of the links and they don’t work, you should be able to just search the bus route on your own, and you’ll be able to find the link that they’re currently using.
Youbike
The bus stop is also home to a large Youbike Station where you can swipe your EasyCard and hop on one of the shared bicycles. If you’ve taken a Youbike on the ride from Tainan, you can easily dock the bicycle at the docking station in front of the train station and check out the train station, or take the train back to the city.
If you haven’t already, I highly recommend downloading the Youbike App to your phone so that you’ll have a better idea of the location where you’ll be able to find the closest docking station.
Whether you’re simply on your way to the much larger, and (probably) much more interesting Chimei Museum nearby, a stop by this historic train station is an added bonus to your excursion out of Tainan. There aren’t too many stations like this left in Taiwan, and the fact that it still looks so great after nearly one hundred years is a testament to the skills of the carpenters and architects of the era. If you're just getting off the train to before heading else, make sure to take a few minutes to enjoy the historic station, and don’t forget to take a few photos at the same time.
References
Bao'an Railway Station | 保安車站 中文 | 保安駅 日文 (Wiki)
保安車站 (國家文化資產網)
保安車站 (國家文化記憶庫)
保安車站 (鐵貓)
保安車站 (臺灣驛站之旅)
保安車站 (Blair and Kate's 旅遊與美食)
臺南市文化資產 (Wiki)
112 年度臺南市文資防護專業服務中心成果報告書 (臺南市文化資產管理處)
臺灣鐵道旅行案內 (臺灣總督府交通局鐵道部)
台南縱貫線木造車站巡禮 - 保安車站、林鳳營車站、後壁車站 (LINE Today)
仁德糖廠 (Wiki)
木造車站-海線五寶 (張誌恩 / 許正諱)